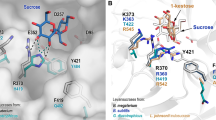
Abstract
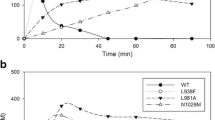
Levansucrases, which belong to the glycoside hydrolase family 68 (GH68), synthesize β (2-6)-linked fructan levan with sucrose as substrate. We described the use of a levansucrase (Bl_SacB) from Bacillus licheniformis 8-37-0-1 for catalysis of fructosyl transfer to obtain high levan yield previously. In the present study, six variants (Y246A, N251A, K372A, R369A, R369S, and R369K) were constructed through sequence alignment and structural analysis to explore the synthesis mechanism of Bl_SacB. The selected residues were predicted to localize to the substrate-entering channel of the active cavity and close to or remote from the catalytic triad. The products of these variants ranged from homopolymers levan to fructo-oligosaccharides (FOSs). The primary FOSs were identified through MS and NMR analyses as neolevan-type neokestose [β-d-Fru-(2-6)-α-d-Glc-(1-2)-β-d-Fru], levan-type 6-kestose [β-d-Fru-(2-6)-β-d-Fru-(2-1)-α-d-Glc], and inulin-type 1-kestose [β-d-Fru-(2-1)-β-d-Fru-(2-1)-α-d-Glc]. The mutation at Tyr246 located remote from the catalytic triad led to the production of short-chain oligosaccharides with degree of polymerization (DP) of up to 25. The replaced Arg369 located close to the catalytic triad resulted in either elimination of polysaccharide synthesis or complete change in the dominant linkage of the products. The Michaelis constants (Km) of Y246A, N251A, K372A, and R369K were found to be similar to that of the wild type (WT). However, the turnover number (kcat) and the value of transfructosylation versus hydrolysis activity of the six variants decreased compared with those of the WT. Hence, the residues located on the surface of the substrate-entering channel of Bl_SacB can be critical in product linkage type and/or elongation mechanism.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Fattah AM, Gamal-Eldeen AM, Helmy WA, Esawy MA (2012) Antitumor and antioxidant activities of levan and its derivative from the isolate Bacillus subtilis NRC1aza. Carbohydr Polym 89(2):314–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.02.041
Bekers M, Laukevics J, Upite D, Kaminska E, Vigants A, Viesturs U, Pankova L, Danilevics A (2002) Fructooligosaccharide and levan producing activity of Zymomonas mobilis extracellular levansucrase. Process Biochem 38(5):701–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(02)00189-9
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Byun BY, Lee SJ, Mah JH (2014) Antipathogenic activity and preservative effect of levan (β-2, 6-fructan), a multifunctional polysaccharide. Int J Food Sci Technol 49(1):238–245. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.12304
Caputi L, Nepogodiev SA, Malnoy M, Rejzek M, Field RA, Benini S (2013) Biomolecular characterization of the levansucrase of Erwinia amylovora, a promising biocatalyst for the synthesis of fructooligosaccharides. J Agric Food Chem 61(50):12265–12273. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf4023178
Chambert R, Petit-Glatron M (1991) Polymerase and hydrolase activities of Bacillus subtilis levansucrase can be separately modulated by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochem J 279(1):35–41. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2790035
Dahech I, Belghith KS, Belghith H, Mejdoub H (2012) Partial purification of a Bacillus licheniformis levansucrase producing levan with antitumor activity. Int J Biol Macromol 51(3):329–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.04.030
Gimeno-Pérez M, Linde D, Fernández-Arrojo L, Plou FJ, Fernández-Lobato M (2015) Heterologous overproduction of β-fructofuranosidase from yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous, an enzyme producing prebiotic sugars. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(8):3459–3467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6145-1
Hendry GAF, Wallace RK (1993) The origin, distribution and evolutionary significance of fructans. In: Suzuki M, Chatterton JN (eds) Science and technology of fructans. CPR Press, Florida, pp 119–139
Homann A, Biedendieck R, Götze S, Jahn D, Seibel J (2007) Insights into polymer versus oligosaccharide synthesis: mutagenesis and mechanistic studies of a novel levansucrase from Bacillus megaterium. Biochem J 407(2):189–198. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20070600
Kelley LA, Mezulis S, Yates CM, Wass MN, Sternberg MJ (2015) The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat Protoc 10(6):845–858. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2015.053
Kilian S, Kritzinger S, Rycroft C, Gibson G, Du Preez J (2002) The effects of the novel bifidogenic trisaccharide, neokestose, on the human colonic microbiota. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 18(7):637–644. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016808015630
Lee SM, Chang JY, Wu JS, Sheu DC (2015) Antineoplastic effect of a novel chemopreventive agent, neokestose, on the Caco-2 cell line via inhibition of expression of nuclear factor-κB and cyclooxygenase-2. Mol Med Rep 12(1):1114–1118. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3507
Liu C, Lu J, Lu L, Liu Y, Wang F, Xiao M (2010) Isolation, structural characterization and immunological activity of an exopolysaccharide produced by Bacillus licheniformis 8-37-0-1. Bioresour Technol 101(14):5528–5533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.151
Lombard V, Golaconda Ramulu H, Drula E, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B (2014) The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res 42(D1):D490–D495. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1178
Lu L, Fu F, Zhao R, Jin L, He C, Xu L, Xiao M (2014) A recombinant levansucrase from Bacillus licheniformis 8-37-0-1 catalyzes versatile transfructosylation reactions. Process Biochem 49(9):1503–1510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.05.012
Martínez-Fleites C, Ortíz-Lombardía M, Pons T, Tarbouriech N, Taylor EJ, Arrieta JG, Hernández L, Davies GJ (2005) Crystal structure of levansucrase from the Gram-negative bacterium Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus. Biochem J 390(1):19–27. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20050324
Marx SP, Winkler S, Hartmeier W (2000) Metabolization of β-(2, 6)-linked fructose-oligosaccharides by different bifidobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 182(1):163–169. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb08891.x
Meng G, Fütterer K (2003) Structural framework of fructosyl transfer in Bacillus subtilis levansucrase. Nat Struct Mol Biol 10(11):935–941. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb974
Meng G, Fütterer K (2008) Donor substrate recognition in the raffinose-bound E342A mutant of fructosyltransferase Bacillus subtilis levansucrase. BMC Struct Biol 8(1):16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6807-8-16
Öner ET, Hernández L, Combie J (2016) Review of Levan polysaccharide: from a century of past experiences to future prospects. Biotech Adv 34(5):827–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.05.002
Ortiz-Soto ME, Rivera M, Rudiño-Piñera E, Olvera C, López-Munguía A (2008) Selected mutations in Bacillus subtilis levansucrase semi-conserved regions affecting its biochemical properties. Protein Eng Des Sel 21(10):589–595. https://doi.org/10.1093/protein/gzn036
Ozimek LK, Kralj S, Van der Maarel MJ, Dijkhuizen L (2006) The levansucrase and inulosucrase enzymes of Lactobacillus reuteri 121 catalyse processive and non-processive transglycosylation reactions. Microbiology 152(4):1187–1196. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.28484-0
Park H-E, Park NH, Kim M-J, Lee TH, Lee HG, Yang J-Y, Cha J (2003) Enzymatic synthesis of fructosyl oligosaccharides by levansucrase from Microbacterium laevaniformans ATCC 15953. Enzym Microb Technol 32(7):820–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(03)00062-0
Raga-Carbajal E, Carrillo-Nava E, Costas M, Porras-Dominguez J, López-Munguía A, Olvera C (2016) Size product modulation by enzyme concentration reveals two distinct levan elongation mechanisms in Bacillus subtilis levansucrase. Glycobiology 26(4):377–385. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwv112
Sabater-Molina M, Larqué E, Torrella F, Zamora S (2009) Dietary fructooligosaccharides and potential benefits on health. J Physiol Biochem 65(3):315–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03180584
Santos-Moriano P, Fernandez-Arrojo L, Poveda A, Jimenez-Barbero J, Ballesteros AO, Plou FJ (2015) Levan versus fructooligosaccharide synthesis using the levansucrase from Zymomonas mobilis: effect of reaction conditions. J Mol Catal B Enzym 119:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2015.05.011
Shih I-L, Yu Y-T, Shieh C-J, Hsieh C-Y (2005) Selective production and characterization of levan by Bacillus subtilis (Natto) Takahashi. J Agric Food Chem 53(21):8211–8215. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf058084o
Strube CP, Homann A, Gamer M, Jahn D, Seibel J, Heinz DW (2011) Polysaccharide synthesis of the levansucrase SacB from Bacillus megaterium is controlled by distinct surface motifs. J Biol Chem 286(20):17593–17600. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.203166
Tanaka T, Susumu O, Yamamoto T (1980) The molecular structure of low and high molecular weight levans synthesized by levansucrase. J Biochem 87(1):297–303
Tieking M, Ehrmann MA, Vogel RF, Gänzle MG (2005) Molecular and functional characterization of a levansucrase from the sourdough isolate Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis TMW 1.392. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66(6):655–663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1773-5
Trujillo L, Arrieta J, Dafhnis F, Garcıa J, Valdes J, Tambara Y, Pérez M, Hernández L (2001) Fructo-oligosaccharides production by the Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus levansucrase expressed in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Enzym Microb Technol 28(2):139–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(00)00290-8
Van Hijum S, Van Der Maarel M, Dijkhuizen L (2003) Kinetic properties of an inulosucrase from Lactobacillus reuteri 121. FEBS Lett 534(1–3):207–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03841-3
Visnapuu T, Mardo K, Alamaee T (2015) Levansucrases of a Pseudomonas syringae pathovar as catalysts for the synthesis of potentially prebiotic oligo-and polysaccharides. New Biotechnol 32(6):597–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2015.01.009
Visnapuu T, Mardo K, Mosoarca C, Zamfir AD, Vigants A, Alamäe T (2011) Levansucrases from Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato and P. chlororaphis subsp. aurantiaca: substrate specificity, polymerizing properties and usage of different acceptors for fructosylation. J Biotechnol 155(3):338–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.07.026
Waldherr FW, Meissner D, Vogel RF (2008) Genetic and functional characterization of Lactobacillus panis levansucrase. Arch Microbiol 190(4):497–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-008-0404-4
Weijers CA, Franssen MC, Visser GM (2008) Glycosyltransferase-catalyzed synthesis of bioactive oligosaccharides. Biotechnol Adv 26(5):436–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.05.001
Wu JS, Chang JY, Chen CW, Lin MT, Sheu DC, Lee SM (2017) Neokestose suppresses the growth of human melanoma A2058 cells via inhibition of the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 16(1):295–300. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6594
Wuerges J, Caputi L, Cianci M, Boivin S, Meijers R, Benini S (2015) The crystal structure of Erwinia amylovora levansucrase provides a snapshot of the products of sucrose hydrolysis trapped into the active site. J Struct Biol 191(3):290–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2015.07.010
Yamamoto S, Iizuka M, Tanaka T, Yamamoto T (1985) The mode of synthesis of levan by Bacillus subtilis levansucrase. Agric Biol Chem 49(2):343–349. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb1961.49.343
Yanase H, Maeda M, Hagiwara E, Yagi H, Taniguchi K, Okamoto K (2002) Identification of functionally important amino acid residues in Zymomonas mobilis levansucrase. J Biochem 132(4):565–572. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a003258
Funding
This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31670062 and 31070064), the Science and Technology Development Project of Shandong Province (2016GGH4502 and 2015GSF121004), and the Fundamental Research Funds of Shandong University (2016JC028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human and animal participants.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1873 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, C., Yang, Y., Zhao, R. et al. Rational designed mutagenesis of levansucrase from Bacillus licheniformis 8-37-0-1 for product specificity study. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 3217–3228 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8854-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8854-3