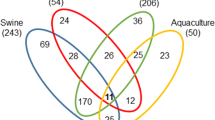
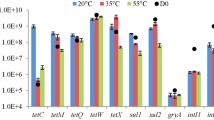
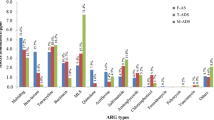
Abstract
The introduction of antibiotics to animal feed has contributed to the selection of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in concentrated animal feeding operations. The aim of this work was to characterize the impact of an aerobic thermophilic biotreatment on anaerobic antibiotic-resistant bacteria in swine waste. Despite 162- to 6,166-fold reduction in antibiotic-resistant populations enumerated in the swine waste at 25°C and 37°C, resistant populations remained significant (104 to 105 most probable number per milliliter) in the treated swine waste. Five resistance genes were detected before [tet(LMOS) erm(B)], and six resistance genes were detected after [tet(LMOSY) erm(B)] biotreatment. However, the biotreatment decreased the frequency of detection of resistance genes by 57%. Analysis by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified 16 S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) fragments showed that the biotreatment reduced the bacterial diversity of resistant populations enumerated at 37°C. Cloning and sequencing of the 16 S rDNA of these populations revealed that most clones in the treated swine waste were closely similar to some of the clones retrieved from the untreated swine waste. This study revealed that the aerobic thermophilic biotreatment developed in our laboratory does not prevent the introduction of facultatively anaerobic antibiotic-resistant bacteria and their resistance genes into agricultural ecosystems. Horizontal transfer of ecologically advantageous genes within microbial communities are likely to prevent thermophilic biotreatments from completely eliminating antibiotic-resistant bacteria and their resistance genes in animal wastes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agersø Y, Sandvang D (2005) Class 1 integrons and tetracycline resistance genes in Alcaligenes, Arthrobacter, and Pseudomonas spp. isolated from pigsties and manured soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7941–7947
Akwar TR, Poppe C, Wilson J, Reid-Smith RJ, Dyck M, Waddington J, Shang D, Dassie N, McEwen SA (2007) Risk factors for antimicrobial resistance among fecal Escherichia coli from residents on forty-three swine farms. Microb Drug Resist 13:69–76
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, USA
Aminov RI, Chee-Sanford JC, Garrigues N, Teferedegne B, Krapac IJ, White BA, Mackie RI (2002) Development, validation, and application of PCR primers for detection of tetracycline efflux genes of Gram-negative bacteria. Appl Environ Microb 68:1786–1793
Aminov RI, Garrigues-Jeanjean N, Mackie RI (2001) Molecular ecology of tetracycline resistance: development and validation of primers for detection of tetracycline resistance genes encoding ribosomal protection proteins. Appl Environ Microb 67:22–32
Barza M, Travers K (2002) Excess infections due to antimicrobial resistance: the “attributable fraction”. Clin Infect Dis 34:S126–S130
Bergey DH, Holt JG (1994) Bergey's manual of determinative bacteriology, 9th edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, USA
Canadian Food Inspection Agency (2008) Compendium of Medicating Ingredient Brochures. 8th edition, http://www.inspection.gc.ca/english/anima/feebet/mib/cmibe.shtml
Centre d'expertise en analyse environnementale du Québec (2003) Dénombrement des salmonelles: méthode par tubes multiples. MA. 700-Sal-tm 1.0. Ministère de l'environnement du QuébecMinistère de l'environnement du Québec
Chee-Sanford JC, Aminov RI, Krapac IJ, Garrigues-Jeanjean N, Mackie RI (2001) Occurrence and diversity of tetracycline resistance genes in lagoons and groundwater underlying two swine production facilities. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1494–1502
Chevalier P, Levallois P, Michel P (2004) Waterborne enteric infections potentially linked to livestock production: a literature review. Vecteur Environnement 37:90–106
Chinivasagam HN, Thomas RJ, Casey K, McGahan E, Gardner EA, Rafiee M, Blackall PJ (2004) Microbiological status of piggery effluents from 13 piggeries in the south east Queensland region of Australia. J Appl Microbiol 97:883–891
Chopra I, Roberts M (2001) Tetracyclines antibiotics: mode of action, applications, molecular biology, and epidemiology of bacterial resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65:232–260
Committe on drug use in food animals (1999) The use of drugs in food animals, benefits and risks. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Côté C, Leblanc M, Cloutier D, Quessy S (2002) Peut-on fertiliser les légumes avec du lisier de porc? Vecteur Environnement 35:36–38
Cotta MA, Whitehead TR, Zeltwanger RL (2003) Isolation, characterization and comparison of bacteria from swine faeces and manure storage pits. Environ Microbiol 5:737–745
De Leener E, Martel A, De Graef EM, Top J, Butaye P, Haesebrouck F, Willems R, Decostere A (2005) Molecular analysis of human, porcine, and poultry Enterococcus faecium isolates and their erm(B) genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2766–2770
Doyle M, Jaykus L-A, Metz M (2005) Research opportunities in food and agriculture microbiology. American Academy of Microbiology, Washington DC, USA, p 17
Edwards U, Rogall T, Blöcker H, Emde M, Böttger EC (1989) Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16 S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 17:7843–7853
Good I (1953) The population frequencies of species and the estimation of population of parameters. Biometrika 40:237–264
Helmuth R, Protz D (1997) How to modify conditions limiting resistance in bacteria in animals and other reservoirs. Clin Infect Dis 24:S136–S138
Hill VR, Sobsey MD (1998) Microbial indicator reductions in alternative treatment systems for swine wastewater. Wat Sci Tech 38:119–122
Hinton M, Hampson DJ, Hampson E, Linton AH (1985) The effects of oxytetracycline on the intestinal Escherichia coli flora of newly weaned pigs. J Hyg (Lond) 95:77–85
Hooper DG, Hirsh DC (1977) Changes of resistance of enteric bacteria in mice given tetracycline in drinking water. Am J Vet Res 38:565–567
Huber T, Faulkner G, Hugenholtz P (2004) Bellerophon: a program to detect chimeric sequences in multiple sequence alignments. Bioinformatics 20:2317–2319
Huys G, D'Haene K, Van Eldere J, von Holy A, Swings J (2005) Molecular diversity and characterization of tetracycline-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from a poultry processing plant. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:574–579
Institute of Food Technologists (2000) IFT expert report on emerging microbiological food safety issues. Implications for control in the 21st century: 107 pages
Institute of Food Technologists (2006) Antimicrobial resistance: implications for the food system. Compr Rev Food Sc Food Safety 5:71–137
Isaacson RE, Torrence ME (2002) The role of antibiotics in agriculture. American Academy of Microbiology, Washington, DC, p 15
Jensen BB, Jorgensen BB (1994) Effect of dietary fiber on microbial activity and microbial gas production in various regions of the gastrointestinal tract of pigs. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:1897–1904
Juteau P (2006) Review of the use of aerobic thermophilic bioprocesses for the treatment of swine waste. Livestock Sci 102:187–196
Juteau P, Tremblay D, Ould-Moulaye C-B, Bisaillon J-G, Beaudet R (2004) Swine waste treatment by self-heating aerobic thermophilic bioreactors. Wat Res 38:539–546
Juteau P, Tremblay D, Villemur R, Bisaillon J-G, Beaudet R (2004) Analysis of the bacterial community inhabiting an aerobic thermophilic sequencing batch reactor (AT-SBR) treating swine waste. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:115–122
Khachatourians GG (1998) Agricultural use of antibiotics and the evolution and transfer of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Can Med Assoc J 159:1129–1136
Krebs C (1989) Ecological methodology. HarperCollins, New York, NY, USAHarperCollins, , New York, NY, USA
Langlois BE, Dawson KA, Stahly TS, Cromwell GL (1984) Antibiotic resistance of fecal coliforms from swine fed subtherapeutic and therapeutic levels of chlortetracycline. J Anim Sci 58:666–674
Langvad B, Skov MN, Rattenborg E, Olsen JE, Baggesen DL (2006) Transmission routes of Salmonella typhimurium DT 104 between 14 cattle and pig herds in Denmark demonstrated by molecular fingerprinting. J Appl Microbiol 101:883–890
Leser TD, Amenuvor JA, Jensen TK, Lindecrona RH, Boye M, Møller K (2002) Culture-independent analysis of gut bacteria: the pig gastrointestinal tract microbiota revisited. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:673–690
Leung K, Topp E (2001) Bacterial community dynamics in liquid swine manure during storage: molecular analysis using DGGE/PCR of 16 S rDNA. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 38:169–177
Linton AH (1984) Antibiotic-resistant bacteria in animal husbandry. Br Med Bull 40:91–95
Lu H-Z, Weng X-H, Li H, Yin Y-K, Pang M-Y, Tang YW (2002) Enterococcus faecium-related outbreak with molecular evidence of transmission from pigs to humans. J Clin Microbiol 40:913–917
Mackie RI, Koike S, Krapac I, Chee-Sanford J, Maxwell S, Aminov RI (2006) Tetracycline residues and tetracycline resistance genes in groundwater impacted by swine production facilities. Anim Biotechnol 17:157–176
Magurran A (1988) Ecological diversity and its measurement. University Press, Princeton, NJ, USA.University Press, Princeton, NJ, USA
Majdoub R, Côté C, Duchemin M (2004) Risque de contamination microbiologique des eaux souterraines et mesures préventives à adopter. Vecteur Environnement 37:61–66
Mellon M, Benbrook C, Benbrook K (2001) Hogging it: estimates of antimicrobial abuse in livestock. UCS, Cambridge
Michalova E, Novotna P, Schlegelova J (2004) Tetracyclines in veterinary medicine and bacterial resistance to them. Vet Med - Czech 49:79–100
Molbak K, Baggessen DL, Aarestrup FM, Ebbesen JM, Engberg J, Frydendahl K, Gerner-Smidt P, Peterson AM, Wegener HC (1999) An outbreak of multidrug-resistant, quinolone-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium DT104. N Engl J Med 341:1420–1425
Muyzer G, de Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16 S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (2002) Performance standards for antimicrobial disk and dilution susceptibility tests for bacteria isolated from animals: approved standard-second edition. NCCLS document M31-A2. NCCLS. NCCLS. Wayne, PA, USANCCLS
Pei R, Cha J, Carlson KH, Pruden A (2007) Response of antibiotic resistance genes (ARG) to biological treatment in dairy lagoon water. Environ Sci Technol 41:5108–5113
Perreault N, Andersen DT, Pollard WH, Greer CW, Whyte LG (2007) Characterization of the prokaryotic diversity in cold saline perennial springs of the Canadian High Arctic. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:1532–1543
Roberts MC (2005) Update on acquired tetracycline resistance genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 245:195–203
Roberts MC, Sutcliffe J, Courvalin P, Jensen LB, Rood J, Seppala H (1999) Nomenclature for macrolide and macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance determinants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:2823–2830
Rosser SJ, Young H-K (1999) Identification and characterization of class 1 integrons in bacteria from an aquatic environment. J Antimicrob Chemother 44:11–18
Sapkota AR, Ojo KK, Roberts MC, Schwab KJ (2006) Antibiotic resistance genes in multidrug-resistant Enterococcus spp. and Streptococcus spp. recovered from the indoor air of a large-scale swine-feeding operation. Lett Appl Microbiol 43:534–540
Segura I, Casadesùs J, Ramos-Morales F (2004) Use of mixed infections to study cell invasion and intracellular proliferation of Salmonella enterica in eukaryotic cell cultures. J Microbiol Meth 56:83–91
Skirrow MB, Blaser MJ (2000) Clinical aspects of Campylobacter infection. In: Nachamkin I, Blaser MJ (eds) Campylobacter. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C, pp 69–88
Smith HW, Tucker JF (1975) The effect of antibiotic therapy on the faecal extretion of Salmonella typhimurium by experimentally infected chickens. J Hyg (Lond) 75:275–292
Smith KE, Besser JM, Hedberg CW, Leano FT, Bender JB, Wicklund JH, Johnson BP, Moore KA, Osterholm MT (1999) Quinolone-resistant Campylobacter jejuni infections in Minnesota, 1992–1998. N Engl J Med 340:1525–1532
Stanton TB, Humphrey SB (2003) Isolation of tetracycline-resistant Megasphaera elsdenii strains with novel mosaic gene combinations of tet(O) and tet(W) from swine. Appl Environ Microb 69:3874–3882
Stockstad ELR, Jukes TH, Pierce J, Page AC, Franklin AL (1949) The multiple nature of the animal protein factor. J Biol Chem 180:647–654
Sutcliffe J, Grebe T, Tait-Kamradt A, Wondrack L (1996) Detection of erythromycin-resistant determinants by PCR. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 40:2562–2566
Sutcliffe J, Tait-Kamradt A, Wondrack L (1996) Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes resistant to macrolides but sensitive to clindamycin: a common resistance pattern mediated by an efflux system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 40:1817–1824
Swann MM (1969) Report of joint committee on the use of antibiotics in animal husbandry and veterinary medicine. Cmnd. 4190. In: Editor (ed.)^(eds.) Book Report of joint committee on the use of antibiotics in animal husbandry and veterinary medicine. Cmnd. 4190., vol. Her Majesty's Stationery Office, London, UK
US FDA (1998) Guidance for industry. Guide to minimize microbial food safety hazards for fresh fruits and vegetables. US Food and Drug Administration Report
Wegener HC, Aarestrup FM, Jensen LB, Hammerum AM, Bager F (1999) Use of antimicrobial growth promoters in food animals and Enterococcus faecium resistance to therapeutic antimicrobial drugs in Europe. Emerg Infect Dis 5:329–335
Whittle G, Whitehead TR, Hamburger N, Shoemaker NB, Cotta MA, Salyers AA (2003) Identification of new ribosomal protection type of tetracycline resistant gene, tet(36), from swine manure pits. Appl Environ Microb 69:4151–4158
Witte W (1998) Medical consequences of antibiotic use in agriculture. Science 279:996–997
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada to P.J., and by Postdoctoral Fellowships from the Fonds québécois de Recherche sur la Nature et les Technologies du Québec (FQRNT) and the Fondation Armand-Frappier to M.R.C. We thank Dr. Josée Harel (Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Université de Montréal), Dr. Roland Brousseau (Biotechnology Research Institute, National Research Council Canada, Montreal) and Dr. Marilyn C. Roberts (University of Washington) for providing positive control strains for PCR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chénier, M.R., Juteau, P. Impact of an Aerobic Thermophilic Sequencing Batch Reactor on Antibiotic-Resistant Anaerobic Bacteria in Swine Waste. Microb Ecol 58, 773–785 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-009-9546-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-009-9546-4