Abstract
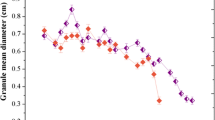
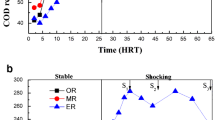
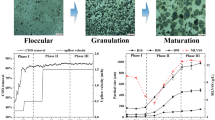
Three sequencing batch reactors (M1, M2, and M3) were set up to investigate the influence of different lengths of starvation time (3, 5, and 7 h) on aerobic granulation in the perspective of quorum sensing (QS). Autoinducer-2 (AI-2) level was quantified to evaluate the QS ability of aerobic granules. The results indicated that AI-2 level increased steadily during a cycle of sequencing batch reactors, suggesting that starvation was closely related to AI-2 secretion. In the long-term operation, aerobic granules cultivated using a prolonged starvation period had a better integrity and a higher level of cell adhesiveness despite a slower formation speed. With the extension of the starvation period, the total amount of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) displayed an increasing tendency. EPS with large molecular weight (MW) also reached a higher level using a prolonged starvation period. However, a higher level of AI-2 and cell adhesiveness was observed in M2, which might be related to more stable granules. The results implied that the starvation period could trigger AI-2 secretion and promoted the production of large MW EPS, leading to cell adhesiveness enhancement and granule formation. Therefore, a combination of different starvation periods was proposed in this study in order to improve aerobic granulation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Show KY, Tay JH (2008) Aerobic granular sludge: recent advances. Biotechnol Adv 26:411–423
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Cheng W, Zhang J, Wang Z, Wang M, Xie S (2014) Bacterial communities in sediments of a drinking water reservoir. Ann Microbiol 64:875–878
Eberl L (1999) N-acyl homoserinelactone-mediated gene regulation in gram-negative bacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 22:493–506
Galloway WR, Hodgkinson JT, Bowden SD, Welch M, Spring DR (2010) Quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria: small-molecule modulation of AHL and AI-2 quorum sensing pathways. Chem Rev 111:28–67
Gao D, Liu L, Wu WM (2011) Comparison of four enhancement strategies for aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactors. J Hazard Mater 186:320–327
Garnier C, Görner T, Lartiges BS, Abdelouhab S, De Donato P (2005) Characterization of activated sludge exopolymers from various origins: a combined size-exclusion chromatography and infrared microscopy study. Water Res 39:3044–3054
Han X, Lu C (2009) Detection of autoinducer-2 and analysis of the profile of luxS and pfs transcription in Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Curr Microbiol 58:146–152
Herbert D, Phipps P, Strange R (1971) Chemical analysis of microbial cells. Meth Microbiol 5:209–344
Jiang B, Liu Y (2013) Dependence of structure stability and integrity of aerobic granules on ATP and cell communication. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:5105–5112
Jin H, Lee NK, Shin MK, Kim SK, Kaplan DL, Lee JW (2003) Production of gellan gum by Sphingomonas paucimobilis NK2000 with soybean pomace. Biochem Eng J 16:357–360
Lee DJ, Chen YY, Show KY, Whiteley CG, Tay JH (2010) Advances in aerobic granule formation and granule stability in the course of storage and reactor operation. Biotechnol Adv 28:919–934
Lesprit P, Faurisson F, Join-Lambert O, Roudot-Thoraval F, Foglino M, Vissuzaine C, Carbon C (2003) Role of the quorum-sensing system in experimental pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in rats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167:1478–1482
Liu YQ, Tay JH (2007) Characteristics and stability of aerobic granules cultivated with different starvation time. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:205–210
Liu YQ, Tay JH (2008) Influence of starvation time on formation and stability of aerobic granules in sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour Technol 99:980–985
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lv J, Wang Y, Zhong C, Li Y, Hao W, Zhu J (2014) The effect of quorum sensing and extracellular proteins on the microbial attachment of aerobic granular activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 152:53–58
Mosquera-Corral A, De Kreuk M, Heijnen J, Van Loosdrecht M (2005) Effects of oxygen concentration on N-removal in an aerobic granular sludge reactor. Water Res 39:2676–2686
Pijuan M, Werner U, Yuan Z (2009) Effect of long term anaerobic and intermittent anaerobic/aerobic starvation on aerobic granules. Water Res 43:3622–3632
Sun S, Liu X, Ma B, Wan C, Lee DJ (2016) The role of autoinducer-2 in aerobic granulation using alternating feed loadings strategy. Bioresour Technol 201:58–64
Tan CH, Koh KS, Xie C, Tay M, Zhou Y, Williams R, Ng WJ, Rice SA, Kjelleberg S (2014) The role of quorum sensing signalling in EPS production and the assembly of a sludge community into aerobic granules. ISME J 8:1186–1197
Tay JH, Liu QS, Liu Y (2001) The effects of shear force on the formation, structure and metabolism of aerobic granules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:227–233
Tsuneda S, Aikawa H, Hayashi H, Yuasa A, Hirata A (2003) Extracellular polymeric substances responsible for bacterial adhesion onto solid surface. FEMS Microbiol Lett 223:287–292
Wan C, Zhang P, Lee DJ, Yang X, Liu X, Sun S, Pan X (2013) Disintegration of aerobic granules: role of second messenger cyclic di-GMP. Bioresour Technol 146:330–335
Wang F, Yang FL, Zhang XW, Liu YH, Zhang HM, Zhou J (2005) Effects of cycle time on properties of aerobic granules in sequencing batch airlift reactors. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:1379–1384
Wang Z, Liu L, Yao J, Cai W (2006) Effects of extracellular polymeric substances on aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactors. Chemosphere 63:1728–1735
Wang ZW, Liu Y, Tay JH (2007) Biodegradability of extracellular polymeric substances produced by aerobic granules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:462–466
Xiao C, Huang H, Ye J, Wu X, Zhu J, Zhan B, Bao S (2011) Ornithinibacter aureus gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family Intrasporangiaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:659–664
Xiong Y, Liu Y (2012) Essential roles of eDNA and AI-2 in aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactors operated at different settling times. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:2645–2651
Yan M, Korshin G, Wang D, Cai Z (2012) Characterization of dissolved organic matter using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-size exclusion chromatography (SEC) with a multiple wavelength absorbance detector. Chemosphere 87:879–885
Yi Y, Huang W, Ge Y (2008) Exopolysaccharide: a novel important factor in the microbial dissolution of tricalcium phosphate. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:1059–1065
Zhang SH, Yu X, Guo F, Wu ZY (2011) Effect of interspecies quorum sensing on the formation of aerobic granular sludge. Water Sci Technol 64:1284–1290
Zhang J, Zhang X, Liu Y, Xie S, Liu Y (2014) Bacterioplankton communities in a high-altitude freshwater wetland. Ann Microbiol 64:1405–1411
Zhou D, Li Y, Yang Y, Wang Y, Zhang C, Wang D (2015) Granulation, control of bacterial contamination, and enhanced lipid accumulation by driving nutrient starvation in coupled wastewater treatment and Chlorella regularis cultivation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:1531–1541
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51108093, 51278128, and 41301332), Shanghai International Science and Technology Cooperation Fund (No. 14230700400), Outstanding Talent Plan of Fudan University (JJH1829029), and Key Laboratory of Reservoir Aquatic Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. RAE2014CB05B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 378 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Sun, S., Ma, B. et al. Understanding of aerobic granulation enhanced by starvation in the perspective of quorum sensing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 3747–3755 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7246-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7246-1