Abstract
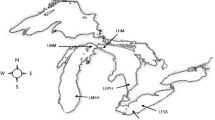
The bacterial community inhabiting the water column at Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica) was examined by the fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) technique and the genotypic and phenotypic characterization of 606 bacterial isolates. Overall, the FISH analysis revealed a bacterioplankton composition that was typical of Antarctic marine environments with the Cytophaga/Flavobacter (CF) group of Bacteroidetes that was equally dominant with the Actinobacteria and Gammaproteobacteria. As sampling was performed during the decay of sea-ice, it is plausible to assume the origin of Bacteroidetes from the sea-ice compartment where they probably thrive in high concentration of DOM which is efficiently remineralized to inorganic nutrients. This finding was supported by the isolation of Gelidibacter, Polaribacter, and Psychroflexus members (generally well represented in Antarctic sea-ice) which showed the ability to hydrolyze macromolecules, probably through the production of extracellular enzymes. A consistently pronounced abundance of the Gammaproteobacteria (67.8%) was also detected within the cultivable fraction. Altogether, the genera Psychromonas and Pseudoalteromonas accounted for 65.4% of total isolates and were ubiquitous, thus suggesting that they may play a key role within the analyzed bacterioplankton community. In particular, Pseudoalteromonas isolates possessed nitrate reductase and were able to hydrolyze substrates for protease, esterase, and β-galactosidase, thus indicating their involvement in the carbon and nitrogen cycling. Finally, the obtained results highlight the ability of the Actinobacteria to survive and proliferate in the Terra Nova Bay seawater as they generally showed a wide range of salt tolerance and appeared to be particularly competitive with strictly marine bacteria by better utilizing supplied carbon sources.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agoguè H, Casamayor EO, Bourrain M, Obernosterer I, Joux F, Herndl GJ, Lebaron P (2005) A survey on bacteria inhabiting the sea surface microlayer of coastal ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 54:269–280
Altschul SF, Madden TI, Schäffer AA, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped blast and psi-blast: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acid Res 25:3389–3402
Baldi F, Marchetto D, Pini F, Fani R, Michaud L, Lo Giudice A, Berto D, Giani M (2010) Biochemical and microbial features of shallow marine sediments along the Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). Cont Shelf Res 30:1614–1625
Bano N, Hollibaugh JT (2002) Phylogenetic composition of bacterioplankton assemblages from the Arctic Ocean. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:505–518
Bowman JP, McCammon SA, Brown MV, Nichols DS, McMeekin TA (1997) Diversity and association of psychrophilic bacteria in Antarctic sea-ice. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3068–3078
Brinkmeyer R, Knittel K, Jurgens J, Weyland H, Amann R, Helmke E (2003) Diversity and structure of bacterial communities in Arctic versus Antarctic pack ice. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6610–6619
Brown MV, Bowman JP (2001) A molecular phylogenetic survey of sea-ice microbial communities (SIMCO). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35:267–275
Bruni V, Gugliandolo C, Maugeri T, Allegra A (1999) Psychrotrophic bacteria from a coastal station in the Ross Sea (Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica). Microbiologica 22:357–363
Buchan A, Gonzàlez JM, Moran MA (2005) Overview of the marine Roseobacter lineage. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5665–5677
Celussi M, Cataletto B, Fonda Umani S, Del Negro P (2009) Depth profiles of bacterioplankton assemblages and their activities in the Ross Sea. Deep Sea Res 56:2193–2205
Celussi M, Paoli A, Crevatin E, Bergamasco A, Margiotta F, Saggiomo V, Fonda Umani S, Del Negro P (2009) Short-term under-ice variability of prokaryotic plankton communities in coastal Antarctic waters (Cape Hallett, Ross Sea). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 81:491–500
Celussi M, Bergamasco A, Cataletto B, Fonda Umani S, Del Negro P (2010) Water masses' bacterial community structure and microbial activities in the Ross Sea, Antarctica. Antarct Sci 22:361–370
Church MJ, DeLong EF, Ducklow HW, Karner MB, Preston CM, Karl DM (2003) Abundance and distribution of planktonic Archaea and Bacteria in the waters west of the Antarctic Peninsula. Limnol Oceanogr 48:1893–1902
Cottrell WT, Kirchman DL (2000) Community composition of marine bacterioplankton determined by 16S rRNA gene clone libraries and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5116–5122
DeLong EF, Wickham G, Pace N (1989) Phylogenetic stains: ribosomal RNA-based probes for the identification of single cells. Science 243:1360–1363
DeLong EF, Wu KY, Prezelin BB, Jovine RVM (1994) High abundance of Archaea in marine picoplankton. Nature 371:695–697
Ducklow H (2000) Bacterial production and biomass in the oceans. In: Kirchman O (ed) Microbial ecology of the oceans. Wiley, New York
Egli K, Bosshard F, Werlen C, Lais P, Siegrist H, Zehnder AJB, van der Meer JR (2003) Microbial composition and structure of rotating biological contactor biofilm treating ammonium-rich wastewater without organic carbon. Microb Ecol 45:419–432
Eilers H, Pernthaler J, Glöckner FO, Amann R (2000) Culturability and in situ abundance of pelagic bacteria from the North Sea. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3044–3051
Eilers H, Pernthaler J, Peplies J, Glöckner FO, Gerdts G, Amann R (2001) Isolation of novel pelagic bacteria from the German Bight and their seasonal contributions to surface picoplankton. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5134–5142
Ellis RJ, Morgan P, Weightman AJ, Fry JC (2003) Cultivation-dependent and -independent approaches for determining bacterial diversity in heavy-metal-contaminated soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3223–3230
Fabiano M, Pusceddu A (1998) Total and hydrolizable particulate organic matter (carbohydrates, proteins and lipids) at a coastal station in Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). Polar Biol 19:125–132
Ferguson RL, Buckley EN, Palumbo AV (1984) Response of marine bacterioplankton to differential filtration and confinement. Appl Environ Microbiol 47:49–55
Gentile G, Giuliano L, D'Auria G, Smedile F, Azzaro M, De Domenico M, Yakimov MM (2006) Study of bacterial communities in Antarctic coastal waters by a combination of 16S rRNA and 16S rDNA sequencing. Environ Microbiol 8:2150–2161
Glöckner FO, Fuchs BM, Amann R (1999) Bacterioplankton compositions of lakes and oceans: a first comparison based on fluorescence in situ hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3721–3726
Grossart HP, Schlingloff A, Bernhard M, Simon M, Brinkhoff T (2004) Antagonistic activity of bacteria isolated from organic aggregates of the German Wadden Sea. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 47:387–396
Jaspers E, Nauhaus K, Cypionka H, Overmann J (2001) Multitude and temporal variability of ecological niches as indicated by the diversity of cultivated bacterioplankton. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 36:153–164
Joint I, Mühling M, Querellou J (2010) Culturing marine bacteria—an essential prerequisite for biodiscovery. Microb Biotechnol 3:564–575
La Ferla R, Lo Giudice A, Maimone G (2004) Morphology and LPS content for the estimation of the bacterial biomass in the Ionian Sea. Sci Mar 68:23–31
Lo Giudice A, Michaud L, de Pascale D, De Domenico M, di Prisco G, Fani R, Bruni V (2006) Lipolytic activity of Antarctic cold-adapted marine bacteria (Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea). J Appl Microbiol 101:1039–1048
Lo Giudice A, Brilli M, Bruni V, De Domenico M, Fani R, Michaud L (2007) Bacterium-bacterium inhibitory interactions among psychrotrophic bacteria isolated from Antarctic seawaters (Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 60:383–396
Lo Giudice A, Bruni V, Michaud L (2007) Characterization of Antarctic psychrotrophic bacteria with antibacterial activities against terrestrial microorganisms. J Basic Microbiol 47:496–505
Manz W, Amann R, Ludwig W, Wagner M, Schleifer KH (1992) Phylogenetic oligodeoxynucleotide probes for the major subclasses of Proteobacteria—problems and solutions. Syst Appl Microbiol 15:593–600
Massana R, Taylor LT, Murray AE, Wu KY, Jeffrey WH, DeLong EF (1998) Vertical distribution and temporal variation of marine planktonic Archaea in the Gerlache Strait, Antarctica, during early spring. Limnol Oceanogr 43:607–617
Meier H, Amann R, Ludwig W, Schleifer K-H (1999) Specific oligonucleotide probes for in situ detection of a major group of Gram-positive bacteria with low DNA G + C content. Syst Appl Microbiol 22:186–196
Michaud L, Di Cello F, Brilli M, Fani R, Lo Giudice A, Bruni V (2004) Biodiversity of cultivable psychrotrophic marine bacteria isolated from Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). FEMS Microbiol Lett 230:67–71
Murray AE, Grzymski JJ (2007) Diversity and genomics of Antarctic marine micro-organisms. Philos T R Soc B 362:2259–2271
Murray AE, Preston CM, Massana R, Taylor LT, Blakis A, Wu K, DeLong EF (1998) Seasonal and spatial variability of bacteria and archaeal assemblages in the coastal waters near Anvers Island, Antarctica. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2585–2595
Murray AE, Wu K, Moyer C, Karl DM, DeLong EF (1999) Evidence for circumpolar distribution of planktonic Archaea in the Southern Ocean. Aquat Microb Ecol 18:263–273
Nichols D (2007) Cultivation gives context to the microbial ecologists. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 60:351–357
Nichols D, Bowman J, Sanderson K, Mancuso Nichols C, Lewis T, McMeekin T, Nichols PD (1999) Development with Antarctic microorganisms: culture collections, bioactivity screening, taxonomy, PUFA production and cold-adapted enzymes. Curr Op Biotechnol 10:240–246
Piquet AM, Bolhuis H, Davidson AT, Buma AG (2010) Seasonal succession and UV sensitivity of marine bacterioplankton at an Antarctic coastal site. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 73:68–82
Porter KG, Feig YS (1980) The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora. Limnol Oceanogr 25:943–948
Prabagaran SR, Manorama R, Delille D, Shivaji S (2007) Predominance of Roseobacter, Sulfitobacter, Glaciecola and Psychrobacter in seawater collected off Ushuaia, Argentina, Sub-Antarctica. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59:342–355
Pusceddu A, Cattaneo-Vietti R, Albertelli G, Fabiano M (1999) Origin, biochemical composition and vertical flux of particulate organic matter under the pack ice in Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica) during late summer 1995. Polar Biol 22:124–132
Roller C, Wagner M, Amann R, Ludwig W, Schleifer K-H (1994) In situ probing of Gram-positive bacteria with high DNA G + C content using 23S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotides. Microbiology 140:2849–2858
Selje N, Simon M, Brinkhoff T (2004) A newly discovered Roseobacter cluster in temperate and polar oceans. Nature 427:445–448
Simon M, Glöckner FO, Amann R (1999) Different community structure and temperature optima of heterotrophic picoplankton in various regions of the Southern Ocean. Aquat Microb Ecol 18:275–284
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RG, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular microbiology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 611–654
Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM (1994) Taxonomic note: a place for DNA–DNA reassociation and 16S sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:846–849
Stahl DA, Amann R (1991) Development and application of nucleic acid probes. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. John Wiley & Sons Ltd., Whichester, England, pp 205–248
Topping JN, Heywood JL, Ward P, Zubkow MV (2006) Bacterioplankton composition in the Scotia Sea, Antarctica, during the austral summer of 2003. Aquat Microb Ecol 45:229–235
Van Trappen S, Mergaert J, Van Eygen S, Dawyndt P, Cnockaert MC, Swings J (2002) Diversity of 746 heterotrophic bacteria isolated from microbial mats from ten Antarctic lakes. Syst Appl Microbiol 25:603–610
Vera J, Alvarez R, Murano E, Slebe JC, Leon O (1998) Identification of a marine agarolytic Pseudoalteromonas isolate and characterization of its extracellular agarase. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4378–4383
Vincent WF (2000) Evolutionary origins of Antarctic microbiota: invasion, selection and endemism. Antarct Sci 12:374–385
Xu Y, Nogi Y, Kato C, Liang Z, Rüger H-R, De Kegel D, Glansdorff N (2003) Psychromonas profunda sp. nov., a psychropiezophilic bacterium from deep Atlantic sediments. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:527–532
Zeng Y, Liu W, Li H, Yu Y, Chen B (2007) Effect of restriction endonucleases on assessment of biodiversity of cultivable polar marine planktonic bacteria by amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis. Extremophiles 11:685–692
Zhang XF, Yao TD, Tian LD, Xu SJ, An LZ (2008) Phylogenetic and physiological diversity of bacteria isolated from Puruogangri ice core. Microb Ecol 55:476–488
Acknowledgments
L Michaud and A Lo Giudice wish to thank the colleagues Michela Castellano and Enrico Olivari (University of Genoa, Italy) and the crew of the boat “Malippo”, for assistance with sample collections, and to all of the staff at “Mario Zucchelli” Station, for the logistic help and support, which made possible the expedition. We also thank Rosabruna La Ferla and Giovanna Maimone (IAMC-CNR Messina, Italy) for supplying the epifluorescence microscope, and four anonymous reviewers for helpful comments on the manuscript. This research was supported by grants from PNRA (Programma Nazionale di Ricerche in Antartide), Italian Ministry of Education and Research (PEA 2004, Research Project PNRA 2004/1.6), and from MNA (Museo Nazionale dell'Antartide).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lo Giudice, A., Caruso, C., Mangano, S. et al. Marine Bacterioplankton Diversity and Community Composition in an Antarctic Coastal Environment. Microb Ecol 63, 210–223 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-011-9904-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-011-9904-x