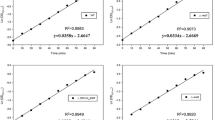
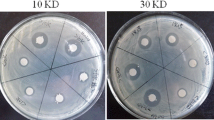
Abstract
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is an important foodborne pathogen that causes serious and extensive food contamination as well as disease and death worldwide. Considering the increasing severity of antibiotic resistance, antibiotic alternatives are urgently needed. As a natural biocide and a component of some essential oils from herbs, thymol is capable of killing various bacteria through a potentially unique mechanism, although the targets of thymol have not been completely elucidated. In this study, the variation in the whole proteome of Salmonella after thymol stress was evaluated using the SWATH multiplex technique. The strain Salmonella Typhimurium CVCC541 was treated with a sublethal concentration (75 μg/mL) of thymol, which rapidly increased the permeability of bacterial membranes at the tested concentration. Thymol destroyed the integrity of the bacterial membrane, as observed by transmission electron microscopy. The proteomes of the treated and untreated cells were characterized after an 8-h treatment. The proteomic analysis of thymol-treated cells indicated that 144 proteins exhibited upregulation or downregulation compared with the control cells, particularly those involved in cellular structure and metabolism. The results of this study showed that thymol may play an antimicrobial role in altering the membrane permeability, virulence change, and antioxidant response of Salmonella Typhimurium. The results of the present study provide an improved understanding of the proteomic response of Salmonella Typhimurium to thymol stress, including the identification of promising targets for the future exploration of innovative approaches to control Salmonella Typhimurium.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Als D, Radhakrishnan A, Arora P, Gaffey MF, Campisi S, Velummailum R, Zareef F, Bhutta ZA (2018) Global trends in typhoidal salmonellosis: a systematic review. Am J Trop Med Hyg 99(3 Suppl):10–19. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.18-0034
Andersen JL, He GX, Kakarla P, Ranjana KC, Kumar S, Lakra WS, Mukherjee MM, Ranaweera I, Shrestha U, Tran T, Varela MF (2015) Multidrug efflux pumps from Enterobacteriaceae, Vibrio cholerae and Staphylococcus aureus bacterial food pathogens. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12(2):1487–1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120201487
Authority EFS, Authority EFS, EFSA CDPC (2018) The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2017. EFSA J 16(12):22–67. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2018.5500
Baron F, Bonnassie S, Alabdeh M, Cochet MF, Nau F, Guerin-Dubiard C, Gautier M, Andrews SC, Jan S (2017) Global gene-expression analysis of the response of Salmonella Enteritidis to egg white exposure reveals multiple egg white-imposed stress response. Front Microbiol 8:829. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00829
Bode M, Longen S, Morgan B, Peleh V, Dick TP, Bihlmaier K, Herrmann JM (2013) Inaccurately assembled cytochrome c oxidase can lead to oxidative stress-induced growth arrest. Antioxid Redox Signal 18(13):1597–1612. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.4685
Boyen F, Haesebrouck F, Maes D, Van Immerseel F, Ducatelle R, Pasmans F (2008) Non-typhoidal Salmonella infections in pigs: a closer look at epidemiology, pathogenesis and control. Vet Microbiol 130(1–2):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2007.12.017
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(7):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55(4):611–622. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797
Chen C, Deutscher MP (2005) Elevation of RNase R in response to multiple stress conditions. J Biol Chem 280(41):34393–34396. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C500333200
Choi H, Nesvizhskii AI (2008) False discovery rates and related statistical concepts in mass spectrometry-based proteomics. J Proteome Res 7(1):47–50. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr700747q
CLSI (2012) Performance standard for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; twenty second informational supplement. CLSI Document (M100-S22). Wayne, Pennsylvania
Curry A, Appleton H, Dowsett B (2006) Application of transmission electron microscopy to the clinical study of viral and bacterial infections: present and future. Micron 37(2):91–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2005.10.001
De Cesare A (2018) Salmonella in foods: a reemerging problem. Adv Food Nutr Res 86:137–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.afnr.2018.02.007
Di Pasqua R, Mamone G, Ferranti P, Ercolini D, Mauriello G (2010) Changes in the proteome of Salmonella enterica serovar Thompson as stress adaptation to sublethal concentrations of thymol. Proteomics 10(5):1040–1049. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.200900568
Ellermeier JR, Slauch JM (2007) Adaptation to the host environment: regulation of the SPI1 type III secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Curr Opin Microbiol 10(1):24–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2006.12.002
Foley SL, Lynne AM (2008) Food animal-associated Salmonella challenges: pathogenicity and antimicrobial resistance. J Anim Sci 86(14 Suppl):E173–E187. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2007-0447
Fu J, Qi L, Hu M, Liu Y, Yu K, Liu Q, Liu X (2017) Salmonella proteomics under oxidative stress reveals coordinated regulation of antioxidant defense with iron metabolism and bacterial virulence. J Proteome 157:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2017.02.004
Futoma-Koloch B, Bugla-Ploskonska G, Dudek B, Dorotkiewicz-Jach A, Drulis-Kawa Z, Gamian A (2018) Outer membrane proteins of Salmonella as potential markers of resistance to serum, antibiotics and biocides. Curr Med Chem 26:1960–1978. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867325666181031130851
Gal-Mor O, Boyle EC, Grassl GA (2014) Same species, different diseases: how and why typhoidal and non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica serovars differ. Front Microbiol 5:391. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00391
Gotz S, Garcia-Gomez JM, Terol J, Williams TD, Nagaraj SH, Nueda MJ, Robles M, Talon M, Dopazo J, Conesa A (2008) High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the Blast2GO suite. Nucleic Acids Res 36(10):3420–3435. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn176
Hensel M (2004) Evolution of pathogenicity islands of Salmonella enterica. Int J Med Microbiol 294(2–3):95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2004.06.025
Horiyama T, Yamaguchi A, Nishino K (2010) TolC dependency of multidrug efflux systems in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. J Antimicrob Chemother 65(7):1372–1376. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkq160
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Furumichi M, Tanabe M (2012) KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res 40(D1):D109–D114. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr988
Karkey A, Thwaites GE, Baker S (2018) The evolution of antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella Typhi. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 34(1):25–30. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOG.0000000000000406
Kirk MD, Pires SM, Black RE, Caipo M, Crump JA, Devleesschauwer B, Dopfer D, Fazil A, Fischer-Walker CL, Hald T, Hall AJ, Keddy KH, Lake RJ, Lanata CF, Torgerson PR, Havelaar AH, Angulo FJ (2015) World Health Organization estimates of the global and regional disease burden of 22 foodborne bacterial, protozoal, and viral diseases, 2010: a data synthesis. PLoS Med 12(12):e1001921. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001921
Lamas A, Miranda JM, Regal P, Vazquez B, Franco CM, Cepeda A (2018) A comprehensive review of non-enterica subspecies of Salmonella enterica. Microbiol Res 206:60–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2017.09.010
Li H, Zhang DF, Lin XM, Peng XX (2015) Outer membrane proteomics of kanamycin-resistant Escherichia coli identified MipA as a novel antibiotic resistance-related protein. FEMS Microbiol Lett 362(11):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnv074
Majowicz SE, Musto J, Scallan E, Angulo FJ, Kirk M, O'Brien SJ, Jones TF, Fazil A, Hoekstra RM, International Collaboration on Enteric Disease 'Burden of Illness S (2010) The global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin Infect Dis 50(6):882–889. https://doi.org/10.1086/650733
Ma J, Chen T, Wu S, Yang C, Bai M, Shu K, Li K, Zhang G, Jin Z, He F, Hermjakob H, Zhu Y (2019) iProX: an integrated proteome resource. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):D1211–D1217. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky869
Marri L, Dallai R, Marchini D (1996) The novel antibacterial peptide ceratotoxin A alters permeability of the inner and outer membrane of Escherichia coli K-12. Curr Microbiol 33(1):40–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900071
Miller SI (2016) Antibiotic resistance and regulation of the gram-negative bacterial outer membrane barrier by host innate immune molecules. MBio 7(5):e01541–e01516. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01541-16
Nazzaro F, Fratianni F, De Martino L, Coppola R, De Feo V (2013) Effect of essential oils on pathogenic bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 6(12):1451–1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6121451
Peng B, Wang C, Li H, Su YB, Ye JZ, Yang MJ, Jiang M, Peng XX (2017) Outer membrane proteins form specific patterns in antibiotic-resistant Edwardsiella tarda. Front Microbiol 8:69. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00069
Qin X, He S, Zhou X, Cheng X, Huang X, Wang Y, Wang S, Cui Y, Shi C, Shi X (2018) Quantitative proteomics reveals the crucial role of YbgC for Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis survival in egg white. Int J Food Microbiol 289:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.08.010
Rost HL, Rosenberger G, Navarro P, Gillet L, Miladinovic SM, Schubert OT, Wolski W, Collins BC, Malmstrom J, Malmstrom L, Aebersold R (2014) Open SWATH enables automated, targeted analysis of data-independent acquisition MS data. Nat Biotechnol 32(3):219–223. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2841
Schwanhausser B, Busse D, Li N, Dittmar G, Schuchhardt J, Wolf J, Chen W, Selbach M (2011) Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature 473(7347):337–342. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10098
Seeger MA, van Veen HW (2009) Molecular basis of multidrug transport by ABC transporters. Biochim Biophys Acta 1794(5):725–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2008.12.004
Shilov IV, Seymour SL, Patel AA, Loboda A, Tang WH, Keating SP, Hunter CL, Nuwaysir LM, Schaeffer DA (2007) The paragon algorithm, a next generation search engine that uses sequence temperature values and feature probabilities to identify peptides from tandem mass spectra. Mol Cell Proteomics 6(9):1638–1655. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.T600050-MCP200
Silva AF, Dos Santos AR, Coelho Trevisan DA, Ribeiro AB, Zanetti Campanerut-Sa PA, Kukolj C, de Souza EM, Cardoso RF, Estivalet Svidzinski TI, de Abreu Filho BA, Junior MM, Graton Mikcha JM (2018) Cinnamaldehyde induces changes in the protein profile of Salmonella Typhimurium biofilm. Res Microbiol 169(1):33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2017.09.007
Sterling C, Crouch R, Russell DJ, Calderon AI (2013) (1) H-NMR quantification of major saccharides in acai raw materials: a comparison of the internal standard methodology with the absolute intensity qNMR method. Phytochem Anal 24(6):631–637. https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.2442
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos A, Tsafou KP, Kuhn M, Bork P, Jensen LJ, von Mering C (2015) STRING v10: protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res 43(D1):D447–D452. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1003
Tang J, Jia JT, Chen Y, Huang XH, Zhang XL, Zhao LQ, Hu W, Wang CJ, Lin C, Wu ZX (2018) Proteomic analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus under cold stress. Curr Microbiol 75(1):20–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-017-1345-4
Tatusov RL, Galperin MY, Natale DA, Koonin EV (2000) The COG database: a tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res 28(1):33–36. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.33
Wu S, Zhu Z, Fu L, Niu B, Li W (2011) WebMGA: a customizable web server for fast metagenomic sequence analysis. BMC Genomics 12:444. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-444
Yun SH, Park EC, Lee SY, Lee H, Choi CW, Yi YS, Ro HJ, Lee JC, Jun S, Kim HY, Kim GH, Kim SI (2018) Antibiotic treatment modulates protein components of cytotoxic outer membrane vesicles of multidrug-resistant clinical strain, Acinetobacter baumannii DU202. Clin Proteomics 15:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12014-018-9204-2
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Qiu J, Luo ZQ, Deng X (2018) The herbal compound thymol protects mice from lethal infection by Salmonella Typhimurium. Front Microbiol 9:1022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01022
Funding
This study was financed by the Postdoctoral Research Funding of Shanxi Province, the Postdoctoral Research Funding of Shanxi Agricultural University, the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (162300410109), the Key Research Project of Henan Provincial Department of Education (19A230008), and the Research Program of Xinxiang University (XXUTD201701106 and 1333020286).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Yonghua Qi, Hongquan Li. Formal analysis: Yonghua Qi. Funding acquisition: Xuannian Wang, Hongquan Li. Investigation: Wei Zhao, Min Yue, Feng Li. Methodology: Tao Wang, Fangying Pei. Supervision: Xingyou Liu, Hongquan Li. Writing—original draft preparation: Yonghua Qi, Wei Zhao. Writing—review and editing: Yonghua Qi.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1073 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Y., Zhao, W., Wang, T. et al. Proteomic analysis of the antimicrobial effects of sublethal concentrations of thymol on Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 3493–3505 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10390-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10390-9