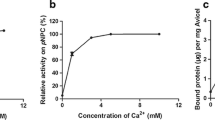
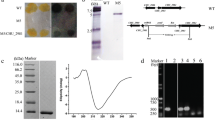
Abstract
Cytophaga hutchinsonii is a Gram-negative gliding bacterium which can efficiently degrade crystalline cellulose by an unknown strategy. Genomic analysis suggests the C. hutchinsonii genome lacks homologs to an obvious exoglucanase that previously seemed essential for cellulose degradation. One of the putative endoglucanases, CHU_2103, was successfully expressed in Escherichia coli JM109 and identified as a processive endoglucanase with transglycosylation activity. It could hydrolyze carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) into cellodextrins and rapidly decrease the viscosity of CMC. When regenerated amorphous cellulose (RAC) was degraded by CHU_2103, the ratio of the soluble to insoluble reducing sugars was 3.72 after 3 h with cellobiose and cellotriose as the main products, indicating that CHU_2103 was a processive endoglucanase. CHU_2103 could degrade cellodextrins of degree of polymerization ≥3. It hydrolyzed p-nitrophenyl β-d-cellodextrins by cutting glucose or cellobiose from the non-reducing end. Meanwhile, some larger-molecular-weight cellodextrins could be detected, indicating it also had transglycosylation activity. Without carbohydrate-binding module (CBM), CHU_2103 could bind to crystalline cellulose and acted processively on it. Site-directed mutation of CHU_2103 demonstrated that the conserved aromatic amino acid W197 in the catalytic domain was essential not only for its processive activity, but also its cellulose binding ability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai T, Araki R, Tanaka A, Karita S, Kimura T, Sakka K, Ohmiya K (2003) Characterization of a cellulase containing a family 30 carbohydrate-binding module (CBM) derived from Clostridium thermocellum CelJ: importance of the CBM to cellulose hydrolysis. J Bacteriol 185(2):504–512. doi:10.1128/jb.185.2.504-512.2003
Bayer EA, Belaich JP, Shoham Y, Lamed R (2004) The cellulosome: multienzyme machines for degradation of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Annu Rev Microbiol 58:521–554. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.57.030502.091022
Bhatia Y, Mishra S, Bisaria VS (2002) Microbial β-glucosidases: cloning, properties, and applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol 22(4):375–407. doi:10.1080/07388550290789568
Cohen R, Suzuki MR, Hammel KE (2005) Processive endoglucanase active in crystalline cellulose hydrolysis by the brown rot basidiomycete Gloeophyllum trabeum. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(5):2412–2417. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.5.2412-2417.2005
Davis BG (2000) Recent developments in oligosaccharide synthesis. J Chem Soc Perkin 1:2137–2160
Harjunpää V, Helin J, Koivula A, Siika-aho M, Drakenberg T (1999) A comparative study of two retaining enzymes of Trichoderma reesei: transglycosylation of oligosaccharides catalysed by the cellobiohydrolase I, Cel7A, and the β-mannanase, Man5A. FEBS Lett 443:149–153
Ho SN, Hunt HD, Horton RM, Pullen JK, Pease LR (1989) Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 77(1):51–59. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2
Irwin D, Shin D, Zhang S, Barr BK, Sakon J, Karplus PA, Wilson DB (1998) Roles of the catalytic domain and two cellulose binding domains of Thermomonospora fusca E4 in cellulose hydrolysis. J Bacteriol 180(7):1709–1714
Ji X, Xu Y, Zhang C, Chen N, Lu X (2012) A new locus affects cell motility, cellulose binding, and degradation by Cytophaga hutchinsonii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96(1):161–170. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4051-y
Kurasin M, Valjamae P (2011) Processivity of cellobiohydrolases is limited by the substrate. J Biol Chem 286(1):169–177. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.161059
Kwon I, Ekino K, Oka T, Goto M, Furukawa K (2002) Effects of amino acid alteration on the transglycosylation reaction of endoglucanase I from Trichoderma viride HK-75. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66(1):110–116
Li Y, Irwin DC, Wilson DB (2007) Processivity, substrate binding, and mechanism of cellulose hydrolysis by Thermobifida fusca Cel9A. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(10):3165–3172. doi:10.1128/AEM.02960-06
Louime C, Abazinge M, Johnson E, Latinwo L, Ikediobi C, Clark AM (2007) Molecular cloning and biochemical characterization of a family-9 endoglucanase with an unusual structure from the gliding bacteria Cytophaga hutchinsonii. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 141(1):127–138
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, Van Zyl WH, Pretorius IS (2002) Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66(3):506–577. doi:10.1128/mmbr.66.3.506-577.2002
Meinke A, Damude HG, Tomme P, Emily Kwan E, Kilburn DG, Miller RC Jr, Warren RA, Gilkes NR (1994) Enhancement of the endo-β-1,4-glucanase activity of an exocellobiohydrolase by deletion of a surface loop. J Biol Chem 270(9):4383–4386
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31(3):426–428
Murashima K, Kosugi A, Doi RH (2005) Site-directed mutagenesis and expression of the soluble form of the family IIIa cellulose binding domain from the cellulosomal scaffolding protein of Clostridium cellulovorans. J Bacteriol 187(20):7146–7149. doi:10.1128/JB.187.20.7146-7149.2005
Petersen TN, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2011) SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods 8(10):785–786. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1701
Reverbel-Leroy C, Pages S, Belaich A, Belaich J, Tardif C (1997) The processive endocellulase CelF, a major component of the Clostridium cellulolyticum cellulosome: purification and characterization of the recombinant form. J Bacteriol 179(1):46–52
Sakon J, Irwin D, Wilson DB, Karplus PA (1997) Structure and mechanism of endo/exocellulase E4 from Thermomonospora fusa. Nat Struct Biol 4:810–818. doi:10.1038/nsb1097-810
Santos CR, Paiva JH, Sforca ML, Neves JL, Navarro RZ, Cota J, Akao PK, Hoffmam ZB, Meza AN, Smetana JH, Nogueira ML, Polikarpov I, Xavier-Neto J, Squina FM, Ward RJ, Ruller R, Zeri AC, Murakami MT (2012) Dissecting structure–function–stability relationships of a thermostable GH5-CBM3 cellulase from Bacillus subtilis 168. Biochem J 441(1):95–104. doi:10.1042/BJ20110869
Teunissen MJ, Smits AAM, Opden Camp HJM, Veld JHJ H i't, Vogel GD (1991) Fermentation of cellulose and production of cellulolytic and xylanolytic enzymes by anaerobic fungi from ruinant and non-ruminant herbivores. Arch Microbiol 156:290–296
Walker E, Warren FL (1938) Decomposition of cellulose by Cytophaga. Biochem J 32(1):31–43
Watson BJ, Zhang H, Longmire AG, Moon YH, Hutcheson SW (2009) Processive endoglucanases mediate degradation of cellulose by Saccharophagus degradans. J Bacteriol 191(18):5697–5705. doi:10.1128/JB.00481-09
Wilson DB (2008) Three microbial strategies for plant cell wall degradation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1125:289–297. doi:10.1196/annals.1419.026
Xiao Z, Zhang X, Gregg D, Saddler J (2004) Effects of sugar inhibition on cellulases and β-glucosidase during enzymatic hydrolysis of softwood substrates. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 115:1115–1126
Xie G, Bruce DC, Challacombe JF, Chertkov O, Detter JC, Gilna P, Han CS, Lucas S, Misra M, Myers GL, Richardson P, Tapia R, Thayer N, Thompson LS, Brettin TS, Henrissat B, Wilson DB, McBride MJ (2007) Genome sequence of the cellulolytic gliding bacterium Cytophaga hutchinsonii. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(11):3536–3546. doi:10.1128/AEM.00225-07
Xu Y, Ji X, Chen N, Li P, Liu W, Lu X (2012) Development of replicative oriC plasmids and their versatile use in genetic manipulation of Cytophaga hutchinsonii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93(2):697–705. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3572-0
Zhang YH, Cui J, Lynd LR, Kuang LR (2006) A transition from cellulose swelling to cellulose dissolution by o-phosphoric acid: evidence from enzymatic hydrolysis and supramolecular structure. Biomacromolecules 7:644–648
Zheng F, Ding S (2013) Processivity and enzymatic mode of a glycoside hydrolase family 5 endoglucanase from Volvariella voloacea. Appl Environ Microbiol 7(3):989–996. doi:10.1128/AEM.02725-12
Zhu Y, Zhou H, Bi Y, Zhang W, Chen G, Liu W (2013) Characterization of a family 5 glycoside hydrolase isolated from the outer membrane of cellulolytic Cytophaga hutchinsonii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(9):3925–3937. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4259-x
Zverlov VV, Schantz N, Schwarz WH (2005) A major new component in the cellulosome of Clostridium thermocellum is a processive endo-β-1,4-glucanase producing cellotetraose. FEMS Microbiol Lett 249(2):353–358. doi:10.1016/j.femsle.2005.06.037
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2011CB707402) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31170051 and 31371262). We sincerely thank Dr. Mark J. McBride (University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee, Milwaukee, WI, USA) for providing C. hutchinsonii ATCC 33406. Thanks to Dr. Edward C. Mignot, Shandong University, for linguistic advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 324 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Wang, Y., Li, Z. et al. Characterization of a multi-function processive endoglucanase CHU_2103 from Cytophaga hutchinsonii . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 6679–6687 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5640-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5640-8