Abstract
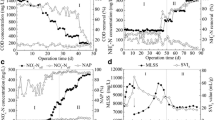
Two sequencing batch reactors were synchronously operated to investigate the effect of manganese (II) (Mn2+) augmentation on aerobic granulation. Reactor 1 (R1) was added with 10 mg/L Mn2+, while there was no Mn2+ augmentation in reactor 2 (R2). Results showed that R1 had a faster granulation process than R2 and R1 performed better in chemical oxygen demand (COD) and ammonium nitrogen (NH +4 –N) removal efficiencies. Moreover, the mature granules augmented with Mn2+ behaved better on their physical characteristics and size distributions, and they also had higher production of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) content. The result of three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence showed that Mn2+ had the function of causing organic material diversity (especially proteins diversity) in EPS fraction from granules. Polymerase chain reaction and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis techniques were employed to analyze the microbial and genetic characteristics in mature granules. The results exhibited that Mn2+ augmentation was mainly responsible for the higher microbial diversity of granules from R1 compared with that from R2. Uncultured sludge bacterium A16 (AF234726) and Rhodococcus sp. WTZ-R2 (HM004214) were the major species in R1, while only uncultured sludge bacterium A16 (AF234726) in R2. Moreover, there were eight species of organisms found in both two aerobic granules, and three species were found only in aerobic granules from R1. It could be concluded that Mn2+ could enhance the sludge granulation process and have a key effect role on the biological properties during the sludge granulation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Lai JY (2009) Biological nitrification–denitrification with alternating oxic and anoxic operations using aerobic granules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84(6):1181–1189
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Chen W, Westerhoff P, Leenheer JA, Booksh K (2003) Fluorescence excitation–emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 37(24):5701–5710
Chen H, Wu RR, Xu GZ, Fang X, Qiu XL, Guo HY, Tian B, Hua YJ (2010) DR2539 is a novel DtxR-like regulator of Mn/Fe ion homeostasis and antioxidant enzyme in Deinococcus radiodurans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 396(2):413–418
China SEPA (2002) Monitoring and analysis methods of water and wastewater, 4th edn. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Christianson DW (1997) Structural chemistry and biology of manganese metalloenzymes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 67(2–3):217–243
Chu LB, Zhang XW, Li XH, Yang FL (2005) Simultaneous removal of organic substances and nitrogen using a membrane bioreactor seeded with anaerobic granular sludge under oxygen-limited conditions. Desalination 172(3):271–280
Davies P, Brown DR (2009) Manganese enhances prion protein survival in model soils and increases prion infectivity to cells. PLoS One 4(10):e7518
De Kreuk MK, Van Loosdrecht MCM (2004) Selection of slow growing organisms as a means for improving aerobic granular sludge stability. Water Sci Technol 49(11–12):9–17
Di Iaconi C, Ramadori R, Lopez A, Passino R (2004) Hydraulic shear stress calculation in a sequencing batch biofilm reactor with granular biomass. Environ Sci Technol 39(3):889–894
Etterer T, Wilderer PA (2001) Generation and properties of aerobic granular sludge. Water Sci Technol 43(3):19–26
Jiang HL, Tay JH, Liu Y, Tiong-Lee Tay S (2003) Ca2+ augmentation for enhancement of aerobically grown microbial granules in sludge blanket reactors. Biotechnol Lett 25(2):95–99
Li XM, Liu QQ, Yang Q, Guo L, Zeng GM, Hu JM, Zheng W (2009) Enhanced aerobic sludge granulation in sequencing batch reactor by Mg2+ augmentation. Bioresour Technol 100(1):64–67
Liu YQ, Tay JH (2007) Characteristics and stability of aerobic granules cultivated with different starvation time. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75(1):205–210
Liu L, Gao DW, Zhang M, Fu Y (2010) Comparison of Ca2+ and Mg2+ enhancing aerobic granulation in SBR. J Hazard Mater 181(1–3):382–387
Morgan JW, Forster CF, Evison L (1990) A comparative study of the nature of biopolymers extracted from anaerobic and activated sludges. Water Res 24(6):743–750
Moy BP, Tay JH, Toh SK, Liu Y, Tay SL (2002) High organic loading influences the physical characteristics of aerobic sludge granules. Lett Appl Microbiol 34(6):407–412
Muyzer G, De Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for {16S} {rRNA}. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(3):695–700
Qin L, Liu Y, Tay JH (2004) Effect of settling time on aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactor. Biochem Eng J 21(1):47–52
Rudd T, Sterritt RM, Lester JN (1984) Complexation of heavy metals by extracellular polymers in the activated sludge process. J Water Pollut Control Fed 56(12):1260–1268
Shen CF, Kosaric N, Blaszczyk R (1993) The effect of selected heavy metals (Ni, Co and Fe) on anaerobic granules and their extracellular polymeric substance (EPS). Water Res 27(1):25–33
Sun FY, Yang CY, Li JY, Yang YJ (2006) Influence of different substrates on the formation and characteristics of aerobic granules in sequencing batch reactors. J Environ Sci 18(5):864–871
Tay JH, Liu QS, Liu Y (2002) Characteristics of aerobic granules grown on glucose and acetate in sequential aerobic sludge blanket reactors. Environ Technol 23(8):931–936
Wang ZW, Liu Y, Tay JH (2005) Distribution of EPS and cell surface hydrophobicity in aerobic granules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69(4):469–473
Wang Z, Liu L, Yao J, Cai W (2006) Effects of extracellular polymeric substances on aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactors. Chemosphere 63(10):1728–1735
Wang ZW, Li Y, Liu Y (2007) Mechanism of calcium accumulation in acetate-fed aerobic granule. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74(2):467–473
Wang XH, Song RH, Teng SX, Gao MM, Ni JY, Liu FF, Wang SG, Gao BY (2010) Characteristics and mechanisms of Cu(II) biosorption by disintegrated aerobic granules. J Hazard Mater 179(1–3):431–437
Zheng YM, Yu HQ, Sheng GP (2005) Physical and chemical characteristics of granular activated sludge from a sequencing batch airlift reactor. Process Biochem 40(2):645–650
Zheng YM, Yu HQ, Liu SJ, Liu XZ (2006) Formation and instability of aerobic granules under high organic loading conditions. Chemosphere 63(10):1791–1800
Zhu L, Xu X, Luo W, Tian Z, Lin H, Zhang N (2008) A comparative study on the formation and characterization of aerobic 4-chloroaniline-degrading granules in SBR and SABR. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79(5):867–874
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge financial support for this work provided by Shandong Province Postdoctoral Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, L., Yang, T., Wang, W. et al. Effect of Mn2+ augmentation on reinforcing aerobic sludge granulation in a sequencing batch reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93, 2615–2623 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3555-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3555-1