Abstract
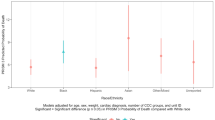
Racially disparate health outcomes exist for a multitude of populations and illnesses. It is unknown how race and ethnicity impact mortality for children with cardiomyopathy or myocarditis. This retrospective cross-sectional study employed the Kids’ Inpatient Database to analyze 34,617 hospital admissions for patients ≤ 18 years old with cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, or both, without concomitant congenital heart disease. Multivariate logistic regression models investigated the impact of race/ethnicity on in-hospital mortality adjusting for age, calendar year, sex, insurance type, diagnostic category, treatment at a pediatric hospital, and non-cardiac organ dysfunction. African American race and Hispanic ethnicity were independent risk factors for mortality (African American: odds ratio (OR) 1.25, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.01–1.53 and Hispanic: OR 1.29, 95% CI 1.03–1.60). African American race was also found to be significantly associated with the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), mortality while on ECMO, and cardiac arrest. Adjusting the regression model for ECMO and arrest attenuated the impact of African American race on mortality, suggesting that these variables may indeed play a role in explaining the impact of race on mortality for African American patients with myocardial disease. Hispanic ethnicity remained associated with higher risk of mortality despite controlling for all mechanical circulatory support and transplant (OR 1.30, 95% CI 1.04–1.63). Children of racial and ethnic minorities hospitalized with cardiomyopathy or myocarditis are more likely to die than their white counterparts, a trend that may be due at least in part to in-hospital differences in care or response to therapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Guagliardo MF, Teach SJ, Huang ZJ, Chamberlain JM, Joseph JG (2003) Racial and ethnic disparities in pediatric appendicitis rupture rate. Acad Emerg Med 10(11):1218–1227
Attenello FJ, Ng A, Wen T et al (2015) Racial and socioeconomic disparities in outcomes following pediatric cerebrospinal fluid shunt procedures. J Neurosurg Pediartr 15(6):560–566
Flores G (2010) Technical report—racial and ethnic disparities in the health and health care of children. Pediatrics 125(4):e979
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2001) Racial disparities in median age at death of persons with Down syndrome: United States, 1968–1997. MMWR Morbid Mortal Wkly Rep 50(22):463–465
Kadan-Lottick NS, Ness KK, Bhatia S, Gurney JG (2003) Survival variability by race and ethnicity in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. JAMA 290(15):2008–2014
Kokoska ER, Bird TM, Robbins JM, Smith SD, Corsi JM, Campbell BT (2007) Racial disparities in the management of pediatric appendicitis. J Surg Res 137(1):83–88
Nembhard WN, Salemi JL, Ethen MK, Fixler DE, DiMaggio A, Canfield MA (2011) Racial/ethnic disparities in risk of early childhood mortality among children with congenital heart defects. Pediatrics 127(5):e1128–e1138
Collins JW, Soskolne G, Rankin KM, Ibrahim A, Matoba N (2017) African-American: white disparity in infant mortality due to congenital heart disease. J Pediatr 181:131–136
Chan T, Pinto NM, Bratton SL (2012) Racial and insurance disparities in hospital mortality for children undergoing congenital heart surgery. Pediatr Cardiol 33:1026–1039
Chan T, Lion KC, Mangione-Smith R (2015) Racial disparities in failure-to-rescue among children undergoing congenital heart surgery. J Pediatr 166:812–818
Benavidez O, Gauvreau K, Jenkins K (2006) Racial and ethnic disparities in mortality following congenital heart surgery. Pediatr Cardiol 27(3):321–328
Gonzalez PC, Gauvreau K, DeMone JA, Piercey GE, Jenkins KJ (2003) Regional racial and ethnic differences in mortality for congenital heart surgery in children may reflect unequal access to care. Pediatr Cardiol 24:103–108
Oster ME, Strickland MJ, Mahle WT (2011) Racial and ethnic disparities in post-operative mortality following congenital heart surgery. J Pediatr 159:222–226
DiBardino DJ, Pasquali SK, Hirsch JC et al (2012) Effect of sex and race on outcome in patients undergoing congenital heart surgery: an analysis of the society of thoracic surgeons congenital heart surgery database. Ann Thorac Surg 94:2054–2060
Pietra BA, Kantor PF, Bartlett HL et al (2012) Early predictors of survival to and after heart transplantation in children with dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation 126:1079–1086
Green DJ, Brooks MM, Burckart GJ (2017) The influence of race and common genetic variations on outcomes after pediatric heart transplantation. Am J Transplant 17:1525–1539
Morris AA, Kransdorf EP, Coleman BL, Colvin M (2016) Racial and ethnic disparities in outcomes after heart transplantation: a systematic review of contributing factors and future directions to close the outcomes gap. J Heart Lung Transplant 35:953–961
Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR (2001) Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med 29(7):1303–1310
Rehmani SS, Liu B, Al-Ayoubi AM et al (2018) Racial disparity in utilization of high-volume hospitals for surgical treatment of esophageal cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 106:346–353
Rangrass G, Ghaferia AA, Dimick JB (2014) Explaining racial disparities in outcomes after cardiac surgery: the role of hospital quality. JAMA Surg 149:223–227
Dimick J, Ruhter J, Sarrazin MV et al (2013) Black patients more likely than whites to undergo surgery at low-quality hospitals in segregated regions. Health Aff 32:1046–1053
Demone JA, Gonzalez PC, Gauvreau K, Piercey GE, Jenkins KJ (2003) Risk of death for Medicaid recipients undergoing congenital heart surgery. Pediatr Cardiol 24:97–102
Rusconi P, Wilkinson J, Sleeper L et al (2017) Differences in presentation and outcomes between children with familial dilated cardiomyopathy and children with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ Heart Fail 10(2):e2637
Towbin JA, Lowe AM, Colan SD et al (2006) Incidence, causes, and outcomes in dilated cardiomyopathy in children. JAMA 296:1867–1876
Alvarez J, Wilkinson J, Lipshultz S (2007) Outcome predictors for pediatric dilated cardiomyopathy: a systematic review. Progr Pediatr Cardiol 23:25–32
Butts RJ, Boyle GJ, Deshpande SR (2017) Characteristics of clinically diagnosed pediatric myocarditis in a contemporary multi-center cohort. Pediatr Cardiol 38:1175–1182
Sachdeva S, Song X, Dham N, Heath DM, DeBiasi RL (2015) Analysis of clinical parameters and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging as predictors of outcome in pediatric myocarditis. Am J Cardiol 115:499–504
Ortega AN, Stewart DC, Dowshen SA, Katz SH (2000) Perceived access to pediatric primary care by insurance status and race. J Community Health 25(6):481–493
Raphael JL, Guadagnolo BA, Beal AC, Giardino AP (2009) Racial and ethnic disparities in indicators of a primary care medical home for children. Acad Pediatr 9(4):221–227
Taira DA, Safran DG, Seto TB et al (2001) Do patient assessments of primary care differ by patient ethnicity? Health Serv Res 36:1059–1071
Stevens GD, Shi L (2002) Racial and ethnic disparities in the quality of primary care for children. J Fam Pract 51:573
Flores G, Abreau M, Tomany-Korman SC (2005) Limited english proficiency, primary language at home, and disparities in children’s health care: how language barriers are measured matters. Public Health Rep 120:418–430
Enirez-Wiemer M, Sanders LM, Barr DA, Mendoza FS (2014) Parental limited english proficiency and health outcomes for children with special health care needs: a systematic review. Acad Pediatr 14:128–136
Colan SD, Lipshultz SE, Lowe AM (2007) Epidemiology and cause-specific outcome of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in children. Circulation 115:773–781
Martinez PA, Balagandahar RT (2016) The epidemiology and outcomes of pediatric in-hospital cardiopulmonary arrest in the United States during 1997 to 2012. Resuscitation 105:177–181
Chan T, Barrett CS, Tjoeng YL, Wilkes J, Bratton SL, Thiagarajan RR (2018) Racial variations in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation use following congenital heart surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 156:306–315
Ghelani SJ, Spaeder MC, Pastor W, Spurney CF, Klugman D (2012) Demographics, trends, and outcomes in pediatric acute myocarditis in the United States, 2006 to 2011. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 5:622–627
Chan T, Di Gennaro J, Farris RWD, Radman M, McMullan DM (2017) Racial and ethnic variation in pediatric cardiac extracorporeal life support survival. Crit Care Med 45:670–678
Sherwin ED, Gauvreau K, Scheurer MA et al (2012) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation after stage 1 palliation for hypoplastic left heart syndrome. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 144:1337–1343
Thiagarajan RR, Laussen PC, Rycus PT, Bartlett RH, Bratton SL (2007) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation to aid cardiopulmonary resuscitation in infants and children. Circulation 116:1693–1700
Sabin JA, Greenwald AG (2012) The influence of implicit bias on treatment recommendations for 4 common pediatric conditions: pain, urinary tract infection, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and asthma. Am J Public Health 102:988–995
Katz AD, Hoyt WT (2014) The influence of multicultural counseling competence and anti-Black prejudice on therapists' outcome expectancies. J Couns Psychol 61:299–305
Green A, Carney D, Pallin D, Ngo L et al (2007) Implicit bias among physicians and its prediction of thrombolysis decisions for black and white patients. J Gen Intern Med 22:1231–1238
Maina IW, Belton TD, Ginzberg S, Singh A, Johnson TJ (2018) A decade of studying implicit racial/ethnic bias in healthcare providers using the implicit association test. Soc Sci Med 199:219–229
Barnato AE, Anthony DL, Skinner J, Gallagher PM, Fisher ES (2007) Racial and ethnic differences in preferences for end-of-life treatment. J Gen Intern Med 24(6):695–701
Blackhall LJ, Frank G, Murphy ST et al (1999) Ethnicity and attitudes towards life sustaining technology. Soc Sci Med 48:1779–1789
Johnston EE, Bogetz J, Saynina O, Chamberlain LJ, Bhatia S, Sanders L (2019) Disparities in inpatient intensity of end-of-life care for complex chronic conditions. Pediatrics 143(5):e20182228
Mack JW, Paulk E, Viswanath K, Prigerson HG (2010) Racial disparities in the outcomes of communication on medical care received near death. Arch Intern Med 170(17):1533–1540
Smith AK, Earle CC, McCarthy EP (2009) Racial and ethnic differences in end-of-life care in fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries with advanced cancer. J Am Geriatr Soc 57:153–158
Parikh K, Berry J, Hall M et al (2017) Racial and ethnic differences in pediatric readmissions for common chronic conditions. J Pediatr 186:158–164
US Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (2020) Healthy People 2020. https://www.healthypeople.gov/2020/about/foundation-health-measures/Disparities. Accessed 3 April 2020
Funding
No external funding was used in performing this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was waved by the Institutional Review Board of Seattle Children’s Hospital for this retrospective administrative data review.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix 1
ICD-9 Codes Included for Cardiomyopathy and Myocarditis
Cardiomyopathy
- 425.0:
-
Endomyocardial fibrosis
- 425.1:
-
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- 425.11:
-
Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
- 425.18:
-
Other hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- 425.2:
-
Obscure cardiomyopathy of Africa
- 425.3:
-
Endocardial fibroelastosis
- 425.4:
-
Other primary cardiomyopathies
- 425.5:
-
Alcoholic cardiomyopathy
- 425.7:
-
Nutritional and metabolic cardiomyopathy
- 425.8:
-
Cardiomyopathy in other diseases classified elsewhere
- 425.9:
-
Secondary cardiomyopathy, unspecified
- 674.5:
-
Peripartum cardiomyopathy
Myocarditis
- 32.82:
-
Diphtheritic myocarditis
- 36.43:
-
Meningococcal myocarditis
- 74.23:
-
Coxsackie myocarditis
- 93.82:
-
Syphilitic myocarditis
- 130.3:
-
Myocarditis due to toxoplasmosis
- 391.2:
-
Acute rheumatic myocarditis
- 420.0:
-
Acute pericarditis in diseases classified elsewhere
- 420.9:
-
Other and unspecified acute pericarditis
- 420.90:
-
Acute pericarditis, unspecified
- 420.91:
-
Acute idiopathic pericarditis
- 420.99:
-
Other acute pericarditis
- 422.0:
-
Acute myocarditis in diseases classified elsewhere
- 422.9:
-
Other and unspecified acute myocarditis
- 422.90:
-
Acute myocarditis, unspecified
- 422.91:
-
Idiopathic myocarditis
- 422.92:
-
Septic myocarditis
- 422.93:
-
Toxic myocarditis
- 422.99:
-
Other acute myocarditis
- 429.0:
-
Myocarditis, unspecified
Appendix 2
ICD-9 Codes Included for Organ Dysfunction
Cardiac Dysfunction
- 458.8:
-
Other specified hypotension
- 458.9:
-
Hypotension, unspecified
- 785.50:
-
Shock, unspecified
- 785.51:
-
Cardiogenic shock
- 785.52:
-
Septic shock
- 785.59:
-
Other shock without mention of trauma
Respiratory Dysfunction
- 518.0:
-
Pulmonary collapse
- 518.81:
-
Acute respiratory failure
- 518.82:
-
Other pulmonary insufficiency, not elsewhere classified
- 786.09:
-
Other respiratory abnormalities
- 799.1:
-
Respiratory arrest
(Also included mechanical ventilation as coded in KID).
Neurologic Dysfunction
- 293.0:
-
Delirium due to conditions classified elsewhere
- 293.1:
-
Subacute delirium
- 293.8:
-
Other specified transient mental disorders due to conditions classified elsewhere
- 293.81:
-
Psychotic disorder with delusions in conditions classified elsewhere
- 293.82:
-
Psychotic disorder with hallucinations in conditions classified elsewhere
- 293.83:
-
Mood disorder in conditions classified elsewhere
- 293.84:
-
Anxiety disorder in conditions classified elsewhere
- 293.89:
-
Other specified transient mental disorders due to conditions classified elsewhere, other
- 293.9:
-
Unspecified transient mental disorder in conditions classified elsewhere
- 348.1:
-
Anoxic brain damage
- 348.3:
-
Encephalopathy, not elsewhere specified
- 348.30:
-
Encephalopathy, unspecified
- 348.31:
-
Metabolic encephalopathy
- 348.39:
-
Other encephalopathy
Hematologic Dysfunction
- 286.6:
-
Defibrination syndrome
- 286.9:
-
Other and unspecified coagulation defects
- 287.4:
-
Secondary thrombocytopenia
- 287.5:
-
Thrombocytopenia, unspecified
Hepatic Dysfunction
- 570:
-
Acute and subacute necrosis of liver
- 573.4:
-
Hepatic infarction
Renal Dysfunction
- 584:
-
Acute kidney failure
- 584.5:
-
Acute kidney failure with lesion of tubular necrosis
- 584.6:
-
Acute kidney failure with lesion of renal cortical necrosis
- 584.7:
-
Acute kidney failure with lesion of renal medullary [papillary] necrosis
- 584.8:
-
Acute kidney failure with other specified pathological lesion in kidney
- 584.9:
-
Acute kidney failure, unspecified
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olsen, J., Tjoeng, Y.L., Friedland-Little, J. et al. Racial Disparities in Hospital Mortality Among Pediatric Cardiomyopathy and Myocarditis Patients. Pediatr Cardiol 42, 59–71 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-020-02454-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-020-02454-4