Abstract
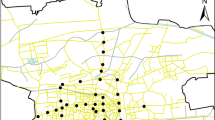
Concentrations and compositions of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in particle size fractions of road dust sampled from contrasting areas of an industrialised city in Korea are reported. The largest amounts of road dust were present in industrial areas, followed by areas subject to heavy traffic, and the lowest amounts were associated with a residential area. The highest concentrations of PAHs were recorded in road dust sampled from the areas with the heaviest traffic (0.45–4.1 μg/g), followed by industrial areas (0.1–3.56 μg/g), with the lowest concentrations associated with a residential area (0.32–1.95 μg/g). PAH concentrations in the fractionated dust from the industrialised areas exhibited an inverse correlation with particle size. Although a similar general pattern was observed in the areas of heavy traffic, some increased concentrations associated with larger particles possibly reflect petrogenic contributions. Particles in road dusts from the residential area were generally smaller than those from the other areas, with PAH composition dominated by pyrogenic sources. PAH compositional profiles, evaluated through diagnostic isomeric ratios, indicate that exhaust emissions, rather than crankcase oils or tire and asphalt abrasion, are the major polluting source.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi K, Tainosho Y (2005) Single particle characterization of size-fractionated road sediments. Appl Geochem 20:849–859
Apeagyei E, Bank MS, Spengler JD (2011) Distribution of heavy metals in road dust along an urban-rural gradient in Massachusetts. Atmos Environ 45:2310–2323
Boonyatumanond R, Murakami M, Wayyatakorn G, Togo A, Takada H (2007) Sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in street dust in a tropical Asian mega-city, Bangkok, Thailand. Sci Total Environ 384:420–432
Brown JN, Peake BM (2006) Sources of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban stormwater runoff. Sci Total Environ 359:145–155
Brown RC, Pierce RH, Rice SA (1985) Hydrocarbon contamination in sediment from urban stormwater runoff. Mar Pollut Bull 16:236–240
Cornelissen G, Gustafsson O, Bucheli TD, Jonker MTO, Koelmans AA, Van Noort PCM (2005) Extensive sorption of organic compounds to black carbon, coal, and kerogen in sediments and soils: mechanisms and consequences for distribution, bioaccumulation, and biodegradation. Environ Sci Technol 39:6881–6895
Dong TTT, Lee BK (2009) Characteristic, toxicity, and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in road dust of Ulsan, Korea. Chemosphere 74:1245–1253
Gyengsangnam-do Provincial Government (GSND) (2006) Annual statistics of average road pavement rate in Gyengsangnam-do: Changwon and Masan city, Korea. Available at http://stat.gsnd.net/jsp/main/main.jsp. Accessed 9 Dec 2006
Hildemann LM, Markowski GR, Cass GR (1991) Chemical composition of emission from urban sources of fine organic aerosol. Environ Sci Technol 25:744–759
Hwang HM, Foster GD (2006) Characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban stormwater runoff flowing into the tidal Anacostia River, Washington, DC, USA. Environ Pollut 140:416–426
International Agency for Research on Cancer (1987) IARC monographs on the evaluation of the carcinogenic risk of chemicals to humans, overall evaluation of carcinogenicity: an updating of IAPC Monographs, vol 1–42. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon
Jiang YF, Wang XT, Wang F, Jia Y, Wu MH, Sheng GY et al (2009) Levels, composition profiles and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soil of Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 75:1112–1118
Kavouras IG, Koutrakis P, Tsapakis M, Lagoudaki E, Stephanou EG, Baer DV (2001) Source apportionment of urban particulate aliphatic and polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) using multivariate methods. Environ Sci Technol 35:2288–2294
Krein A, Schorer M (2000) Road runoff pollution by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and its contribution to river sediments. Water Res 34:4110–4115
Kumata H, Sanada Y, Takada H, Ueno T (2002) Historical trends of N-cyclohexyl-2-benzothiazolamine,2-(4-morpholinyl)benzothiazole, and other anthropogenic contaminants in the urban reservoir sediment core. Environ Sci Technol 34:246–253
Kupiainen K (2007) Road dust from pavement wear and traction sanding. Monogr Boreal Environ Res 26:1–50
Lau SL, Stenstrom MK (2005) Metals and PAHs absorbed to street particles. Water Res 39:4083–4092
Lee BK, Dong TTT (2010) Effects of road characteristics on distribution and toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban road dust of Ulsan, Korea. J Hazard Mater 175:540–550
Lee BC, Shimizu Y, Matsuda T, Matsui S (2005) Characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in different size fractions in deposited road particles (DRPs) from Lake Biwa Area, Japan. Environ Sci Technol 39:7402–7409
MacKenzie MJ, Hunter JV (1979) Source and fates of aromatic compounds in urban stormwater runoff. Environ Sci Technol 13:179–183
Maltby L, Forrow DM, Boxall ABA, Calow P, Betton CI (1995a) The effects of motorway runoff on fresh-water ecosystems. 1. Field-study. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:1079–1092
Maltby L, Forrow DM, Boxall ABA, Calow P, Betton CI (1995b) The effects of motorway runoff on fresh-water ecosystems. 2. Identifying major toxicants. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:1093–1101
Means JC, Wood SG, Hassett JJ, Gschwend PM (1980) Sorption of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons by sediments and soils. Environ Sci Technol 14:1524–1528
Murakami M, Nakajima F, Furumai H (2004) Modelling of runoff behaviour of particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from roads and roofs. Water Res 38:4475–4483
Murakami M, Nakajima F, Furumai H (2005) Size- and density-distributions and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban road dust. Chemosphere 61:783–791
Readman JW, Mantoura RFC, Rhead MM (1984) The physic-chemical speciation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in aquatic systems. Fresenius Z Anal Chem 319:126–131
Rogge WF, Hidemann LM, Mazurek MA, Cass GR (1993) Sources of fine organic aerosol. 3. Road dust, tire debris, and organometallic brake lining dust: Roads as sources and sinks. Environ Sci Technol 27:1892–1904
Sartor JD, Boyd GB, Agardy FJ (1974) Water pollution aspects of street surface contaminants. J Water Pollut Control Fed 46:458–467
Smith DJT, Edelhauser EC, Harrison RM (1995) Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon concentrations in road dust and soil samples collected in the United Kingdom and Pakistan. Environ Technol 16:45–53
Takada H, Onda T, Ogura N (1990) Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban street dusts and their source materials by capillary gas chromatography. Environ Sci Technol 24:1179–1186
Takada H, Onda T, Ogyra N (1991) Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in street dust from the Tokyo Metropolitan Area. Sci Total Environ 107:45–69
Tang L, Tang XY, Zhu YG, Zheng MH, Miao QL (2005) Contamination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban soils in Beijing, China. Environ Int 31:822–828
Traffic Management System Center (TMSC) (2005) Statistics of the traffic volume in the main road. Available at http://www.road.re.kr/tms/cover.asp. Accessed 13 Aug 2005
Youngblood WW, Blumer M (1975) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the environment: homologous series in soils and recent marine sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 39:1303–1314
Yunker MB, Macdonald RW, Vingarzan R, Mitchell RH, Goyette D, Sylvestre S (2002) PAHs in the Fraser River basin: a critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Org Geochem 33:489–515
Zeng EY, Tran K, Young D (2004) Evaluation of potential molecular markers for urban stormwater runoff. Environ Monit Assess 90:23–43
Zhou J, Wang T, Huang Y, Mao T, Zhong N (2005) Size distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban and suburban sites of Beijing, China. Chemosphere 61:792–799
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants-in-aids from Korea Ocean Research and Development Institute (PE98745) and the Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs, Korea (PM56381).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ha, S.Y., Kim, G.B., Yim, U.H. et al. Particle-Size Distribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Urban Road Dust of Masan, Korea. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 63, 189–198 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-012-9765-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-012-9765-4