Abstract
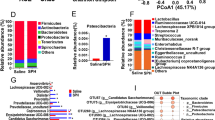
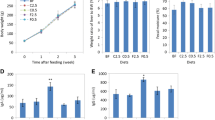
To clarify the effect of type of foods on the intestinal environment, Far East Asian- (FEA; rich in rice starch, soy protein and soy oil) and Far East Asian marine- (FEAM; rich in rice starch, fish meal, fish oil and brown alga) modelled diets and sucrose, casein and beef tallow-rich (SCB) diet were prepared. After the 2-week administration of diets in rats, caecal organic acids and putrefactive compounds (ammonia, indole, phenol and H2S, which are regarded as putative risk factors for tumours) were determined. The caecal microbiota was also analyzed using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and pyrosequencing with bar-coded primers targeting the bacterial 16S rRNA gene. Levels of n-butyrate, acetate, indole and phenol were high in rats fed FEA. On the other hand, H2S was clearly suppressed by both FEA and FEAM comparing with SCB. These results suggest that FEAM is preferable to FEA for optimal intestinal environment and host health. Both microbial analyses showed that the diversity of microbiota in the FEAM group was lower than in the other diet groups. Ratio of Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes and Proteobacteria in the SCB group was about 5:4:1. Firmicutes, particularly Lachnospiraceae, was promoted by FEA and FEAM.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera AA, Díaz GH, Barceleta ML, Guerrero OA, Roes RMO (2004) Effects of fish oil on hypertension, plasma lipids, and tumour necrosis factor-α in rats with sucrose-induced metabolic syndrome. J Nutr Biochem 15:350–357. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2003.12.008
An C, Takahashi H, Kimura B, Kuda T (2010) Comparison of PCR-DGGE and PCR-SSCP analysis for bacterial flora of Japanese traditional fermented fish products, aji-narezushi and iwashi-nukazuke. J Sci Food Agric 90:1796–1801. doi:10.1002/jsfa.4015
An C, Kuda T, Yazaki T, Takahashi H, Kimura B (2013a) FLX pyrosequencing analysis of the effects of the brown-algal fermentable polysaccharides alginate and laminaran on rat caecal microbiotas. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:860–866. doi:10.1128/AEM.02354-12
An C, Yazaki T, Takahashi H, Kuda T, Kimura B (2013b) Diet-induced changes in alginate- and laminaran-fermenting bacteria levels in the caecal contents of rats. J Funct Foods 5:389–394. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2012.11.011
An C, Kuda T, Yazaki T, Takahashi H, Kimura B (2014) Caecal fermentation, putrefaction and microbiotas in rats fed milk casein, soy protein or fish meal. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-5271-5
Biagi E, Candela M, Franceschi C, Brigidi P (2011) The aging gut microbiota: new perspectives. Ageing Res Rev 10:428–429. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2011.03.004
Chung H, Pamp SJ, Hill JA, Surana NK, Edelman SM, Troy EB, Reading NC, Villablanca EJ, Wang S, Mora JR, Umesaki Y, Mathis D, Benoist C, Relman DA, Kasper DL (2012) Gut immune maturation depends on colonization with a host-specific microbiota. Cell 149:1578–1593. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.04.037
Davila AM, Blachier F, Gotteland M, Andriamihaja M, Benetti PH, Sanz Y (2013) Intestinal luminal nitrogen metabolism: role of the gut microbiota and consequences for the host. Pharmacol Res 68:95–107. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2012.11.005
De-Filippo CD, Cavalieri D, Paola MD, Ramazzoth M, Poullet JB, Massart S, Collini S, Pieraccini G, Lionetti P (2010) Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:14691–14696. doi:10.1073/pnas.1005963107
Dethlefsen L, Huse S, Sogin ML, Relman DA (2008) The pervasive effects of an antibiotic on the human gut microbiota, as revealed by deep 16S rRNA sequencing. PLoS Biol 6:e280. doi:10.1371/journal. pbio.0060280
Feng T, Elson CO, Cong Y (2011) Treg cell–IgA axis in maintenance of host immune homeostasis with microbiota. Int Immunopharmacol 11:589–592. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2010.11.016
Kibe R, Sakamoto M, Yokota H, Ishikawa H, Aiba Y, Koga Y, Benno Y (2005) Movement and fixation of intestinal microbiota after administration of human feces to germfree mice. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3171–3178. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.6.3171-3178.2005
Kim NY, Song EJ, Kwon DY, Kim HP, Heo MY (2008) Antioxidant and antigenotoxic activities of Korean fermented soybean. Food Chem Toxicol 46:1184–1189. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2007.12.003
Kuda T, Ikemori T (2009) Minerals, polysaccharides and antioxidant properties of aqueous solutions obtained from macroalgal beach-casts in the Noto Peninsula, Ishikawa, Japan. Food Chem 112:575–581. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.06.008
Kuda T, Yano T (2009) Changes of radical-scavenging capacity and ferrous reducing power in chub mackerel Scomber japonicus and Pacific saury Cololabis saira during 4 °C storage and retorting. LWT Food Sci Technol 42:1070–1075. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2009.02.005
Kuda T, Fujii T, Hasegawa A, Okuzumi M (1992) Effects of degraded products of laminaran by Clostridium ramosum on the growth of intestinal bacteria. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 58:1307–1311
Kuda T, Enomoto T, Yano T, Fujii T (2000) Caecal environment and TBARS level in mice fed corn oil, beef tallow and menhaden fish oil. J Nutr Vitaminol 46:65–70
Kuda T, Yano T, Matsuda N, Nishizawa M (2005) Inhibitory effects of laminaran and low molecular alginate against the putrefactive compounds produced by intestinal microflora in vitro and in rats. Food Chem 91:745–749. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.06.047
Kuda T, Kunii T, Goto H, Suzuki T, Yano T (2007) Varieties of antioxidant and antibacterial properties of Ecklonia stolonifera and Ecklonia kurome products harvested and processed in the Noto peninsula, Japan. Food Chem 103:900–905. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.09.042
Kuda T, Kaneko N, Yano T, Mori M (2010) Induction of superoxide anion radical scavenging capacity in Japanese white radish juice and milk by Lactobacillus plantarum isolated from aji-narezushi and kaburazushi. Food Chem 120:517–522. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.10.046
Kuda T, Nakamura S, An C, Takahashi H, Kimura B (2012a) Effect of soy and milk protein-related compounds on Listeria monocytogenes infection in human enterocyte Caco-2 cells and A/J mice. Food Chem 134:1719–1723. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.03.031
Kuda T, Nakamura S, An C, Takahashi H, Kimura B, Nishizawa M (2012b) Effects of holdfast of Laminaria japonica on Listeria invasion on enterocyte-like Caco-2 cells and NO production of macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168:928–935. doi:10.1007/s12010-012-9831-4
Kulagina EV, Efimov BA, Maximov PY, Kafarskaia LI (2012) Species composition of Bacteroidales order bacteria in the feces of healthy people of various ages. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 76:169–171. doi:10.1271/bbb.110434
Lee GH, Rhee MS, Chang DH, Lee J, Kim S, Yoon MH, Kim BC (2013) Oscillibacter ruminantium sp. nov., isolated from the rumen of Korean native cattle. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1942–1946. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.041749-0
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI (2006) Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 444:1022–1023. doi:10.1126/science.1155725
Lombard GL, Dowell VR (1983) Comparison of three reagents for detecting indole production by anaerobic bacteria in microtest systems. J Clin Microbiol 18:609–613
Martínez I, Wallace G, Zhang C, Legge R, Benson AK, Carr TP, Moriyama EN, Walter J (2009) Diet-induced metabolic improvements in a hamster model of hypercholesterolemia are strongly linked to alterations of the gut microbiota. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:4175–4184. doi:10.1128/AEM.00380-09
Middelbos IS, Boler BMV, Qu A, White BA, Swanson KS, Fahey GC Jr (2010) Phylogenetic characterization of fecal microbial communities of dogs fed diets with or without supplemental dietary fiber using 454 pyrosequencing. PloS One 5:e9768. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009768
Miriam B, Buenviaje MD (1989) Quantitative sputum culture and gram stain: pulmonary infection vs. colonization. Philipp J Microbiol Infect Dis 18:350–356
Morishita Y (1990) Structure and function of the intestinal flora. Asakurasyoten, Tokyo, pp 116–126, in Japanese
Murata M, Sano Y, Ishihara K, Uchida M (2002) Dietary fish oil and Undaria pinnatifida (wakame) synergistically decrease rat serum and liver triacylglycerol. J Nutr 132:742–747
Ogawa K, Tsubono Y, Nishino Y, Watanabe Y, Ohkubo T, Watanabe T, Nakatsuka H, Takahashi N, Kawamura M, Tsuji I, Hisamichi S (2002) Dietary sources of nutrient consumption in a rural Japanese population. J Epidemiol 12:1–8
Poothullil JM (1993) Obesity, hyperlipidemia and non-insulin-dependent diabetes: a unified theory. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 17:85–89
Salyers AA, Vercellotti JR, West SE, Wilkins TD (1977) Fermentation of mucin and plant polysaccharides by strains of Bacteroides from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol 33:319–322
Simrén M, Barbara G, Flint HJ, Spiegel BMR, Spiller RC, Vanner S, Verdu EF, Whorwell PJ, Zoetendal EG, Rome Foundation Committee (2013) Intestinal microbiota in functional bowel disorders: a Rome foundation report. Gut 62:159–176. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302167
Turnbaugh PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T, Cantarel BL, Duncan A, Ley RE, Sogin ML, Jones WJ, Roe BA, Affourtit JP, Egholm M, Henrissat B, Heath AC, Knight R, Gordon JI (2009) A core intestinal microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 457:480–484. doi:10.1038/nature07540
Van den Bogert B, de Vos WM, Zoetendal EG, Kleerebezem M (2011) Microarray analysis and barcoded pyrosequencing provide consistent microbial profiles depending on the source of human intestinal samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2071–2080. doi:10.1128/AEM.02477-10
Varel VH, Fryda SJ, Robinson IR (1984) Cellulolytic bacteria from pig large intestine. Appl Environ Microbiol 47:219–221
Willing BP, Van Kessel AG (2010) Host pathways for recognition: establishing gastrointestinal microbiota as relevant in animal health and nutrition. Livest Sci 133:82–91. doi:10.1016/j.livsci.2010.06.031
Wylie KM, Truly RM, Sharpton TJ, Mihindukulasuriya KA (2012) Novel bacterial taxa in the human microbiome. PLoS One 7:e35294. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035294
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported in part by the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture, Japan, Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C), #25450300, 2013–2015 and was also supported by a 2013 Grant from Fuji Foundation for Protein Research (Osaka, Japan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, C., Kuda, T., Yazaki, T. et al. Caecal environment of rats fed far East Asian-modelled diets. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 4701–4709 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5535-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5535-8