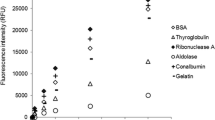
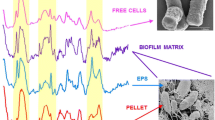
Abstract
Multiple fluorochrome experiments with as many fluorochromes as possible are desired for exploring the detailed structure of bioaggregates. Spectral peak interference and other practical limitations, however, restrict the maximum number of stains used simultaneously to three. This current study proposes a sixfold labelled scheme to stain the total cells, dead cells, proteins, lipids, and α- and β-polysaccharides in bioaggregates. Two aerobic granule systems, the phenol-fed and the acetate-fed granules, were utilized as the testing samples for demonstrating the use of the proposed scheme.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boessmann M, Staudt C, Neu TR, Horn H, Hempel DC (2003) Investigation and modeling of growth, structure and oxygen penetration in particle supported biofilms. Chem Eng Technol 26(2):219–222
Boessmann M, Neu TR, Horn H, Hempel DC (2004) Growth, structure and oxygen penetration in particle supported autotrophic biofilms. Water Sci Technol 49:371–377
Bockelmann U, Manz W, Neu TR, Szewzyk U (2002) Investigation of lotic microbial aggregates by a combined technique of fluorescent in situ hybridization and lectin-binding analysis. J Microbiol Methods 49:75–87
Cerca N, Martins S, Sillankorva S, Jefferson KK, Pier GB, Oliveira R, Azeredo J (2005) Effects of growth in the presence of subinhibitory concentrations of dichloroaxacillin on Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus haemolyticus biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8677–8682
Costeron JW, Irvin RT, Cheng KJ (1981) The bacterial glycocalyx in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol 35:299–324
De Beer D, O’Flaharty V, Thaveesri J, Lens P, Verstraete W (1996) Distribution of extracellular polysaccharides and flotation of anaerobic sludge. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 46:197–201
Frolund B, Palmgren R, Keiding K, Nielsen PH (1996) Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin. Water Res 30:1749–1758
Jiang HL, Tay JH, Tay STL (2002) Aggregation of immobilized activated sludge cells into aerobically grown microbial granules for the aerobic biodegradation of phenol. Lett Appl Microbiol 35:439–445
Lawrence TR, Neu TR, Swerhone GDW (1998) Application of multiple parameter imaging for the quantification of algae, bacterial, and exopolymer components of microbial biofilms. J Microbial Methods 32:253–261
Lawrence JR, Swerhone GDW, Leppard GG, ArakiT, Zhang X, West MM, Hitchcock AP (2003) Scanning transmission X-ray, laser scanning, and transmission electron microscopy mapping of the exopolymeric matrix of microbial biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5543–5554
Lawrence JR, Chenier MR, Roy R, Beaumier D, Fortin N, Swerhone GDW, Neu TR, Greer CW (2004) Microscale and molecular assessment of impacts of nickel, nutrients, and oxygen level on structure and function of river biofilm communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4326–4339
Lawrence JR, Swerhone GDW, Wassenaar LI, Neu TR (2005) Effects of selected pharmaceuticals on riverine biofilm communities. Can J Microbiol 51:655–669
McSwain BS, Irvine RL, Hausner M, Wilderer PA (2005) Composition and distribution of extracellular polymeric substances in aerobic flocs and granular sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1051–1057
Michael T, Smith CM (1995) Lectins probe molecular film in biofouling: characterization of early films on non-living and living surfaces. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 119:229–236
Murray JM (2005) Confocal microscopy, deconvolution, and structured illumination methods. In: Spector DL, Goldman RD (eds) Basic methods in microscopy. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Neu TR (1996) Significance of bacterial surface-active compounds in interaction of bacteria with interfaces. Microbiol Rev 60:151–166
Neu TR (2000) In situ cell and glycoconjugate distribution in river snow studied by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Aquat Microb Ecol 21:85–95
Neu TR, Lawrence JR (1997) Development and structure of microbial biofilms in river water studied by confocal laser scanning microscopy. FEMS Microbiol Immunol 24:11–25
Neu TR, Swerhone GDW, Lawrence JR (2001) Assessment of lectin-binding analysis for in situ detection of glycoconjugates in biofilm systems. Microbiology 147:299–313
Neu TR, Woelfl S, Lawrence JR (2004) Three-dimensional differentiation of photo-autotrophic biofilm constituents by multi-channel laser scanning microscopy single-photon and two-photon excitation. J Microbiol Methods 56:161–172
Nielsen PH, Jahn A (1999) Extraction of EPS. In: Wingender J, Neu TR, Flemming HC (eds) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 21–47
Nielsen PH, Jahn A, Palmgren R (1997) Conceptual model for production and composition of exopolymers in biofilms. Water Sci Technol 36:11–19
Schmid M, Thill A, Purkhold U, Walcher M, Bottero JY, Ginestet P, Nielsen PH, Wuertz S, Wagner M (2003) Characterization of activated sludge flocs by confocal laser scanning microscopy and image analysis. Water Res 37:2043–2052
Staudt C, Horn H, Hempel DC, Neu TR (2004) Volumeric measurements of bacterial cells and extracellular polymeric substance glycoconjugates in biofilms. Biotechnol Bioeng 88:585–592
Strathmann M, Wingender J, Flemming HC (2003). Application of fluorescently labeled lectins for the visualization and biochemical characteristics of polysaccharides in biofilm of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Microbiol Methods 50:237–248
Takeda M, Nakano F, Nagase T, Iohara K, Koizumi JI (1998) Isolation and chemical composition of the sheath of Sphaerotilus natans. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62:1138–1143
Tay JH, Lin QS, Liu Y (2001) The role of cellular polysaccharide in the formation and stability of aerobic granules. Lett Appl Microbiol 33:222–226
Tay JH, Ivanov V, Pan S, Tay STL (2002) Specific layers in aerobically grown microbial granules. Lett Appl Microbiol 34:254–257
Wang ZW, Liu Y, Tay JH (2005) Distribution of EPS and cell surface hydrophobicity in aerobic granules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:469–473
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, MY., Lee, DJ., Tay, JH. et al. Staining of extracellular polymeric substances and cells in bioaggregates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75, 467–474 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0816-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0816-5