Abstract
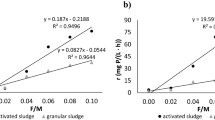
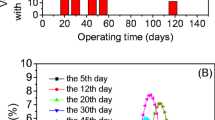
Aerobic granules were adopted to degrade high-strength phenol wastewater in batch experiments. The acclimated granules effectively degraded phenol at a concentration of up to 5,000 mg l−1 without severe inhibitory effects. The biodegradation of phenol by activated sludge was inhibited at phenol concentrations >3,000 mg l−1. The granules were composed of cells embedded in a compact extracellular matrix. After acid or alkaline pretreatment, the granules continued to degrade phenol at an acceptable rate. The polymerase chain reaction-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis technique was employed to monitor the microbial communities of the activated sludge and the aerobic granules following their being used to treat high concentrations of phenol in batch tests.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adav SS, Lee DJ (2008) Single-culture aerobic granules with Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:551–557
Adav SS, Chen MY, Lee DJ, Ren NQ (2007a) Degradation of phenol by Acinetobacter strain isolated from aerobic granules. Chemosphere 67:1566–1572
Adav SS, Chen MY, Lee DJ, Ren NQ (2007b) Degradation of phenol by aerobic granules and isolated yeast Candida tropicalis. Biotechnol Bioeng 96:844–852
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Lai JY (2009a) Functional consortium from aerobic granules under high organic loading rates. Bioresour Technol 100:3465–3470
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Lai JY (2009b) Aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactors at different settling times. Bioresour Technol 100:5359–5361
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Lai JY (2009c) Proteolytic activity in stored aerobic granular sludge and stability loss. Bioresour Technol 100:68–73
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Arutchelvan V, Kanakasabai V, Elangovan R, Nagarajan S, Muralikrishnan V (2006) Kinetics of high strength phenol degradation using Bacillus brevis. J Hazard Mater 28:216–222
Baek SH, Kim KH, Yin CR, Jeon CO, Im WT, Kim KK, Lee ST (2003) Isolation and characterization of bacteria capable of degrading phenol and reducing nitrate under low-oxygen conditions. Curr Microbiol 47:462–466
Bai J, Wen JP, Li HM, Jiang Y (2007) Kinetic modeling of growth and biodegradation of phenol and m-cresol using Alcaligenes faecalis. Process Biochem 42:510–517
Brinkrolf K, Brune I, Tauch A (2006) Transcriptional regulation of catabolic pathways for aromatic compounds in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Genet Mol Res 7:773–789
Chen MY, Lee DJ, Tay JH (2007) Distribution of extracellular polymeric substances in aerobic granules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:1463–1469
Chiu ZC, Chen MY, Lee DJ, Wang CH, Lai JY (2007) Oxygen diffusion in active layer of aerobic granule considering steady-state and transient responses. Water Res 41:884–892
Cho YG, Yoon JH, Park YH, Lee ST (1998) Simultaneous degradation of p-nitrophenol and phenol by a newly isolated Nocardioides sp. J Gen Appl Microbiol 44:303–309
El-Naas MH, Al-Muhtaseb SA, Makhlouf S (2009) Biodegradation of phenol by Pseudomonas putida immobilized in polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) gel. J Hazard Mater 164:720–725
He Z, Wiegel J (1995) Purification and characterization of an oxygen-sensitive reversible 4-hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase from Clostridium hydroxybenzoicum. Eur J Biochem 229:77–82
Ho KL, Lin B, Chen YY, Lee DJ (2009) Biodegradation of phenol using Corynebacterium sp. DJ1 aerobic granules. Bioresource Technol. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.05.050
Hu B, Chen S (2007) Pretreatment of methanogenic granules for immobilized hydrogen fermentation. Int J Hydrogen Energy 32:3266–3273
Jiang HL, Tay JH, Tay ST (2002) Aggregation of immobilized activated sludge cells into aerobically grown microbial granules for the aerobic biodegradation of phenol. Lett Appl Microbiol 35:439–445
Jiang HL, Tay JH, Maszenan AM, Tay STL (2004) Bacterial diversity and function of aerobic granules engineered in a sequencing batch reactor for phenol degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6767–6775
Kanekar PP, Sarnaik SS, Kelkar AS (1999) Bioremediation of phenol by alkaliphilic bacteria isolated from alkaline lake of Lonar. Indian J Appl Microbiol 85:128S–133S
Karigar C, Mahesh A, Nagenahalli M, Yun DJ (2006) Phenol degradation by immobilized cells of Arthrobacter citreus. Biodegradation 17:47–55
Kibret M, Somitsch W, Robra KH (2000) Characterization of phenol degrading mixed population by enzyme assay. Water Res 34:1127–1134
Kumar A, Kumar S, Kumar S (2005) Biodegradation kinetics of phenol and catechol using Pseudomonas putida MTCC 1194. Biochem Eng J 22:151–159
Liu Y, Tay JH (2004) State of the art of biogranulation technology for wastewater treatment. Biotechnol Adv 22:533–563
Liu QS, Liu Y, Show KY, Tay JH (2009) Toxicity effect of phenol on aerobic granules. Environ Technol 30:69–74
Loh KC, Chung TS, Ang WF (2000) Immobilized-cell membrane bioreactor for high-strength phenol wastewater. J Environ Eng 126:75–79
Markelova NY (2007) Survival strategy of Bdellovibrio. Microbiol 76:769–774
Saravanan P, Pakshirajan K, Saha P (2008) Growth kinetics of an indigenous mixed microbial consortium during phenol degradation in a batch reactor. Bioresour Technol 99:205–209
Shen XH, Huang Y, Liu SJ (2005) Genomic analysis and identification of catabolic pathways for aromatic compounds in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microbes Environ 20:160–167
Tay JH, Jiang HL, Tay STL (2004) High-rate biodegradation of phenol by aerobically grown microbial granules. J Environ Eng 130:1415–1423
Tay ST, Moy BY, Maszenan AM, Tay JH (2005a) Comparing activated sludge and aerobic granules as microbial inocula for phenol biodegradation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:708–713
Tay ST, Zhuang WQ, Tay JH (2005b) Start-up, microbial community analysis and formation of aerobic granules in a tert-butyl alcohol degrading sequencing batch reactor. Environ Sci Technol 39:5774–5780
Uygur A, Kargi F (2004) Phenol inhibition of biological nutrient removal in four step sequencing batch reactor. Process Biochem 39:2123–2128
Watanabe K, Hino S, Takahashi N (1996) Responses of activated sludge to an increase in phenol loading. J Ferment Bioeng 82:522–524
Watanabe K, Teramoto M, Harayama S (2002) Stable augmentation of activated sludge with foreign catabolic genes harboured by an indigenous dominant bacterium. Environ Microbiol 4:577–583
Yemendzhiev H, Gerginova M, Krastanov A, Stoilova I, Alexieva Z (2008) Growth of Trametes versicolor on phenol. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 35:1309–1312
Yu GH, Juang YC, Lee DJ, He PJ, Shao LM (2009) Enhanced aerobic granulation with extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)-free pellets. Bioresour Technol 100:4611–4615
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported by the National Taiwan University (Toward Top University Project) and National Science Council (ROC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ho, KL., Chen, YY., Lin, B. et al. Degrading high-strength phenol using aerobic granular sludge. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85, 2009–2015 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2321-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2321-0