Abstract
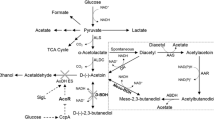
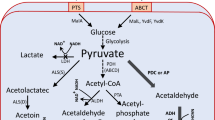
2-Phenylethanol is a valuable flavoring agent with many applications. Although the bioproduction of 2-phenylethanol has been achieved by microbial fermentation, the low titer and high cost hinder its industrial-scale production. The goal of this study is to develop an efficient process for high-level production of 2-phenylethanol from L-phenylalanine. Firstly, candidate hosts for 2-phenylethanol synthesis were screened by evaluating their tolerance to 2-phenylethanol, and Bacillus licheniformis DW2 was proven to be a promising strain for 2-phenylethanol production. Subsequently, phenylpyruvate decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase from different hosts were screened, and the combination of KivD from Lactococcus lactis and YqhD from Escherichia coli owned the best performance on 2-phenylethanol synthesis, and the attained strain DE4 produced 3.04 g/L 2-phenylethanol from 5.00 g/L L-phenylalanine using glucose as carbon source. Furthermore, the fermentation process was optimized using molasses as carbon source, and 2-phenylethanol titer was increased to 4.41 g/L. In fed-batch fermentation, the maximum 2-phenylethanol titer reached 5.16 g/L, with a yield of 0.65 g/g on L-phenylalanine and productivity of 0.12 g/(L.h), which was the highest 2-phenylethnol titer reported to date when molasses was used as carbon source. Collectively, this study develops a robust strain as well as the cost-efficient process for 2-phenylethanol production, which lays a substantial foundation for industrial production of 2-phenylethanol.
Key points •Bacillus licheniformis is an excellent 2-PE stress-tolerant strain. •Coexpressed kivD and yqhD is most suitable for 2-PE production in B. licheniformis. •High-level production of 2-PE (5.16 g/L) was obtained by engineered strain DE4. |






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Achmon Y, Ben-Barak Zelas Z, Fishman A (2014) Cloning Rosa hybrid phenylacetaldehyde synthase for the production of 2-phenylethanol in a whole cell Escherichia coli system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(8):3603–3611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5269-z
Alrumman SA, Mostafa YS, Al-Izran KA, Alfaifi MY, Taha TH, Elbehairi SE (2019) Production and anticancer activity of an L-Asparaginase from Bacillus licheniformis isolated from the Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. Sci Rep 9(1):3756. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40512-x
Atsumi S, Hanai T, Liao JC (2008) Non-fermentative pathways for synthesis of branched-chain higher alcohols as biofuels. Nature 451(7174):86–89. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06450
Buescher JM, Moco S, Sauer U, Zamboni N (2010) Ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for fast and robust quantification of anionic and aromatic metabolites. Anal Chem 82(11):4403–4412. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac100101d
Cai D, Zhu J, Zhu S, Lu Y, Zhang B, Lu K, Li J, Ma X, Chen S (2019) Metabolic engineering of main transcription factors in carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus metabolisms for enhanced production of bacitracin in Bacillus licheniformis. ACS Synth Biol 8(4):866–875. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.9b00005
Carlquist M, Gibson B, Karagul Yuceer Y, Paraskevopoulou A, Sandell M, Angelov AI, Gotcheva V, Angelov AD, Etschmann M, de Billerbeck GM, Liden G (2015) Process engineering for bioflavour production with metabolically active yeasts - a mini-review. Yeast 32(1):123–143. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.3058
Chen X, Wang Z, Guo X, Liu S, He X (2017) Regulation of general amino acid permeases Gap1p, GATA transcription factors Gln3p and Gat1p on 2-phenylethanol biosynthesis via Ehrlich pathway. J Biotechnol 242:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.11.028
Eshkol N, Sendovski M, Bahalul M, Katz-Ezov T, Kashi Y, Fishman A (2009) Production of 2-phenylethanol from L-phenylalanine by a stress tolerant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. J Appl Microbiol 106(2):534–542. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.04023.x
Etschmann MM, Bluemke W, Sell D, Schrader J (2002) Biotechnological production of 2-phenylethanol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-0992-x
Etschmann MM, Sell D, Schrader J (2003) Screening of yeasts for the production of the aroma compound 2-phenylethanol in a molasses-based medium. Biotechnol Lett 25(7):531–536. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1022890119847
Ge Y, Li K, Li L, Gao C, Zhang L, Ma C, Xu P (2016) Contracted but effective: production of enantiopure 2, 3-butanediol by thermophilic and GRAS Bacillus licheniformis. Green Chem 18(17):4693–4703. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6GC01023G
Gu Y, Ma J, Zhu Y, Xu P (2020) Refactoring Ehrlich pathway for high-yield 2-phenylethanol production in Yarrowia lipolytica. ACS Synth Biol 9(3):623–633. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.9b00468
Hassing EJ, de Groot PA, Marquenie VR, Pronk JT, Daran JG (2019) Connecting central carbon and aromatic amino acid metabolisms to improve de novo 2-phenylethanol production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 56:165–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2019.09.011
Hua D, Xu P (2011) Recent advances in biotechnological production of 2-phenylethanol. Biotechnol Adv 29(6):654–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.05.001
Hwang JY, Park J, Seo JH, Cha M, Cho BK, Kim J, Kim BG (2009) Simultaneous synthesis of 2-phenylethanol and L-homophenylalanine using aromatic transaminase with yeast Ehrlich pathway. Biotechnol Bioeng 102(5):1323–1329. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.22178
Kang Z, Zhang C, Du G, Chen J (2014) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for production of 2-phenylethanol from renewable glucose. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172(4):2012–2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0659-3
Kim B, Cho BR, Hahn JS (2014) Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the production of 2-phenylethanol via Ehrlich pathway. Biotechnol Bioeng 111(1):115–124 doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24993
Koma D, Yamanaka H, Moriyoshi K, Ohmoto T, Sakai K (2012) Production of aromatic compounds by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli with an expanded shikimate pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(17):6203–6216. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01148-12
Kong S, Pan H, Liu X, Li X, Guo D (2020) De novo biosynthesis of 2-phenylethanol in engineered Pichia pastoris. Enzym Microb Technol 133:109459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2019.109459
Lakowitz A, Godard T, Biedendieck R, Krull R (2018) Mini review: recombinant production of tailored bio-pharmaceuticals in different Bacillus strains and future perspectives. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 126:27–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2017.06.008
Li X, Wang D, Cai D, Zhan Y, Wang Q, Chen S (2017) Identification and high-level production of pulcherrimin in Bacillus licheniformis DW2. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 183(4):1323–1335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2500-x
Li X, Chen Z, Wu Y, Yan Y, Sun X, Yuan Q (2018) Establishing an artificial pathway for efficient biosynthesis of hydroxytyrosol. ACS Synth Biol 7(2):647–654. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.7b00385
Liu C, Zhang K, Cao W, Zhang G, Chen G, Yang H, Wang Q, Liu H, Xian M, Zhang H (2018a) Genome mining of 2-phenylethanol biosynthetic genes from Enterobacter sp. CGMCC 5087 and heterologous overproduction in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol biofuels 11:305. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-018-1297-3
Liu J, Jiang J, Bai Y, Fan T, Zhao Y, Zheng X, Cai Y (2018b) Mimicking a new 2-phenylethanol production pathway from Proteus mirabilis JN458 in Escherichia coli. J Agric Food Chem 66(13):3498–3504. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b00627
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lu X, Wang Y, Zong H, Ji H, Zhuge B, Dong Z (2016) Bioconversion of L-phenylalanine to 2-phenylethanol by the novel stress-tolerant yeast Candida glycerinogenes WL2002-5. Bioengineered 7(6):418–423. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2016.1171437
Machas MS, McKenna R, Nielsen DR (2017) Expanding upon styrene biosynthesis to engineer a novel route to 2-phenylethanol. Biotechnol J 12(10). https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201700310
Martinez-Avila O, Sanchez A, Font X, Barrena R (2018) Bioprocesses for 2-phenylethanol and 2-phenylethyl acetate production: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(23):9991–10004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9384-8
Ni J, Liu H, Tao F, Wu Y, Xu P (2018) Remodeling of the photosynthetic chain promotes direct CO2 conversion into valuable aromatic compounds. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng 57(49):15990–15994. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201808402
Pan X, Qi H, Mu L, Wen J, Jia X (2014) Comparative metabolomic-based metabolic mechanism hypothesis for microbial mixed cultures utilizing cane molasses wastewater for higher 2-phenylethanol production. J Agric Food Chem 62(40):9927–9935. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf502239d
Rakicka M, Biegalska A, Rymowicz W, Dobrowolski A, Mironczuk AM (2017) Polyol production from waste materials by genetically modified Yarrowia lipolytica. Bioresour Technol 243:393–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.137
Shen L, Nishimura Y, Matsuda F, Ishii J, Kondo A (2016) Overexpressing enzymes of the Ehrlich pathway and deleting genes of the competing pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for increasing 2-phenylethanol production from glucose. J Biosci Bioeng 122(1):34–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2015.12.022
Shi J, Zhan Y, Zhou M, He M, Wang Q, Li X, Wen Z, Chen S (2019) High-level production of short branched-chain fatty acids from waste materials by genetically modified Bacillus licheniformis. Bioresour Technol 271:325–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.08.134
Shu C, Wang D, Guo J, Song J, Chen S, Chen L, Gao J (2018) Analyzing AbrB-knockout effects through genome and transcriptome sequencing of Bacillus licheniformis DW2. Front Microbiol 9:307. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00307
Stark D, Zala D, Münch T, Sonnleitner B, Marison I, Von Stockar U (2003) Inhibition aspects of the bioconversion of L-phenylalanine to 2-phenylethanol by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzym Microb Technol 32(2):212–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(02)00237-5
Sun Y, Xu Z, Zheng Y, Zhou J, Xiu Z (2019) Efficient production of lactic acid from sugarcane molasses by a newly microbial consortium CEE-DL15. Process Biochem 81:132–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2019.03.022
Vinayavekhin N, Mahipant G, Vangnai AS, Sangvanich P (2015) Untargeted metabolomics analysis revealed changes in the composition of glycerolipids and phospholipids in Bacillus subtilis under 1-butanol stress. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(14):5971–5983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6692-0
Wang J, Yuan H, Wei X, Chen J, Chen S (2016) Enhancement of poly-γ-glutamic acid production by alkaline pH stress treatment in Bacillus licheniformis WX-02. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91(9):2399–2403. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4822
Wang P, Yang X, Lin B, Huang J, Tao Y (2017a) Cofactor self-sufficient whole-cell biocatalysts for the production of 2-phenylethanol. Metab Eng 44:143–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2017.09.013
Wang Z, Bai X, Guo X, He X (2017b) Regulation of crucial enzymes and transcription factors on 2-phenylethanol biosynthesis via Ehrlich pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44(1):129–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1852-5
Wang Z, Jiang M, Guo X, Liu Z, He X (2018) Reconstruction of metabolic module with improved promoter strength increases the productivity of 2-phenylethanol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Factories 17(1):60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-0907-x
Wang Y, Zhang H, Lu X, Zong H, Zhuge B (2019) Advances in 2-phenylethanol production from engineered microorganisms. Biotechnol Adv 37(3):403–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.02.005
Wei X, Ji Z, Chen S (2010) Isolation of halotolerant Bacillus licheniformis WX-02 and regulatory effects of sodium chloride on yield and molecular sizes of poly-gamma-glutamic acid. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160(5):1332–1340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8681-1
Yin S, Zhou H, Xiao X, Lang T, Liang J, Wang C (2015) Improving 2-phenylethanol production via Ehrlich pathway using genetic engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. Curr Microbiol 70(5):762–767. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0785-y
Yu X, Xu J, Liu X, Chu X, Wang P, Tian J, Wu N, Fan Y (2015) Identification of a highly efficient stationary phase promoter in Bacillus subtilis. Sci Rep 5:18405. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18405
Yuan H, Xu Y, Chen Y, Zhan Y, Wei X, Li L, Wang D, He P, Li S, Chen S (2019) Metabolomics analysis reveals global acetoin stress response of Bacillus licheniformis. Metabolomics 15(3):25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1492-7
Zhan Y, Zhu C, Sheng B, Cai D, Wang Q, Wen Z, Chen S (2017) Improvement of glycerol catabolism in Bacillus licheniformis for production of poly-gamma-glutamic acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(19):7155–7164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8459-2
Zhang A, Liu H, Yang M, Gong Y, Chen H (2007) Assay and characterization of a strong promoter element from B. subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 354(1):90–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.12.137
Zhang H, Cao M, Jiang X, Zou H, Wang C, Xu X, Xian M (2014) De-novo synthesis of 2-phenylethanol by Enterobacter sp. CGMCC 5087. BMC Biotechnol 14:30. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-14-30
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFA0900300) and the Technical Innovation Special Fund of Hubei Province (No. 2018ACA149).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S Chen, X Ma, and Y Zhan designed the study; Y Zhan, M Zhou, H Wang, Z Li, and L Chen performed the experiments; Y Zhan and M Zhou analyzed the data; Y Zhan wrote the manuscript; D Cai, Z Wen, X Ma, and S Chen revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent for publication
All authors have approved the manuscript for publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 401 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, Y., Zhou, M., Wang, H. et al. Efficient synthesis of 2-phenylethanol from L-phenylalanine by engineered Bacillus licheniformis using molasses as carbon source. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 7507–7520 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10740-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10740-7