Abstract.
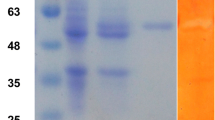
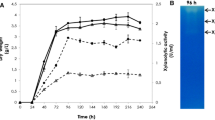
A branching enzyme (EC 2.4.1.18) gene was isolated from an extremely thermophilic bacterium, Rhodothermus obamensis. The predicted protein encodes a polypeptide of 621 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 72 kDa. The deduced amino acid sequence shares 42–50% similarity to known bacterial branching enzyme sequences. Similar to the Bacillus branching enzymes, the predicted protein has a shorter N-terminal amino acid extension than that of the Escherichia coli branching enzyme. The deduced amino acid sequence does not appear to contain a signal sequence, suggesting that it is an intracellular enzyme. The R. obamensis branching enzyme was successfully expressed both in E. coli and a filamentous fungus, Aspergillus oryzae. The enzyme showed optimum catalytic activity at pH 6.0–6.5 and 65 °C. The enzyme was stable after 30 min at 80 °C and retained 50% of activity at 80 °C after 16 h. Branching activity of the enzyme was higher toward amylose than toward amylopectin. This is the first thermostable branching enzyme isolated from an extreme thermophile.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received revision: 5 September 2001
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shinohara, M.L., Ihara, M., Abo, M. et al. A novel thermostable branching enzyme from an extremely thermophilic bacterial species, Rhodothermus obamensis . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57, 653–659 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-001-0841-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-001-0841-3