Abstract
Purpose
Micro fractional anisotropy (μFA) is more accurate than conventional fractional anisotropy (FA) for assessing microscopic tissue properties and can overcome limitations related to crossing white matter fibres. We compared μFA and FA for evaluating white matter changes in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD).
Methods
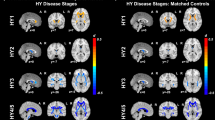
We compared FA and μFA measures between 25 patients with PD and 25 age- and gender-matched healthy controls using tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) analysis. We also examined potential correlations between changes, revealed by conventional FA or μFA, and disease duration or Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS)-III scores.
Results
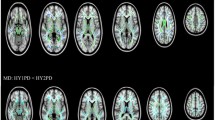
Compared with healthy controls, patients with PD had significantly reduced μFA values, mainly in the anterior corona radiata (ACR). In the PD group, μFA values (primarily those from the ACR) were significantly negatively correlated with UPDRS-III motor scores. No significant changes or correlations with disease duration or UPDRS-III scores with tissue properties were detected using conventional FA.
Conclusion
μFA can evaluate microstructural changes that occur during white matter degeneration in patients with PD and may overcome a key limitation of FA.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fearnley JM, Lees AJ (1991) Ageing and Parkinson’s disease: substantia nigra regional selectivity. Brain 114(Pt 5):2283–2301
Schapira AHV, Chaudhuri KR, Jenner P (2017) Non-motor features of Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 18(7):435–450. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2017.62
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24(2):197–211
Braak H, Bohl JR, Muller CM, Rub U, de Vos RA, Del Tredici K (2006) Stanley Fahn Lecture 2005: the staging procedure for the inclusion body pathology associated with sporadic Parkinson’s disease reconsidered. Mov Disord 21(12):2042–2051. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21065
Kanazawa T, Adachi E, Orimo S, Nakamura A, Mizusawa H, Uchihara T (2012) Pale neurites, premature alpha-synuclein aggregates with centripetal extension from axon collaterals. Brain Pathol 22(1):67–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3639.2011.00509.x
Hattori T, Orimo S, Aoki S, Ito K, Abe O, Amano A, Sato R, Sakai K, Mizusawa H (2012) Cognitive status correlates with white matter alteration in Parkinson’s disease. Hum Brain Mapp 33(3):727–739. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.21245
Kamagata K, Motoi Y, Abe O, Shimoji K, Hori M, Nakanishi A, Sano T, Kuwatsuru R, Aoki S, Hattori N (2012) White matter alteration of the cingulum in Parkinson disease with and without dementia: evaluation by diffusion tensor tract-specific analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33(5):890–895. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A2860
Kamagata K, Motoi Y, Tomiyama H, Abe O, Ito K, Shimoji K, Suzuki M, Hori M, Nakanishi A, Sano T, Kuwatsuru R, Sasai K, Aoki S, Hattori N (2013) Relationship between cognitive impairment and white-matter alteration in Parkinson’s disease with dementia: tract-based spatial statistics and tract-specific analysis. Eur Radiol 23(7):1946–1955. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-013-2775-4
Karagulle Kendi AT, Lehericy S, Luciana M, Ugurbil K, Tuite P (2008) Altered diffusion in the frontal lobe in Parkinson disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29(3):501–505. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0850
Assaf Y, Pasternak O (2008) Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)-based white matter mapping in brain research: a review. J Mol Neurosci 34(1):51–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-007-0029-0
Alexander AL, Lee JE, Lazar M, Field AS (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. Neurotherapeutics 4(3):316–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurt.2007.05.011
Kaden E, Kruggel F, Alexander DC (2016) Quantitative mapping of the per-axon diffusion coefficients in brain white matter. Magn Reson Med 75(4):1752–1763. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.25734
Postuma RB, Berg D, Stern M, Poewe W, Olanow CW, Oertel W, Obeso J, Marek K, Litvan I, Lang AE, Halliday G, Goetz CG, Gasser T, Dubois B, Chan P, Bloem BR, Adler CH, Deuschl G (2015) MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 30(12):1591–1601. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26424
Andersson JL, Sotiropoulos SN (2016) An integrated approach to correction for off-resonance effects and subject movement in diffusion MR imaging. Neuroimage 125:1063–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.10.019
Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LeBihan D (1994) Estimation of the effective self-diffusion tensor from the NMR spin echo. J Magn Reson B 103(3):247–254
Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Smith SM (2012) Fsl. Neuroimage 62(2):782–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.015
Mancall EL, Brock DG, Gray H (2011) Gray’s clinical neuroanatomy: the anatomic basis for clinical neuroscience. Elsevier/Saunders
Braak H, Del Tredici K (2008) Invited Article: nervous system pathology in sporadic Parkinson disease. Neurology 70(20):1916–1925. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000312279.49272.9f
Duncan GW, Firbank MJ, Yarnall AJ, Khoo TK, Brooks DJ, Barker RA, Burn DJ, O’Brien JT (2016) Gray and white matter imaging: a biomarker for cognitive impairment in early Parkinson’s disease? Mov Disord 31(1):103–110. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26312
Shemesh N (2018) Axon and myelin content modulate microscopic fractional anisotropy at short diffusion times in fixed rat spinal cord. Front Phys 6(49). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2018.00049
Nieuwenhuys R, Voogd J, van Huijzen C (2008) The human central nervous system: a synopsis and atlas. Spr Sci Business Media. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-34686-9
Ji GJ, Hu P, Liu TT, Li Y, Chen X, Zhu C, Tian Y, Chen X, Wang K (2018) Functional connectivity of the corticobasal ganglia-thalamocortical network in Parkinson disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis with cross-validation. Radiology 287(3):973–982. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2018172183
Kamagata K, Zalesky A, Hatano T, Di Biase MA, El Samad O, Saiki S, Shimoji K, Kumamaru KK, Kamiya K, Hori M, Hattori N, Aoki S, Pantelis C (2018) Connectome analysis with diffusion MRI in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: evaluation using multi-shell, multi-tissue, constrained spherical deconvolution. Neuroimage Clin 17:518–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2017.11.007
Long Z, Xu Q, Miao HH, Yu Y, Ding MP, Chen H, Liu ZR, Liao W (2017) Thalamocortical dysconnectivity in paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia: combining functional magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion tensor imaging. Mov Disord 32(4):592–600. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26905
Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Jahanshahi M, Krack P, Litvan I, Macias R, Bezard E, Obeso JA (2009) Initial clinical manifestations of Parkinson’s disease: features and pathophysiological mechanisms. Lancet Neurol 8(12):1128–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70293-5
Esmaeeli S, Murphy K, Swords GM, Ibrahim BA, Brown JW, Llano DA (2019) Visual hallucinations, thalamocortical physiology and Lewy body disease: a review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 103:337–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.06.006
Onofrj M, Espay AJ, Bonanni L, Delli Pizzi S, Sensi SL (2019) Hallucinations, somatic-functional disorders of PD-DLB as expressions of thalamic dysfunction. Mov Disord 34(8):1100–1111. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27781
Delli Pizzi S, Franciotti R, Taylor JP, Thomas A, Tartaro A, Onofrj M, Bonanni L (2015) Thalamic involvement in fluctuating cognition in dementia with Lewy bodies: Mag Res Evidences. Cereb Cortex 25(10):3682–3689. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhu220
Delli Pizzi S, Maruotti V, Taylor JP, Franciotti R, Caulo M, Tartaro A, Thomas A, Onofrj M, Bonanni L (2014) Relevance of subcortical visual pathways disruption to visual symptoms in dementia with Lewy bodies. Cortex 59:12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2014.07.003
Delli Pizzi S, Franciotti R, Taylor JP, Esposito R, Tartaro A, Thomas A, Onofrj M, Bonanni L (2015) Structural connectivity is differently altered in dementia with Lewy body and Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 7:208. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2015.00208
Worker A, Blain C, Jarosz J, Chaudhuri KR, Barker GJ, Williams SC, Brown RG, Leigh PN, Dell'Acqua F, Simmons A (2014) Diffusion tensor imaging of Parkinson’s disease, multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy: a tract-based spatial statistics study. PLoS One 9(11):e112638. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0112638
Taylor KI, Sambataro F, Boess F, Bertolino A, Dukart J (2018) Progressive decline in gray and white matter integrity in de novo Parkinson’s disease: an analysis of longitudinal Parkinson progression markers initiative diffusion tensor imaging data. Front Aging Neurosci 10:318. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00318
Mori S, Wakana S, Van Zijl PCM (2005) MRI atlas of human white matter. 1st edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Nilsson M, Szczepankiewicz F, Topgaard D Quantification of microscopic anisotropy with diffusion MRI. Front Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/conf.fnins.2015.88.00004
Alexander AL, Hasan KM, Lazar M, Tsuruda JS, Parker DL (2001) Analysis of partial volume effects in diffusion-tensor MRI. Magn Reson Med 45(5):770–780
Nilsson M, Latt J, Stahlberg F, van Westen D, Hagslatt H (2012) The importance of axonal undulation in diffusion MR measurements: a Monte Carlo simulation study. NMR Biomed 25(5):795–805. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1795
Szczepankiewicz F, Lasic S, van Westen D, Sundgren PC, Englund E, Westin CF, Stahlberg F, Latt J, Topgaard D, Nilsson M (2015) Quantification of microscopic diffusion anisotropy disentangles effects of orientation dispersion from microstructure: applications in healthy volunteers and in brain tumors. Neuroimage 104:241–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.09.057
Lawrenz M, Brassen S, Finsterbusch J (2016) Microscopic diffusion anisotropy in the human brain: age-related changes. Neuroimage 141:313–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.07.031
Lawrenz M, Brassen S, Finsterbusch J (2015) Microscopic diffusion anisotropy in the human brain: reproducibility, normal values, and comparison with the fractional anisotropy. Neuroimage 109:283–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.01.025
Muslimovic D, Post B, Speelman JD, Schmand B (2005) Cognitive profile of patients with newly diagnosed Parkinson disease. Neurology 65(8):1239–1245. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000180516.69442.95
Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Ramani A, Lu H, Kaczynski K (2005) Diffusional kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 53(6):1432–1440. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.20508
Zhang H, Schneider T, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Alexander DC (2012) NODDI: practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. NeuroImage 61(4):1000–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.072
Shemesh N, Jespersen SN, Alexander DC, Cohen Y, Drobnjak I, Dyrby TB, Finsterbusch J, Koch MA, Kuder T, Laun F, Lawrenz M, Lundell H, Mitra PP, Nilsson M, Ozarslan E, Topgaard D, Westin CF (2016) Conventions and nomenclature for double diffusion encoding NMR and MRI. Magn Reson Med 75(1):82–87. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.25901
Kaden E, Kelm ND, Carson RP, Does MD, Alexander DC (2016) Multi-compartment microscopic diffusion imaging. Neuroimage 139:346–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.06.002
Henriques RN, Jespersen SN, Shemesh N (2019) Microscopic anisotropy misestimation in spherical-mean single diffusion encoding MRI. Magn Reson Med 81(5):3245–3261. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.27606
Ianus A, Jespersen SN, Serradas Duarte T, Alexander DC, Drobnjak I, Shemesh N (2018) Accurate estimation of microscopic diffusion anisotropy and its time dependence in the mouse brain. Neuroimage 183:934–949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.08.034
Acknowledgements
We thank Yuki Takenaka and Mana Kuramochi for their research assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by the Brain/MINDS Beyond program from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) under Grant Number JP19dm0307024; JSPS KAKENHI (JP16K19854); a High Technology Research Center Grant from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (MEXT); and the MEXT-Supported Program for the Strategic Research Foundation at Private Universities, 2014–2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in reports involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants before evaluation.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikenouchi, Y., Kamagata, K., Andica, C. et al. Evaluation of white matter microstructure in patients with Parkinson’s disease using microscopic fractional anisotropy. Neuroradiology 62, 197–203 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-019-02301-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-019-02301-1