Abstract
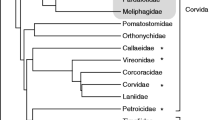
Immunologically important genes of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) have been characterized in a number of avian species with the general finding of considerable variation in size and structural organization among organisms. A range of nonpasserines which represent early-diverging Neoave lineages have been described as having only one MHC class II β locus potentially leading to the conclusion that this is the ancestral condition. Here, we examine the monotypic, early-diverging, critically endangered kakapo, Strigops habroptilus, for allelic variation at MHC class II β exon 2, as part of species’ recovery efforts. We found two to four confirmed sequence variants per individual indicating the presence of more than one MHC class II β locus. Given the kakapo’s basal evolutionary status, evidence for multiple MHC class II β loci seems to counter the proposed mono-locus history of modern birds. However, MHC gene duplication, maintenance, and loss among and within bird species may confound avian relationships making it difficult to elucidate the ancestral state. This study adds essential data for disentangling the course of MHC structural evolution in birds.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcaide M, Edwards SV, Negro JJ (2007) Characterization, polymorphism and evolution of MHC class II B genes in birds of prey. J Mol Evol 65:541–554
Bernatchez L, Landry C (2003) MHC studies in nonmodel vertebrates: what have we learned about natural selection in 15 years? J Evol Biol 16:363–377
Bollmer JL, Herna Vargas F, Parker PG (2007) Low MHC variation in the endangered Galapagos penguin (Spheniscus mendiculus). Immunogenetics 59:593–602
Bollmer JL, Dunn PO, Whittingham LA, Wimpee C (2010) Extensive MHC class II B gene duplication in a passerine, the common yellowthroat (Geothlypis trichas). J Hered 101:448–460
Brown JH, Jardetzky TS, Gorga JC, Stern LJ, Urban RG, Strominger JL, Wiley DC (1993) 3-Dimensional structure of the human class-II histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR1. Nature 364:33–39
Edwards SV, Hess CM, Gasper J, Garrigan D (1999) Toward an evolutionary genomics of the avian MHC. Immunol Rev 167:119–132
Edwards SV, Nusser J, Gasper J (2000) Characterization and evolution of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes in non-model organisms, with examples from birds. In: Baker AJ (ed) Molecular methods in ecology. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 168–207
Galan M, Guivier E, Caraux G, Charbonnel N, Cosson J-F (2010) A 454 multiplex sequencing method for rapid and reliable genotyping of highly polymorphic genes in large-scale studies. BMC Genomics 11:296
Gibb GC, Kardailsky O, Kimball RT, Braun EL, Penny D (2007) Mitochondrial genomes and avian phylogeny: complex characters and resolvability without explosive radiations. Mol Biol Evol 24:269–280
Gyllensten U, Sundvall M, Ezcurra I, Erlich HA (1991) Genetic diversity at class II DRB loci of the primate MHC. J Immunol 146:4368
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hedrick PW (1994) Evolutionary genetics of the major histocompatibility complex. Am Nat 143:945–964
Holt KE, Parkhill J, Mazzoni CJ, Roumagnac P, Weill FX et al (2008) Highthroughput sequencing provides insights into genome variation and evolution in Salmonella typhi. Nat Genet 40:987–993
Hughes CR, Miles S, Walbroehl JM (2008) Support for the minimal essential MHC hypothesis: a parrot with a single, highly polymorphic MHC class IIB gene. Immunogenetics 60:219–231
Huson D (1998) SplitsTree: a progam for analyzing and visualizing evolutionary data. Bioinformatics 14:68–73
Huson D, Bryant D (2006) Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies. Mol Biol Evol 23:254–267
Kaufman J, Völk H, Wallny H (1995) A “minimal essential MHC and an unrecognized MHC”: two extremes in selection for polymorphism. Immunol Rev 143:63–88
Kaufman J, Milne S, Göbel T, Walker BA, Jacob JP, Auffrey C, Zoorob R, Beck S (1999) The chicken B locus is a minimal-essential major histocompatibility complex. Nature 401:923–925
Klein J, Sato A, Nagl S, O’hUigin C (1998) Molecular trans-species polymorphism. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 29:1–21
Kryazhimskiy S, Plotkin JB (2008) The population genetics of dN/dS. PLoS Genet 4:e1000304
Lenz T, Becker S (2008) Simple approach to reduce PCR artifact formation leads to reliable genotyping of MHC and other highly polymorphic loci—implications for evolutionary analysis. Gene 427:117–123
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DNAsp v 5: A software for computational analysis of DNA polymorphism Data. Bioinformatics 25:1451–1452
McCormack WT, Hurley EA, Thompson CB (1993) Germ line maintenance of the pseudogene donor pool for somatic immunoglobulin gene conversion in chickens. Mol Cell Biol 13:821–830
Miller HC, Lambert DM, Millar CD, Robertson BC, Minot EO (2003) Minisatellite DNA profiling detects lineages and parentage in the endangered kakapo (Strigops habroptilus) despite low microsatellite DNA variation. Conserv Genet 4:265–273
Miller HC, Bowker-Wright G, Kharkrang M, Ramstad K (2011) Characterisation of class II B MHC genes from a ratite bird, the little spotted kiwi (Apteryx owenii). Immunogenetics 63:223–233
Moon DA, Veniamin SM, Parks-Dely JA, Magor KE (2005) The MHC of the duck (Anas platyrhynchos) contains five differentially expressed class I genes. J Immunol 175:6702–6712
Nei M, Gu X, Sitnikova T (1997) Evolution by the birth-and-death process in multigene families of the vertebrate immune system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:7799–7806
Powlesland RG, Merton DV, Cockrem JF (2006) A parrot apart: the natural history of the kakapo (Strigops habroptilus), and the context of its conservation. Notornis 53:3–26
Pratt RC, Gibb GC, Morgan-Richards M, Phillips MJ, Hendy MD, Penny D (2009) Toward resolving deep neoaves phylogeny: data, signal enhancement, and priors. Mol Biol Evol 26:313–326
Richardson DS, Westerdahl H (2003) MHC diversity in two Acrocephalus species: the outbreed Great reed Warbler and the inbred Seychelles warbler. Mol Ecol 12:3253–3259
Robertson BC (2006) The role of genetics in kakapo recovery. Notornis 53:173–183
Robertson BC, Minot EO, Lambert DM (2000) Microsatellite primers for the kakapo (Strigops habroptilus) and their utility in other parrots. Cons Gen 1:93–95
Sawyer SA (1999) GENECONV: a computer package for the statistical detection of gene conversion. [Internet]. St. Louis (MO): Distributed by the author, Department of Mathematics, Washington University Available from: http://www.math.wustl.edu/;sawyer. Accessed 5 Oct 2013
Schaschl H, Wandeler P, Suchentrunk F, Obexer-Ruff G, Goodman SJ (2006) Selection and recombination drive the evolution of MHC class II DRB diversity in ungulates. Heredity 97:427–437
Seutin G, White BN, Boag PT (1991) Preservation of avian blood and tissue samples for DNA analysis. Can J Zool 69:82–90
Shiina T, Shimizu S, Hosomichi K, Kohara S, Watanabe S, Hanzawa K, Beck S, Kulski JK, Inoko H (2004) Comparative genomic analysis of two avian (quail and chicken) MHC regions. J Immunol 172:6751–6763
Suh A, Paus M, Kiefmann M, Churakov G, Franke FA, Brosius J, Kriegs JO, Schmitz J (2011) Mesozoic retroposons reveal parrots as the closest living relatives of passerine birds. Nat Commun 2:443. doi:10.1038/ncomms1448
Sutton JT, Nakagawa S, Robertson BC, Jamieson IG (2011) Disentangling the roles of natural selection and genetic drift in shaping variation at MHC immunity genes. Mol Ecol 20:4408–4420
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tsuda TT, Tsuda M, Naruse T, Kawata H, Ando A, Shiina T, Fukuda M, Kurita M, LeMaho I, Kulski JK, Inoko H (2001) Phylogenetic analysis of penguin (Spheniscidae) species based on sequence variation in MHC class II genes. Immunogenetics 53:712–716
Walsh PS, Metzger DA, Higuchi R (1991) Chelex 100 as a medium for simple extraction of DNA for PCR-based typing from forensic material. Biotechniques 10:506–513
Wang Z, Zhou X, Lin Q, Fang W, Chen X (2013) Characterization, polymorphism and selection of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) DAB genes in vulnerable Chinese egret (Egretta eulophotes). PLoS ONE 8:e74185. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074185
Westerdahl H, Wittzell H, von Schantz T, Bensch S (2004) MHC class I typing in a songbird with numerous loci and high polymorphism using motif-specific PCR and DGGE. Heredity 92:534–542. doi:10.1038/sj.hdy.6800450
Wright TF, Schirtzinger EE, Matsumoto T, Eberhard JR, Graves GR, Snachez JJ, Capelli S, Müller H, Sharpegge J, Chambers G, Fleischer RC (2008) A multilocus molecular phylogeny of the parrots (Psittaciformes): support for a Gondwanan origin during the Cretaceous. Mol Biol Evol 25:2141–2156. doi:10.1093/molbev/msn160
Acknowledgments
Thanks to the National Kakapo Team members for collecting the blood samples for DNA analysis. We thank P. Jameson and N. Gemmell for use of laboratory space at the University of Canterbury at the beginning of the study. We are grateful to F. Robertson for assistance with lab work at Otago University and C. Grueber for helpful comments on earlier drafts of the manuscript. Cloning of the kakapo, kea, and kaka MHC was done under ERMA application GMD07039. Funding for this research was provided by the Department of Conservation Kakapo Recovery Group, McKee Trust (funding to BCR) and the Allan Wilson Centre (funding to IGJ). GK was supported by a University of Otago PhD Scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knafler, G.J., Fidler, A., Jamieson, I.G. et al. Evidence for multiple MHC class II β loci in New Zealand’s critically endangered kakapo, Strigops habroptilus . Immunogenetics 66, 115–121 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-013-0750-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-013-0750-5