Abstract
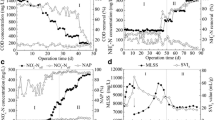
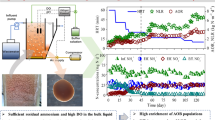
Short initial settling time and rapidly increased ammonium nitrogen loading were employed to cultivate nitrifying granular sludge treating inorganic wastewater with 1000 mg/L ammonium nitrogen. It was found that the nitrifying granule-dominant sludge was formed in a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) with influent ammonium concentration increased from 200 to 1000 mg N/L within 55 days. During the following 155-day operation period, nitrifying granules exhibited good performance with an ammonium removal efficiency of 99 %. In the meantime, sludge volume index (SVI) decreased from 92 to 15 mL/g and the mean size of the nitrifying granules increased from 106 to 369 μm. Mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS) decreased from the initial 6.4 to around 3 g/L during the granulation period and increased to over 10 g/L at the end of the operation. The long-term stability of nitrifying granules and the reactor performance were not negatively affected by inhibition from free ammonia (FA) and free nitrous acid (FNA) in this study. This makes the granule sludge technology promising in treating high-strength ammonium wastewater in practice.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anthonisen AC, Loehr RC, Prakasam TB, Srinath EG (1976) Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid. J Water Pollut Control Fed 48:835–852
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th ed. American Public Health Association, Washington
Belmonte M, Vazquez-Padin JR, Figueroa M, Franco A, Mosquera-Corral A, Campos JL, Mendez R (2009) Characteristics of nitrifying granules developed in an air pulsing SBR. Process Biochem 44:602–606
Bin Z, Zhe C, Zhigang Q, Min J, Zhiqiang C, Zhaoli C, Junwen L, Xuan W, Jingfeng W (2011) Dynamic and distribution of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria communities during sludge granulation in an anaerobic–aerobic sequencing batch reactor. Water Res 45:6207–6216
Chen F, Liu YQ, Tay JH, Ping N (2011) Operational strategies for nitrogen removal in granular sequencing batch reactor. J Hazard Mater 189:342–348
de Kreuk M, Heijnen JJ, van Loosdrecht MCM (2005) Simultaneous COD, nitrogen, and phosphate removal by aerobic granular sludge. Biotechnol Bioeng 90:761–769
Fang F, Ni BJ, Li XY, Sheng GP, Yu HQ (2009) Kinetic analysis on the two-step processes of AOB and NOB in aerobic nitrifying granules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:1159–1169
Ford DL, Churchwell RL, Kachtick JW (1980) Comprehensive analysis of nitrification of chemical processing wastewaters. J Water Pollut Control Fed 52:2726–2746
Jin RC, Zheng P, Mahmood Q, Zhang L (2008) Performance of a nitrifying airlift reactor using granular sludge. Sep Purif Technol 63:670–675
Kishida N, Saeki G, Tsuneda S, Sudo R (2012) Rapid start-up of a nitrifying reactor using aerobic granular sludge as seed sludge. Water Sci Technol 65:581–588
Liu YQ, Tay JH (2006) Variable aeration in sequencing batch reactor with aerobic granular sludge. J Biotechnol 124:338–346
Liu YQ, Tay JH (2007) Cultivation of aerobic granules in a bubble column and an airlift reactor with divided draft tubes at low aeration rate. Biochem Eng J 34:1–7
Liu YQ, Tay JH (2012) The competition between flocculent sludge and aerobic granules during the long-term operation period of granular sludge sequencing batch reactor. Environ Technol 33:2619–2626
Liu YQ, Tay JH, Ivanov V, Moy BYP, Yu L, Tay STL (2005) Influence of phenol on nitrification by microbial granules. Process Biochem 40:3285–3289
Liu YQ, Wu WW, Tay JH, Wang HL (2008) Formation and long-term stability of nitrifying granules in a sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour Technol 99:3919–3922
Liu YQ, Moy B, Kong YH, Tay JH (2010) Formation, physical characteristics and microbial community structure of aerobic granules in a pilot-scale sequencing batch reactor for real wastewater treatment. Enzyme Microbiol Technol 46:520–5252009
Liu YQ, Kong YH, Tay JH, Zhu JR (2011) Enhancement of start-up of pilot-scale granular SBR fed with real wastewater. Sep Purif Technol 82:190–196
Lopez-Palau S, Dosta J, Pericas A, Mata-Alvarez J (2011) Partial nitrification of sludge reject water using suspended and granular biomass. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 86:1480–1487
Moy BYP, Tay JH, Toh SK, Liu Y, Tay STL (2002) High organic loading influences the physical characteristics of aerobic sludge granules. Lett Appl Microbiol 34:407–412
Qin L, Liu Y, Tay JH (2004) Effect of settling time on aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactor. Biochem Eng J 21:47–52
Schepers AW, Thibault J, Lacroix C (2000) Comparison of simple neural networks and nonlinear regression models for descriptive modeling of Lactobacillus helveticus growth in pH-controlled batch cultures. Enzyme Microbiol Technol 26:431–445
Shi XY, Sheng GP, Li X, Yu HQ (2010) Operation of a sequencing batch reactor for cultivating autotrophic nitrifying granules. Bioresour Technol 101:2960–2964
Song Y, Ishii S, Rathnayake L, Ito T, Satoh H, Okabe S (2013) Development and characterization of the partial nitrification aerobic granules in a sequencing batch airlift reactor. Bioresour Technol 139:285–291
Su KZ, Yu HQ (2005) Formation and characterization of aerobic granules in a sequencing batch reactor treating soybean-processing wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 39:2818–2827
Tay JH, Yang SF, Liu Y (2002) Hydraulic selection pressure-induced nitrifying granulation in sequencing batch reactors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:332–337
Tsuneda S, Nagano T, Hoshino T, Ejiri Y, Noda N, Hirata A (2003) Characterization of nitrifying granules produced in an aerobic upflow fluidized bed reactor. Water Res 37:4965–4973
Vadivelu VM, Keller J, Yuan Z (2007) Free ammonia and free nitrous acid inhibition on the anabolic and catabolic processes of Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter. Water Sci Technol 56:89–97
Wang XH, Zhang HM, Yang FL, Xia LP, Gao MM (2007) Improved stability and performance of aerobic granules under stepwise increased selection pressure. Enzyme Microbiol Technol 41:205–211
Wang XH, Diao MH, Yang Y, Shi YJ, Gao MM, Wang SG (2012) Enhanced aerobic nitrifying granulation by static magnetic field. Bioresour Technol 110:105–110
Yang SF, Tay JH, Liu Y (2004) Inhibition of free ammonia to the formation of aerobic granules. Biochem Eng J 17:41–48
Zhang X, Liu YQ, Tay JH, Jiang WJ (2013) Fast granulation under extreme selection pressures and its formation mechanism. Fresenius Environ Bull 22:1330–1338
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, FY., Liu, YQ., Tay, JH. et al. Rapid formation of nitrifying granules treating high-strength ammonium wastewater in a sequencing batch reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 4445–4452 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6363-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6363-6