Abstract
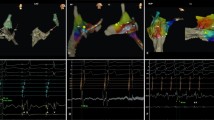
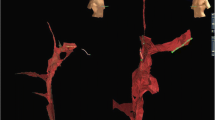
Experience of catheter ablation of pediatric focal atrial tachycardia (FAT) is still limited. There are data which were gathered prior to the introduction of modern 3D mapping and navigation systems into the clinical routine. Accordingly, procedures were associated with significant fluoroscopy and low success rates. The aim of this study was to present clinical and electrophysiological details of catheter ablation of pediatric FAT using modern mapping systems. Since March 2003, 17 consecutive patients <20 years underwent electrophysiological study (EPS) for FAT using the NavX® system (n = 7), the non-contact mapping system (n = 6) or the LocaLisa® system (n = 4), respectively. Radiofrequency was the primary energy source; cryoablation was performed in selected patients with a focus close to the AV node. In 16 patients, a total number of 19 atrial foci (right-sided n = 13, left-sided n = 6) could be targeted. In the remaining patient, FAT was not present/inducible during EPS. On an intention-to-treat basis, acute success was achieved in 14/16 patients (87.5 %) with a median number of 11 (1–31) energy applications. Ablation was unsuccessful in two patients due to an epicardial location of a right atrial focus (n = 1) and a focus close to the His bundle (n = 1), respectively. Median procedure time was 210 (84–332) min, and median fluoroscopy time was 13.1 (4.5–22.5) min. In pediatric patients with FAT, 3D mapping and catheter ablation provided improved clinical quality of care. Catheter ablation may be considered early in the course of treatment of this tachyarrhythmia in symptomatic patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brugada J, Blom N, Sarquella-Brugada G, European Heart Rhythm Association; Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (2013) Pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapy for arrhythmias in the pediatric population: EHRA and AEPC-arrhythmia working group joint consensus statement. Europace 15:1337–1382
Chiladakis JA, Vassilikos VP, Maounis TN, Cokkinos DV, Manolis AS (1997) Successful radiofrequency catheter ablation of automatic atrial tachycardia with regression of the cardiomyopathy picture. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 20:953–959
Cummings RM, Mahle WT, Strieper MJ, Campbell RM, Costello L, Balfour V, Burchfield A, Frias PA (2008) Outcomes following electroanatomic mapping and ablation for the treatment of ectopic atrial tachycardia in the pediatric population. Pediatr Cardiol 29:393–397
Earley MJ, Showkathali R, Alzetani M, Kistler PM, Gupta D, Abrams DJ, Horrocks JA, Harris SJ, Sporton SC, Schilling RJ (2006) Radiofrequency ablation of arrhythmias guided by non-fluoroscopic catheter location: a prospective randomized trial. Eur Heart J 27:1223–1229
Kang KT, Etheridge SP, Kantoch MJ, Tisma-Dupanovic S, Bradley DJ, Balaji S, Hamilton RM, Singh AK, Cannon BC, Schaffer MS, Potts JE, Sanatani S (2014) Current management of focal atrial tachycardia in children: a multicenter experience. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 74:664–670
Knackstedt C, Schauerte P, Kirchhof P (2008) Electro-anatomic mapping systems in arrhythmias. Europace 10(Suppl 3):iii28–iii34
Kugler JD, Danford DA, Houston KA, Felix G, Pediatric Radiofrequency Ablation Registry of the Pediatric Radiofrequency Ablation Registry of the Pediatric Electrophysiology Society (2002) Pediatric radiofrequency catheter ablation registry success, fluoroscopy time, and complication rate for supraventricular tachycardia: comparison of early and recent eras. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 13:336–341
Lee G, Sanders P, Kalman JM (2012) Catheter ablation of atrial arrhythmias: state of the art. Lancet 380:1509–1519
Liew R, Catanchin A, Behr ER, Ward D (2008) Use of non-contact mapping in the treatment of right atrial tachycardias in patients with and without congenital heart disease. Europace 10:972–981
Medi C, Kalman JM, Haqqani H, Vohra JK, Morton JB, Sparks PB, Kistler PM (2009) Tachycardia-mediated cardiomyopathy secondary to focal atrial tachycardia: long-term outcome after catheter ablation. J Am Coll Cardiol 53:1791–1797
Porter MJ, Morton JB, Denman R, Lin AC, Tierney S, Santucci PA, Cai JJ, Madsen N, Wilber DJ (2004) Influence of age and gender on the mechanism of supraventricular tachycardia. Heart Rhythm 1:393–396
Salerno JC, Kertesz NJ, Friedman RA, Fenrich AL Jr (2004) Clinical course of atrial ectopic tachycardia is age-dependent: results and treatment in children <3 or ≥3 years of age. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:438–444
Schilling RJ, Peters NS, Davies DW (1999) Feasibility of a noncontact catheter for endocardial mapping of human ventricular tachycardia. Circulation 99:2543–2552
Schmitt H, Weber S, Schwab JO, Voss RM, Kneller R, Tillmanns H, Waldecker B (2001) Diagnosis and ablation of focal right atrial tachycardia using a new high-resolution, non-contact mapping system. Am J Cardiol 87:1017–1021
Van Hare GF (1999) Supraventricular tachycardia. In: Gilette PC, Garson A (eds) Clinical pediatric arrhythmias, 2nd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 97–120
Van Hare GF, Javitz H, Carmelli D, Saul JP, Tanel RE, Fischbach PS, Kanter RJ, Schaffer M, Dunnigan A, Colan S, Serwer G, Participating Members of the Pediatric Electrophysiology Society (2004) Prospective assessment after pediatric cardiac ablation: recurrence at 1 year after initially successful ablation of supraventricular tachycardia. Heart Rhythm 1:188–196
Walsh EP, Saul JP, Hulse JE, Rhodes LA, Hordof AJ, Mayer JE, Lock JE (1992) Transcatheter ablation of ectopic atrial tachycardia in young patients using radiofrequency current. Circulation 86:1138–1146
Wittkampf FH, Wever EF, Derksen R, Wilde AA, Ramanna H, Hauer RN, Robles de Medina EO (1999) LocaLisa: new technique for real-time 3-dimensional localization of regular intracardiac electrodes. Circulation 99:1312–1317
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dieks, JK., Müller, M.J., Schneider, H.E. et al. Catheter Ablation of Pediatric Focal Atrial Tachycardia: Ten-Year Experience Using Modern Mapping Systems. Pediatr Cardiol 37, 459–464 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-015-1299-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-015-1299-x