Abstract
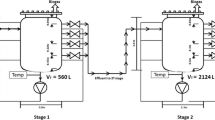
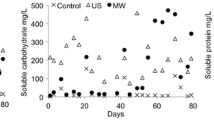
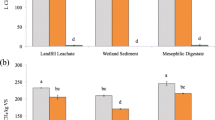
Adding a supporting material to a methanogenic bioreactor treating garbage slurry can improve efficiency of methane production. However, little is known on how characteristics (e.g., porosity and hydrophobicity) of the supporting material affect the bioreactor degrading garbage slurry. We describe the reactor performances and microbial communities in bioreactors containing hydrophilic or hydrophobic sheets, or fibrous hydrophilic or hydrophobic sponges. The porosity affected the efficiency of methane production and solid waste removal more than the hydrophilic or hydrophobic nature of the supporting material. When the terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism technique was used at a lower organic loading rate (OLR), microbial diversities in the suspended fraction were retained on the hydrophobic, but not the hydrophilic, sheets. Moreover, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) performed at a higher OLR revealed that the excellent performance of reactors containing fibrous sponges with high porosity (98%) was supported by a clear increase in the numbers of methanogens on these sponges, resulting in larger total numbers of methanogens in the reactors. In addition, the bacterial communities in fractions retained on both the hydrophobic and hydrophilic fibrous sponges differed from those in the suspended fraction, thus increasing bacterial diversity in the reactor. Thus, higher porosity of the supporting material improves the bioreactor performance by increasing the amount of methanogens and bacterial diversity; surface hydrophobicity contributes to maintaining the suspended microbial community.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahring BK (2003) Perspectives for anaerobic digestion. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 81:1–30
Angelidaki I, Chen X, Cui J, Kaparaju P, Ellegaard L (2006) Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of source-sorted organic fraction of household municipal solid waste: start-up procedure for continuously stirred tank reactor. Water Res 40:2621–2628
Bakker DP, Busscher HJ, Van Zanten J, De Varies J, Klijnstra JW, Van der Mei HC (2004) Multiple linear regression analysis of bacterial deposition to polyurethane coatings after conditioning film formation in the marine environment. Microbiology 150:1779–1784
Bos R, Van der Mei HC, Gold J, Busscher HJ (2000) Retention of bacteria on substratum surface with micro-patterned hydrophobicity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 189:311–315
Chauhan A, Ogram A (2005) Evaluation of support matrices for immobilization of anaerobic consortia for efficient carbon cycling in waste regeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 327:884–893
Davey ME, O’Tool GA (2000) Microbial biofilms: from ecology to molecular genetics. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:847–867
Delong EF (1992) Archaea in coastal marine environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:5685–5689
Farhadian M, Borghei M, Umrania VV (2007) Treatment of beet sugar wastewater by UAFB bioprocess. Bioresour Technol 98:3080–3083
Gjaltema A, Van der Marel N, Van Loosdrecht MCM, Heijnen JJ (1997) Adhesion and biofilm development on suspended carriers in airlift reactors: hydrodynamic conditions versus surface characteristics. Biotechnol Bioeng 55:880–889
Haruta S, Nakamura T, Nakamura K, Hemmi H, Ishii M, Igarashi Y, Nishino T (2005) Microbial diversity in biodegradation and reutilization processes of garbage. J Biosci Bioeng 99:1–11
Huang LN, De Wever H, Diels L (2008) Diverse and distinct bacterial communities induced biofilm fouling in membrane bioreactors operated under different conditions. Environ Sci Technol 42:8360–8366
Hori T, Haruta S, Ueno Y, Ishii M, Igarashi Y (2006) Dynamic transition of the methanogenic population in response to the concentration of volatile fatty acids in a thermophilic anaerobic digestor. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1623–1630
Lane DJ (1991) 16 S/23 S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, New York, pp 115–175
Lee C, Kim J, Shin SG, Hwang S (2008) Monitoring bacterial and archaeal community shifts in a mesophilic batch reactor treating a high-strength organic wastewater. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 65:544–554
Lee C, Kim J, Hwang K, O’Flaherty V, Hwang S (2009) Quantitative analysis of methanogenic community dynamics in three anaerobic batch digesters treating different wastewaters. Water Res 43:157–165
Lueders T, Friedrich MW (2002) Effects of amendment with ferrihydrite and gypsum on the structure and activity of methanogenic populations in rice field soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2484–2494
Lueders T, Manefield M, Friedrich MW (2004) Enhanced sensitivity of DNA- and rRNA-based stable isotope probing by fractionation and quantitative analysis of isopycnic centrifugation gradients. Environ Microbiol 6:73–78
Maidak B, Cole JR, Lilburn TG, Parker CT, Saxman PR, Farris RJ, Garrity GM, Olsen GJ, Schmidt TM, Tiedje JM (2001) The RDP-II (Ribosomal Database Project). Nucleic Acid Res 29:173–174
Ohmura N, Kitamura K, Saiki H (1993) Selective adhesion of Thiobacillus ferroxidans to pyrite. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:4044–4050
Picanço AP, Vallero MVG, Gianotti EP, Zaiat M, Blundi CE (2001) Influence of porosity and composition of supports on the methanogenic biofilm characteristics developed in a fixed bed anaerobic reactor. Water Sci Technol 44:197–204
Pringle JH, Fletcher M (1983) Influence of substratum wettability on attachment of freshwater bacteria to solid surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol 45:811–817
Rickard AH, McBain AJM, Stead AT, Gilbert P (2004) Shear rate moderates community diversity in freshwater biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:7426–7435
Sasaki K, Haruta S, Ueno Y, Ishii M, Igarashi Y (2007) Microbial population in the biomass adhering to supporting material in a packed-bed reactor degrading organic solid waste. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:941–952
Sasaki K, Morita M, Hirano S, Ohmura N, Igarashi Y (2009) Effect of adding carbon fiber textiles to methanogenic bioreactors used to treat an artificial garbage slurry. J Biosci Bioeng 108:130–135
Sawayama S, Tada C, Tsukahara K, Yagishita T (2004) Effect of ammonium addition on methanogenic community in a fluidized bed anaerobic digestion. J Biosci Bioeng 97:65–70
Sekiguchi Y, Kamagata Y, Syutsubo K, Ohashi A, Harada H, Nakamura K (1998) Phylogenetic diversity of mesophilic and thermophilic granular sludges determined by 16 S rRNA gene analysis. Microbiology 144:2655–2665
Show KY, Tay JH (1999) Influence of support media on biomass growth and retention in anaerobic filters. Water Res 33:1471–1481
Stams AJM, Plugge CM (2009) Electron transfer in syntrophic communities of anaerobic bacteria and archaea. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:568–577
Takai K, Horikoshi K (2000) Rapid detection and quatification of members of archaeal community by quantitative PCR using fluorogenic probes. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5066–5072
Tatara M, Yamazawa A, Ueno Y, Fukui H, Goto M, Sode K (2004) High-rate thermophilic methane fermentation on short-chain fatty acids in a down-flow anaerobic packed-bed reactor. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 27:105–113
Tatara M, Makiuchi T, Ueno Y, Goto M, Sode K (2008) Methanogenesis from acetate and propionate by thermophilic down-flow anaerobic packed-bed reactor. Bioresour Technol 99:4786–4795
Ueno Y, Fukui H, Goto M (2007) Operation of a two-stage fermentation process producing hydrogen and methane from organic waste. Environ Sci Technol 41:1413–1419
Umaña O, Nikolaeva S, Sánchez E, Borja R, Raposo F (2008) Treatment of screened dairy manure by upflow anaerobic fixed bed reactors packed with waste type rubber and a combination of waste type rubber and zeolite: Effect of the hydraulic retention time. Bioresour Technol 99:7412–7417
Van Loosdrecht MCM, Lyklema J, Norde W, Schraam G, Zehnder AJB (1987) The role of bacterial cell wall hydrophobicity in adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:1893–1897
Van Pelt AWJ, Weerkamp AH, Uyen MHW, Busscher HJ, De Jong HP, Arends J (1985) Adhesion of Streptococcus sanguis CH3 to polymers with different surface free energies. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:1270–1275
Wasserfallen A, Nölling J, Pfister P, Reeve J, De Macario EC (2000) Phylogenetic analysis of 18 thermophilic Methanobacterium isolates supports the proposals to create a new genus, Methanothermobacter gen. nov., and to reclassify several isolates in three species, Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus comb. nov., Methanobacterium wolfeii comb. nov., and Methanothermobacter marburgensis sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:43–53
Zinder SH, Sowers KR, Ferry JG (1985) Methanosarcina thermophila sp. nov., a thermophilic, acetotrophic, methane-producing bacterium. Int J Syst Bacteriol 35:522–523
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to Yoji Kitajima and Yoshiyuki Ueno (Environmental Engineering and Bioengineering Group, Kajima Technical Research Institute) for their significant advice on the reactor operation. We also thank Eri Ishihara and Mieko Katsuura for their help. This work was supported by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasaki, K., Sasaki, D., Morita, M. et al. Efficient treatment of garbage slurry in methanogenic bioreactor packed by fibrous sponge with high porosity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86, 1573–1583 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2469-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2469-7