Abstract
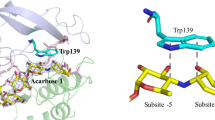
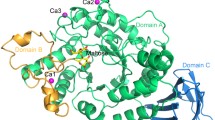
The oligosaccharide-producing multifunctional amylase-N (OPMA-N) is a novel multifunctional amylase and exhibits both hydrolytic and transglycosyl activities, but the molecular mechanism for its multiple catalytic activities is still unknown. Our research investigates the possible catalytic roles of a Trp residue in OPMA-N (Trp358) which is not only near the catalytic site Glu356 but also highly conserved in glycoside hydrolase subfamily 20 (the neopullulanase subfamily). Site-directed mutageneses at this site reveal that the size and charge of the occupying amino acid directly affect substrate binding, orientation of other crucial catalytic residues, the catalytic specificity, the oligomer formation, as well as the thermal stability of the enzyme. These findings may be useful in elucidating the different mechanisms of the multiple catalytic activities of multifunctional amylase OPMA-N and hence for developing an improved multifunctional amylase for the preparation of isomaltooligosaccharides.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accelrys Inc (1999) Homology user guide. Accelrys, San Diego, CA, USA
Ben Mabrouk S, Aghajari N, Ben Ali M, Ben Messaoud E, Juy M, Haser R, Bejar S (2011) Enhancement of the thermostability of the maltogenic amylase MAUS149 by Gly312Ala and Lys436Arg substitutions. Biores Technol 102(2):1740–1746
Bhabha G, Lee J, Ekiert DC, Gam J, Wilson IA, Dyson HJ, Benkovic SJ, Wright PE (2011) A dynamic knockout reveals that conformational fluctuations influence the chemical step of enzyme catalysis. Science 332(6026):234–238
Gumber S, Taylor DL, Whittington RJ (2007) Protein extraction from Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis: comparison of methods for analysis by sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, native PAGE and surface enhanced laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry. J Microbiol Methods 68(1):115–127
Han WW, Li ZS, Zheng QC, Sun CC (2006) Homology modeling and molecular dynamics studies on the tomato methyl jasmonate esterase. Polymer 47(4):1436–1442
Han WW, Wang Y, Zhou YH, Yao Y, Li ZS, Feng Y (2009) Understanding structural/functional properties of amidase from Rhodococcus erythropolis by computational approaches. J Mol Model 15(5):481–487
Han R, Liu L, Shin HD, Chen RR, Du G, Chen J (2012) Site-saturation engineering of lysine 47 in cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from Paenibacillus macerans to enhance substrate specificity towards maltodextrin for enzymatic synthesis of 2-O-d-glucopyranosyl-l-ascorbic acid (AA-2G). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4514-1
Hondoh H, Kuriki T, Matsuura Y (2003) Three-dimensional structure and substrate binding of Bacillus stearothermophilus neopullulanase. J Mol Biol 326(1):177–188
Hondoh H, Saburi W, Mori H, Okuyama M, Nakada T, Matsuura Y, Kimura A (2008) Substrate recognition mechanism of α-1,6-glucosidic linkage hydrolyzing enzyme, dextran glucosidase from Streptococcus mutans. J Mol Biol 378(4):913–922
Horinouchi S, Fukusumi S, Ohshima T, Beppu T (1988) Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of two additional amylase genes of a strictly anaerobic thermophile, Dictyoglomus thermophilum, and their nucleotide sequences with extremely low guanine-plus-cytosine contents. Eur J Biochem 176(2):243–253
Huey R, Morris GM, Olson AJ, Goodsell DS (2007) A semiempirical free energy force field with charge-based desolvation. J Comput Chem 28(6):1145–1152
Ito K, Ito S, Ishino K, Shimizu-Ibuka A, Sakai H (2007) Val326 of Thermoactinomyces vulgaris R-47 amylase II modulates the preference for α-(1,4)- and α-(1,6)-glycosidic linkages. Biochim Biophys Acta 1774(4):443–449
Jung TY, Li D, Park JT, Yoon SM, Tran PL, Oh BH, Janecek S, Park SG, Woo EJ, Park KH (2012) Association of novel domain in active site of archaic hyperthermophilic maltogenic amylase from Staphylothermus marinus. J Biol Chem 287(11):7979–7989
Kim JS, Cha SS, Kim HJ, Kim TJ, Ha NC, Oh ST, Cho HS, Cho MJ, Kim MJ, Lee HS, Kim JW, Choi KY, Park KH, Oh BH (1999) Crystal structure of a maltogenic amylase provides insights into a catalytic versatility. J Biol Chem 274(37):26279–26286
Kosugi T, Hayashi S (2012) Crucial role of protein flexibility in formation of a stable reaction transition state in an α-amylase catalysis. J Am Chem Soc 134(16):7045–7055
Kumar V (2010) Analysis of the key active subsites of glycoside hydrolase 13 family members. Carbohydr Res 345(7):893–898
Laskowski MWMRA, Moss DS, Thornton JM (1993) PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Cryst 26:283–291
Lee HS, Kim JS, Shim K, Kim JW, Inouye K, Oneda H, Kim YW, Cheong KA, Cha H, Woo EJ, Auh JH, Lee SJ, Park KH (2006) Dissociation/association properties of a dodecameric cyclomaltodextrinase. Effects of pH and salt concentration on the oligomeric state. FEBS J 273(1):109–121
Li F, Zhu X, Li Y, Cao H, Zhang Y (2011) Functional characterization of a special thermophilic multifunctional amylase OPMA-N and its N-terminal domain. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 43(4):324–334
Liu YH, Lu FP, Li Y, Wang JL, Gao C (2008) Acid stabilization of Bacillus licheniformis α-amylase through introduction of mutations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80(5):795–803
Majzlová K, Pukajová Z, Janeček S (2013) Tracing the evolution of the α-amylase subfamily GH13_36 covering the amylolytic enzymes intermediate between oligo-1,6-glucosidases and neopullulanases. Carbohydr Res 367:48–57
Matsuura Y, Kusunoki M, Harada W, Kakudo M (1984) Structure and possible catalytic residues of Taka-amylase A. J Biochem 95(3):697–702
Mizuno M, Tonozuka T, Uechi A, Ohtaki A, Ichikawa K, Kamitori S, Nishikawa A, Sakano Y (2004) The crystal structure of Thermoactinomyces vulgaris R-47 α-amylase II (TVA II) complexed with transglycosylated product. Eur J Biochem 271(12):2530–2538
Møller MS, Fredslund F, Majumder A, Nakai H, Poulsen JC, Lo Leggio L, Svensson B, Abou Hachem M (2012) Enzymology and structure of the GH13_31 glucan 1,6-α-glucosidase that confers isomaltooligosaccharide utilization in the probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM. J Bacteriol 194(16):4249–4259
Motyan JA, Gyemant G, Harangi J, Bagossi P (2011) Computer-aided subsite mapping of α-amylases. Carbohydr Res 346(3):410–415
Ohtaki A, Mizuno M, Tonozuka T, Sakano Y, Kamitori S (2004) Complex structures of Thermoactinomyces vulgaris R-47 α-amylase 2 with acarbose and cyclodextrins demonstrate the multiple substrate recognition mechanism. J Biol Chem 279(30):31033–31040
Oslancova A, Janecek S (2002) Oligo-1,6-glucosidase and neopullulanase enzyme subfamilies from the α-amylase family defined by the fifth conserved sequence region. Cell Mol Life Sci 59(11):1945–1959
Park KH, Kim TJ, Cheong TK, Kim JW, Oh BH, Svensson B (2000) Structure, specificity and function of cyclomaltodextrinase, a multispecific enzyme of the α-amylase family. Biochim Biophys Acta 1478(2):165–185
Saam J, Ivanov I, Walther M, Holzhütter HG, Kuhn H (2007) Molecular dioxygen enters the active site of 12/15-lipoxygenase via dynamic oxygen access channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(33):13319–13324
Stam MR, Danchin EG, Rancurel C, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B (2006) Dividing the large glycoside hydrolase family 13 into subfamilies: towards improved functional annotations of α-amylase-related proteins. Protein Eng Des Sel 19(12):555–562
Sundy JS, Baraf HS, Yood RA, Edwards NL, Gutierrez-Urena SR, Treadwell EL, Vazquez-Mellado J, White WB, Lipsky PE, Horowitz Z, Huang W, Maroli AN, Waltrop RW 2nd, Hamburger SA, Becker MA (2011) Efficacy and tolerability of pegloticase for the treatment of chronic gout in patients refractory to conventional treatment: two randomized controlled trials. JAMA 306(7):711–720
Wallnoefer HG, Lingott T, Gutierrez JM, Merfort I, Liedl KR (2010) Backbone flexibility controls the activity and specificity of a protein-protein interface: specificity in snake venom metalloproteases. J Am Chem Soc 132(30):10330–10337
Wang Y, Li F, Gao C, Zhang Y (2009a) Characterization of a novel mesophilic bacterial amylase secreted by ZW2531-1, a strain newly isolated from soil. Chem Res Chin Univ 25(4):198–202
Wang Y, Li F, Zhang Y (2009b) New members of α-amylase family-multifunctional amylases. Chin J Biochem Mol Biol 25(10):104–109
Wang Y, Li F, Zhang Y (2010) Preliminary investigation on the action modes of an oligosaccharide-producing multifunctional amylase. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160(7):1955–1966
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 30870518 and 31170759).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 0.97 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, H., Gao, G., Gu, Y. et al. Trp358 is a key residue for the multiple catalytic activities of multifunctional amylase OPMA-N from Bacillus sp. ZW2531-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 2101–2111 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5085-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5085-5