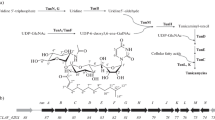
Abstract
Bleomycin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic, has been widely used for various tumor treatments. However, its poor fermentation yield is not satisfactory for industrial production. Here, the ArsR/SmtB family regulator BlmR was characterized as a repressor of bleomycin production. As an autoregulator, BlmR was found to bind to a 12-2-12 imperfect palindrome sequence in its own promoter, and deletion of blmR led to a 34% increase of bleomycin B2 production compared with the wild-type strain. Using reverse transcription and quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR), blmT, which encoded a putative transporter, was identified as the target gene regulated by BlmR. Therefore, high-production strain was constructed by blmT overexpression in a blmR deletion strain, and the bleomycin B2 titer reached to 80 mg/L, which was 1.9-fold higher than the wild-type strain. Moreover, electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) showed neither metal-binding motifs nor redox switches in BlmR. In order to elucidate the regulatory mechanism, a model of BlmR was constructed by homology modeling and protein-protein docking. The BlmR-DNA complex was generated by protein-DNA docking with the assistance of site-directed mutagenesis and molecular dynamic (MD) simulation, which directly revealed several key amino acid residues needed for the maintenance and stabilization of the interface between BlmR and target DNA. The interface information could provide the configuration reference and seek the potential effectors that could interact with BlmR, thereby extending the regulation role of ArsR/SmtB family members on the improvement of antibiotic production.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alper SL, Sharma AK (2013) The SLC26 gene family of anion transporters and channels. Mol Asp Med 34(2-3):494–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2012.07.009
Aravind L, Anantharaman V, Balaji S, Babu MM, Iyer LM (2010) The many faces of the helix-turn-helix domain: transcription regulation and beyond. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29(2):231–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fmrre.2004.12.008
Arunkumar AI, Campanello GC, Giedroc DP (2009) Solution structure of a paradigm ArsR family zinc sensor in the DNA-bound state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(43):18177–18182. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0905558106
Babu M, Greenblatt JF, Emili A, Strynadka NC, Reithmeier RA, Moraes TF (2010) Structure of a SLC26 anion transporter STAS domain in complex with acyl carrier protein: implications for E. coli YchM in fatty acid metabolism. Structure 18(11):1450–1462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2010.08.015
Bose M, Slick D, Sarto MJ, Murphy P, Roberts D, Roberts J, Barber RD (2014) Identification of SmtB/ArsR cis elements and proteins in archaea using the Prokaryotic InterGenic Exploration Database (PIGED). Archaea 2(1):39–49. https://doi.org/10.1155/2006/837139
Burger RM, Peisach J, Horwitz SB (1981) Activated bleomycin. A transient complex of drug, iron, and oxygen that degrades DNA. J Biol Chem 256(22):11636–11644. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-022X(81)90075-0
Busenlehner LS, Pennella MA, Giedroc DP (2010) The SmtB/ArsR family of metalloregulatory transcriptional repressors: structural insights into prokaryotic metal resistance. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27(2-3):131–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-6445(03)00054-8
Chauhan S, Kumar A, Singhal A, Tyagi JS, Prasad HK (2010) CmtR, a cadmium-sensing ArsR–SmtB repressor, cooperatively interacts with multiple operator sites to autorepress its transcription in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. FEBS J 276(13):3428–3439. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07066.x
Contursi P, Farina B, Pirone L, Fusco S, Russo L, Bartolucci S, Fattorusso R, Pedone E (2014) Structural and functional studies of Stf76 from the Sulfolobus islandicus plasmid-virus pSSVx: a novel peculiar member of the winged helix-turn-helix transcription factor family. Nucleic Acids Res 42(9):5993–6011. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku215
Coulocheri SA, Pigis DG, Papavassiliou KA, Papavassiliou AG (2007) Hydrogen bonds in protein-DNA complexes: where geometry meets plasticity. Biochimie 89(11):1291–1303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2007.07.020
Dijk M, Bonvin AMJJ (2009) 3D-DART: a DNA structure modelling server. Nucleic Acids Res 37(Web Server issue):W235–W239. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp287
Du L, Sánchez C, Chen M, Edwards DJ, Shen B (2000) The biosynthetic gene cluster for the antitumor drug bleomycin from Streptomyces verticillus ATCC15003 supporting functional interactions between nonribosomal peptide synthetases and a polyketide synthase. Chem Biol 7(8):623–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1074-5521(00)00011-9
Eicken C, Pennella MA, Chen X, Koshlap KM, Vanzile ML, Sacchettini JC, Giedroc DP (2003) A metal–ligand-mediated intersubunit allosteric switch in related SmtB/ArsR zinc sensor proteins. J Mol Biol 333(4):683–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2003.09.007
Fineran PC, Everson L, Slater H, Salmond GP (2005) A GntR family transcriptional regulator (PigT) controls gluconate-mediated repression and defines a new, independent pathway for regulation of the tripyrrole antibiotic, prodigiosin, in Serratia. Microbiology 151(Pt 12:3833–3845. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.28251-0
Galagan JE, Minch K, Peterson M, Lyubetskaya A, Azizi E, Sweet L, Gomes A, Rustad T, Dolganov G, Glotova I (2013) The Mycobacterium tuberculosis regulatory network and hypoxia. Nature 499(7457):178–183. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12337
Galm U, Hager MH, Van Lanen SG, Ju J, Thorson JS, Shen B (2005) Antitumor antibiotics: bleomycin, enediynes, and mitomycin. Chem Rev 105(2):739–758. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr030117g
Galm U, Wang L, Wendt-Pienkowski E, Yang R, Liu W, Tao M, Coughlin JM, Shen B (2008) In vivo manipulation of the bleomycin biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces verticillus ATCC15003 revealing new insights into its biosynthetic pathway. J Biol Chem 283(42):28236–28245. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M804971200
Galm U, Wendtpienkowski E, Wang L, Huang SX, Unsin C, Tao M, Coughlin JM, Shen B (2011) Comparative analysis of the biosynthetic gene clusters and pathways for three structurally related antitumor antibiotics: bleomycin, tallysomycin, and zorbamycin. J Nat Prod 74(3):526–536. https://doi.org/10.1021/np1008152
Guimarães BG, Barbosa RL, Soprano AS, Campos BM, De TS, Tonoli CC, Leme AF, Murakami MT, Benedetti CE (2011) Plant pathogenic bacteria utilize biofilm growth-associated repressor (BigR), a novel winged-helix redox switch, to control hydrogen sulfide detoxification under hypoxia. J Biol Chem 286(29):26148–26157. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.234039
Gust B, Challis GL, Fowler K, Kieser T, Chater KF (2003) PCR-targeted Streptomyces gene replacement identifies a protein domain needed for biosynthesis of the sesquiterpene soil odor geosmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(4):1541–1546. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0337542100
He H, Bretl DJ, Penoske RM, Anderson DM, Zahrt TC (2011) Components of the Rv0081-Rv0088 locus, which encodes a predicted formate hydrogenlyase complex, are coregulated by Rv0081, MprA, and DosR in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol 193(19):5105–5118. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.05562-11
Kim HM, Ahn BE, Lee JH, Roe JH (2015) Regulation of a nickel-cobalt efflux system and nickel homeostasis in a soil actinobacterium Streptomyces coelicolor. Metallomics 7(4):702–709. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4mt00318g
Lee SG, Krishnan HB, Jez JM (2014) Structural basis for regulation of rhizobial nodulation and symbiosis gene expression by the regulatory protein NolR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(17):6509–6514. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1402243111
Liu M, Naka H, Crosa JH (2010) HlyU acts as an H-NS antirepressor in the regulation of the RTX toxin gene essential for the virulence of the human pathogen Vibrio vulnificus CMCP6. Mol Microbiol 72(2):491–505. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06664.x
Lougher MJ (2015) Functional and structural insights into MmyJ, An ArsR-like transcriptional repressor. Dissertation, University of Warwick
Ma D, Wang C, Chen H, Wen J (2018) Manipulating the expression of SARP family regulator BulZ and its target gene product to increase tacrolimus production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(11):4887–4900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8979-4
Mandelgutfreund Y, Schueler O, Margalit H (1995) Comprehensive analysis of hydrogen bonds in regulatory protein DNA-complexes: in search of common principles. J Mol Biol 253(2):370–382. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1995.0559
Mao XM, Luo S, Li YQ (2017) Negative regulation of daptomycin production by DepR2, an ArsR-family transcriptional factor. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44(12):1653–1658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-017-1983-3
Mou X, Spinard EJ, Driscoll MV, Zhao W, Nelson DR (2013) H-NS is a negative regulator of the two hemolysin/cytotoxin gene clusters in Vibrio anguillarum. Infect Immun 81(10):3566–3576. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00506-13
Mukherjee D, Datta AB, Chakrabarti P (2014) Crystal structure of HlyU, the hemolysin gene transcription activator, from Vibrio cholerae N16961 and functional implications. Biochim Biophys Acta 1844(12):2346–2354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbaapa.2014.09.020
Mukherjee D, Pal A, Chakravarty D, Chakrabarti P (2015) Identification of the target DNA sequence and characterization of DNA binding features of HlyU, and suggestion of a redox switch for hlyA expression in the human pathogen Vibrio cholerae from in silico studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43(3):1407–1417. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1319
Murray V, Chen J, Long C (2018) The interaction of the metallo-glycopeptide anti-tumour drug bleomycin with DNA. Int J Mol Sci 19(5):1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051372
Osman D, Cavet JS (2010) Bacterial metal-sensing proteins exemplified by ArsR-SmtB family repressors. Nat Prod Rep 27(5):668–680. https://doi.org/10.1039/b906682a
Palmano S, Firrao G, Locci R (2000) Sequence analysis of domains III and IV of the 23S rRNA gene of verticillate streptomycetes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50(3):1187–1191. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-50-3-1187
Rohs R, Jin X, West SM, Joshi R, Honig B, Mann RS (2010) Origins of specificity in protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem 79(1):233–269. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060408-091030
Roy R, Samanta S, Patra S, Mahato NK, Saha RP (2018) In silico identification and characterization of sensory motifs in the transcriptional regulators of the ArsR-SmtB family. Metallomics 10:1476–1500. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MT00082D
Shi W, Dong J, Scott RA, Ksenzenko MY, Rosen BP (1996) The role of arsenic-thiol interactions in metalloregulation of the ars Operon. J Biol Chem 271(16):9291–9297. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.271.16.9291
Umezawa H, Maeda K, Takeuchi T, Okami Y (1966) New antibiotics, bleomycin A and B. J Antibiot 19(5):200–209. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.19.200
Vries SJD, Bonvin AMJJ (2011) CPORT: A consensus interface predictor and its performance in prediction-driven docking with HADDOCK. PLoS One 6(3):e17695. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0017695
Wang Y, Kendall J, Cavet JS, Giedroc DP (2010) Elucidation of the functional metal binding profile of a CdII/PbII sensor CmtRSc from Streptomyces coelicolor. Biochemistry 49(31):6617–6626. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi100490u
Zolotarev A, Unnikrishnan M, Shmukler B, Clark J, Vandorpe D, Grigorieff N, Rubin E, Alper S (2008) Increased sulfate uptake by E. coli overexpressing the SLC26-related SulP protein Rv1739c from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 149(3):255–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.12.005
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21676189) and the Key Technologies R&D Program of Tianjin (No. 16YFZCSY00780).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 707 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Wang, J., Cui, J. et al. Negative regulation of bleomycins biosynthesis by ArsR/SmtB family repressor BlmR in Streptomyces verticillus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 6629–6644 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09923-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09923-8