Abstract.
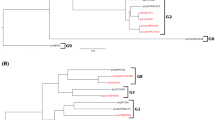
Phytopathogenic Pseudomonas syringae is subdivided into about 50 pathovars due to their conspicuous differentiation with regard to pathogenicity. Based on the results of a phylogenetic analysis of four genes (gyrB, rpoD, hrpL, and hrpS), Sawada et al. (1999) showed that the ancestor of P. syringae had diverged into at least three monophyletic groups during its evolution. Physical maps of the genomes of representative strains of these three groups were constructed, which revealed that each strain had five rrn operons which existed on one circular genome. The fact that the structure and size of genomes vary greatly depending on the pathovar shows that P. syringae genomes are quite rich in plasticity and that they have undergone large-scale genomic rearrangements. Analyses of the codon usage and the GC content at the codon third position, in conjunction with phylogenomic analyses, showed that the gene cluster involved in phaseolotoxin synthesis (argK–tox cluster) expanded its distribution by conducting horizontal transfer onto the genomes of two P. syringae pathovars (pv. actinidiae and pv. phaseolicola) from bacterial species distantly related to P. syringae and that its acquisition was quite recent (i.e., after the ancestor of P. syringae diverged into the respective pathovars). Furthermore, the results of a detailed analysis of argK [an anabolic ornithine carbamoyltransferase (anabolic OCTase) gene], which is present within the argK–tox cluster, revealed the plausible process of generation of an unusual composition of the OCTase genes on the genomes of these two phaseolotoxin-producing pathovars: a catabolic OCTase gene (equivalent to the orthologue of arcB of P. aeruginosa) and an anabolic OCTase gene (argF), which must have been formed by gene duplication, have first been present on the genome of the ancestor of P. syringae; the catabolic OCTase gene has been deleted; the ancestor has diverged into the respective pathovars; the foreign-originated argK–tox cluster has horizontally transferred onto the genomes of pv. actinidiae and pv. phaseolicola; and hence two copies of only the anabolic OCTase genes (argK and argF) came to exist on the genomes of these two pathovars. Thus, the horizontal gene transfer and the genomic rearrangement were proven to have played an important role in the pathogenic differentiation and diversification of P. syringae.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 22 May 2001 / Accepted: 26 September 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sawada, H., Kanaya, S., Tsuda, M. et al. A Phylogenomic Study of the OCTase Genes in Pseudomonas syringae Pathovars: The Horizontal Transfer of the argK–tox Cluster and the Evolutionary History of OCTase Genes on Their Genomes. J Mol Evol 54, 437–457 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-001-0032-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-001-0032-y