Abstract
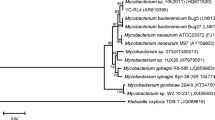
Arthrobacter sp. strain YC-RL1, capable of utilizing bisphenol A (BPA) as sole carbon source for growth, was isolated from petroleum contaminated soil. YC-RL1 could rapidly degrade BPA in a wide range of pH (5.0–9.0) and temperature (20–40 °C). Substrate analysis found that YC-RL1 could also degrade bisphenol F (BPF) and tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA). The maximum and minimum concentrations of BPA (0.2–600 mg/L), BPF (0.2–600 mg/L), and TBBPA (0.2–300 mg/L) for efficient biodegradation were detected. The released bromide ion and metabolic intermediates of BPF and BPA/TBBPA were detected, as well as the degradation pathways for BPF and BPA/TBBPA were deduced tentatively. The present study provides important information for the investigation of BPs degrading mechanism and the application of microbial remediation in BP-contaminated environment. This study is the first report about a genus Arthrobacter bacterium which could simultaneously degrade BPA, BPF, and TBBPA.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
An T, Zu L, Li G, Wan S, Mai B, Wong PK (2011) One-step process for debromination and aerobic mineralization of tetrabromobisphenol-A by a novel Ochrobactrum sp. T isolated from an e-waste recycling site. Bioresour Technol 102:9148–9154
Anwar S, Liaquat F, Khan QM, Khalid ZM, Iqbal S (2009) Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos and its hydrolysis product 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol by Bacillus pumilus strain C2A1. J Hazard Mater 168:400–405
Arbeli Z, Ronen Z (2003) Enrichment of a microbial culture capable of reductive debromination of the flame retardant tetrabromobisphenol-A, and identification of the intermediate metabolites produced in the process. Biodegradation 14:385–395
Arbeli Z, Ronen Z, Diaz-Baez MC (2006) Reductive dehalogenation of tetrabromobisphenol-A by sediment from a contaminated ephemeral streambed and an enrichment culture. Chemosphere 64:1472–1478
Audebert M, Dolo L, Perdu E, Cravedi JP, Zalko D (2011) Use of the gammaH2AX assay for assessing the genotoxicity of bisphenol A and bisphenol F in human cell lines. Arch Toxicol 85:1463–1473
Brenner A, Mukmenev I, Abeliovich A, Kushmaro A (2006) Biodegradability of tetrabromobisphenol A and tribromophenol by activated sludge. Ecotoxicology 15:399–402
Chen MY, Ike M, Fujita M (2002) Acute toxicity, mutagenicity, and estrogenicity of bisphenol-A and other bisphenols. Environ Toxicol 17:80–86
Covaci A, Voorspoels S, Abdallah MAE, Geens T, Harrad S, Law RJ (2009) Analytical and environmental aspects of the flame retardant tetrabromobisphenol-A and its derivatives. J Chromatogr A 1216:346–363
Darnerud PO (2003) Toxic effects of brominated flame retardants in man and in wildlife. Environ Int 29:841–853
Fromme H, Kuchler T, Otto T, Pilz K, Muller J, Wenzel A (2002) Occurrence of phthalates and bisphenol A and F in the environment. Water Res 36:1429–1438
Inoue D, Hara S, Kashihara M, Murai Y, Danzl E, Sei K, Tsunoi S, Fujita M, Ike M (2008) Degradation of bis(4-Hydroxyphenyl)methane (bisphenol F) by Sphingobium yanoikuyae strain FM-2 isolated from river water. Appl Environ MicrobI 74:352–358
Jin Q, Hu Z, Jin Z, Qiu L, Zhong W, Pan Z (2012) Biodegradation of aniline in an alkaline environment by a novel strain of the halophilic bacterium, Dietzia natronolimnaea JQ-AN. Bioresour Technol 117:148–154
Li G, Zu L, Wong PK, Hui X, LuY XJ, An T (2012) Biodegradation and detoxification of bisphenol A with one newly-isolated strain Bacillus sp. GZB: kinetics, mechanism and estrogenic transition. Bioresour Technol 114:224–230
Lin C, Gan L, Chen ZL (2010) Biodegradation of naphthalene by strain Bacillus fusiformis (BFN). J Hazard Mater 182:771–777
Liu J, Wang Y, Jiang B, Wang L, Chen J, Guo H, Ji R (2013) Degradation, metabolism, and bound-residue formation and release of tetrabromobisphenol A in soil during sequential anoxic-oxic incubation. Environ Sci Technol 47:8348–8354
Lobos JH, Leib TK, Su TM (1992) Biodegradation of bisphenol A and other bisphenols by a gram-negative aerobic bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:1823–1831
Matsumura Y, Hosokawa C, Sasaki-Mori M, Akahira A, Fukunaga K, Ikeuchi T, Oshiman K, Tsuchido T (2009) Isolation and characterization of novel bisphenol-A--degrading bacteria from soils. Biocontrol Sci 14:161–169
Matsushima A, Kakuta Y, Teramoto T, Koshiba T, Liu XH, Okada H, Tokunaga T, Kawabata S, Kimura M, Shimohigashi Y (2007) Structural evidence for endocrine disruptor bisphenol A binding to human nuclear receptor ERR gamma. J Biochem 142:517–524
Nyholm JR, Lundberg C, Andersson PL (2010) Biodegradation kinetics of selected brominated flame retardants in aerobic and anaerobic soil. Environ Pollut 158:2235–2240
Peng X, Qu X, Luo W, Jia X (2014) Co-metabolic degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A by novel strains of Pseudomonas sp. and Streptococcus sp. Bioresour Technol 169:271–276
Peng X, Zhang Z, Luo W, Jia X (2013) Biodegradation of tetrabromobisphenol A by a novel Comamonas sp. strain, JXS-2-02, isolated from anaerobic sludge. Bioresour Technol 128:173–179
Peng X, Zhang Z, Zhao Z, Jia X (2012) 16S ribosomal DNA clone libraries to reveal bacterial diversity in anaerobic reactor-degraded tetrabromobisphenol A. Bioresour Technol 112:75–82
Ravit B, Ehrenfeld JG, Haggblom MM (2005) Salt marsh rhizosphere affects microbial biotransformation of the widespread halogenated contaminant tetrabromobisphenol-A (TBBPA). Soil Biol Biochem 37:1049–1057
Rocklin RD, Johnson EL (1983) Determination of cyanide, sulfide, iodide, and bromide by ion chromatography with electrochemical detection. Anal Chem 55:4–7
Ronen Z, Abeliovich A (2000) Anaerobic-aerobic process for microbial degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2372–2377
Saiyood S, Vangnai AS, Thiravetyan P, Inthorn D (2010) Bisphenol A removal by the Dracaena plant and the role of plant-associating bacteria. J Hazard Mater 178:777–785
Sakai K, Yamanaka H, Moriyoshi K, Ohmoto T, Ohe T (2007) Biodegradation of bisphenol A and related compounds by Sphingomonas sp. strain BP-7 isolated from seawater. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:51–57
Satoh K, Ohyama K, Aoki N, Iida M, Nagai F (2004) Study on anti-androgenic effects of bisphenol a diglycidyl ether (BADGE), bisphenol F diglycidyl ether (BFDGE) and their derivatives using cells stably transfected with human androgen receptor, AR-EcoScreen. Food Chem Toxicol 42:983–993
Segev O, Kushmaro A, Brenner A (2009) Environmental impact of flame retardants (persistence and biodegradability). Int J Environ Res Public Health 6:478–491
Staples CA, Dorn PB, Klecka GM, O'Block ST, Harris LR (1998) A review of the environmental fate, effects, and exposures of bisphenol A. Chemosphere 36:2149–2173
Stroheker T, Picard K, Lhuguenot JC, Canivenc-Lavier MC, Chagnon MC (2004) Steroid activities comparison of natural and food wrap compounds in human breast cancer cell lines. Food Chem Toxicol 42:887–897
Suzuki T, Nakagawa Y, Takano I, Yaguchi K, Yasuda K (2004) Environmental fate of bisphenol A and its biological metabolites in river water and their xeno-estrogenic activity. Environ Sci Technol 38:2389–2396
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Telke AA, Kalyani DC, Jadhav UU, Parshetti GK, Govindwar SP (2009) Purification and characterization of an extracellular laccase from a Pseudomonas sp LBC1 and its application for the removal of bisphenol A. J Mol Catal B-Enzym 61:252–260
van Pée K-H, Unversucht S (2003) Biological dehalogenation and halogenation reactions. Chemosphere 52:299–312
Voordeckers JW, Fennell DE, Jones K, Haggblom MM (2002) Anaerobic biotransformation of tetrabromobisphenol A, tetrachlorobisphenol A, and bisphenol A in estuarine sediments. Environ Sci Technol 36:696–701
Wang J, Majima N, Hirai H, Kawagishi H (2012) Effective removal of endocrine-disrupting compounds by lignin peroxidase from the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete sordida YK-624. Cur Microbiol 64:300–303
Wang J, Yamada Y, Notake A, Todoroki Y, Tokumoto T, Dong J, Thomas P, Hirai H, Kawagishi H (2014) Metabolism of bisphenol A by hyper lignin-degrading fungus Phanerochaete sordida YK-624 under non-ligninolytic condition. Chemosphere 109:128–133
Wang X, Qin Y, Zhu L, Tang H (2015) Nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide as a bifunctional material for removing bisphenols: synergistic effect between adsorption and catalysis. Environ Sci Technol 49:6855–6864
Yamada T, Takahama Y, Yamada Y (2008) Biodegradation of 2,4,6-tribromophenol by Ochrobactrum sp. strain TB01. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72:1264–1271
Yamasaki K, Takeyoshi M, Sawaki M, Imatanaka N, Shinoda K, Takatsuki M (2003) Immature rat uterotrophic assay of 18 chemicals and Hershberger assay of 30 chemicals. Toxicology 183:93–115
Yang J, Li H, Ran Y, Chan K (2014) Distribution and bioconcentration of endocrine disrupting chemicals in surface water and fish bile of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Chemosphere 107:439–446
Yin LB, Liu Y, Zhang DY, Zhang SB (2012) Isolation and characterization of Rhodopseudomonas sp S9-1 capable of degrading pyrazosulfuron-ethyl. Adv Mater Res 1–5(356–360):1152–1163
Zhang C, Zeng G, Yuan L, Yu J, Li J, Huang G, Xi B, Liu H (2007) Aerobic degradation of bisphenol A by Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain B-16 isolated from compost leachate of municipal solid waste. Chemosphere 68:181–190
Zhang J, Sun Z, Li Y, Peng X, Li W, Yan Y (2009) Biodegradation of p-nitrophenol by Rhodococcus sp. CN6 with high cell surface hydrophobicity. J Hazard Mater 163:723–728
Zhang W, Yin K, Chen L (2013) Bacteria-mediated bisphenol A degradation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:5681–5689
Zheng D, Bao J, Lu J, Gao C (2015) Isolation and characterization of a furfural-degrading bacterium Bacillus cereus sp. strain DS1. Cur Microbiol 70:199–205
Acknowledgments
We thank Ni Xiang (Department of Entomology & Plant Pathology, Auburn University, USA) and Nahurira Ruth (Graduate School, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences), for the revision of the manuscript, and Lida Han (Public Laboratory, Biotechnology Research Institute of CAAS, China), for great help and good suggestions for HPLC and MS analyses. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, No. 31170119) and Basic Research Fund of CAAS (No. 0042014006, No. 0042012003, and No. 0042011006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Lei Ren and Yang Jia as the co-first author.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 458 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, L., Jia, Y., Ruth, N. et al. Biotransformations of bisphenols mediated by a novel Arthrobacter sp. strain YC-RL1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 1967–1976 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7076-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7076-1