Abstract
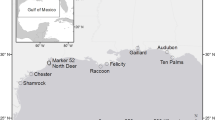
We examined the concentrations of arsenic, cadmium, chromium, lead, manganese, mercury, and selenium in the eggs, leg muscle, and apodeme (carapace musculature) in horseshoe crabs (Limulus polyphemus) from eight places on the New Jersey and Delaware sides of Delaware Bay to determine whether there were locational differences. Although there were locational differences, the differences were not great. Further, contaminant levels were generally low. The levels of contaminants found in horseshoe crabs were well below those known to cause adverse effects in the crabs themselves or in organisms that consume them or their eggs. Contaminant levels have generally declined in the eggs of horseshoe crabs from 1993 to 2001, suggesting that contaminants are not likely to be a problem for secondary consumers or a cause of their decline.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 January 2002/Accepted: 2 June 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burger, J., Dixon, C., Shukla, T. et al. Metals in Horseshoe Crabs from Delaware Bay. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 44, 0036–0042 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-002-2002-9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-002-2002-9