Abstract
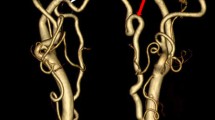
Aneurysms of the cervical vertebral artery (VA) are uncommon; they are often caused by trauma or spontaneous dissection. A fusiform aneurysm without evidence of atherosclerosis or dissection has not been reported previously. A 46-year-old man presented with a pontine infarct. Imaging revealed a fusiform aneurysm of the left VA at the C5–6 level, with occlusion of the basilar artery. Associated minor anomalies included fusion of the vertebral bodies of C5 and C6, cervical rib and platybasia. The left VA arose directly from the aortic arch and entered the transverse foramen at the C4 level. Hyperextension and left lateral flexion of the neck caused kinking of the VA proximal to the aneurysm. Turbulent flow in the aneurysm lumen was noted on angiography.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 9 December 1996 Accepted: 28 May 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, S., Inoue, T., Haga, S. et al. Stroke due to a fusiform aneurysm of the cervical vertebral artery: case report. Neuroradiology 40, 19–22 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050531
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050531