Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the specific metabolic brain pattern characteristic for Parkinson’s disease (PD): Parkinson’s disease-related pattern (PDRP), using network analysis of [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) brain images in a cohort of Slovenian PD patients.
Methods
Twenty PD patients (age 70.1 ± 7.8 years, Movement Disorder Society Unified Parkinson’s Disease Motor Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS-III) 38.3 ± 12.2; disease duration 4.3 ± 4.1 years) and 20 age-matched normal controls (NCs) underwent FDG-PET brain imaging. An automatic voxel-based scaled subprofile model/principal component analysis (SSM/PCA) was applied to these scans for PDRP-Slovenia identification.
Results
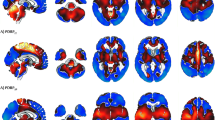
The pattern was characterized by relative hypermetabolism in pallidum, putamen, thalamus, brain stem, and cerebellum associated with hypometabolism in sensorimotor cortex, posterior parietal, occipital, and frontal cortices. The expression of PDRP-Slovenia discriminated PD patients from NCs (p < 0.0001) and correlated positively with patients’ clinical score (MDS-UPDRS-III, p = 0.03). Additionally, its topography agrees well with the original PDRP (p < 0.001) identified in American cohort of PD patients. We validated the PDRP-Slovenia expression on additional FDG-PET scans of 20 PD patients, 20 NCs, and 25 patients with atypical parkinsonism (AP). We confirmed that the expression of PDRP-Slovenia manifests good diagnostic accuracy with specificity and sensitivity of 85–90% at optimal pattern expression cutoff for discrimination of PD patients and NCs and is not expressed in AP.
Conclusion
PDRP-Slovenia proves to be a robust and reproducible functional imaging biomarker independent of patient population. It accurately differentiates PD patients from NCs and AP and correlates well with the clinical measure of PD progression.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:181–184. doi:10.1136/jnnp.55.3.181
Joutsa J, Gardberg M, Röyttä M, Kaasinen V (2014) Diagnostic accuracy of parkinsonism syndromes by general neurologists. Park Relat Disord 20:840–844. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.04.019
Juh R, Kim J, Moon D, Choe B, Suh T (2004) Different metabolic patterns analysis of parkinsonism on the 18F-FDG PET. Eur J Radiol 51:223–233. doi:10.1016/S0720-048X(03)00214-6
Tang CC, Eidelberg D (2010) Abnormal metabolic brain networks in Parkinson’s disease: from blackboard to bedside. Prog Brain Res 184:161–176. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(10)84008-7
Tatsch K (2010) Positron emission tomography in diagnosis and differential diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Neurodegener Dis 7:330–340. doi:10.1159/000314499
Teune LK, Bartels AL, De Jong BM, Willemsen ATM, Eshuis SA, De Vries JJ, Van Oostrom JCH, Leenders KL (2010) Typical cerebral metabolic patterns in neurodegenerative brain diseases. Mov Disord 25:2395–2404. doi:10.1002/mds.23291
Huang C, Tang C, Feigin A, Lesser M, Ma Y, Pourfar M, Dhawan V, Eidelberg D (2007) Changes in network activity with the progression of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 130:1834–1846. doi:10.1093/brain/awm086
Politis M (2014) Neuroimaging in Parkinson disease: from research setting to clinical practice. Nat Rev Neurol 10:708–722. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2014.205
Postuma RB, Berg D, Stern M, Poewe W, Olanow CW, Oertel W, Obeso J, Marek K, Litvan I, Lang AE, Halliday G, Goetz CG, Gasser T, Dubois B, Chan P, Bloem BR, Adler CH, Deuschl G (2015) MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 30:1591–1601. doi:10.1002/mds.26424
Moeller JR, Strother SC (1991) A regional covariance approach to the analysis of functional patterns in positron emission tomographic data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11:A121–A135. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.1991.47
Ma Y, Tang C, Spetsieris PG, Dhawan V, Eidelberg D (2007) Abnormal metabolic network activity in Parkinson’s disease: test-retest reproducibility. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:597–605
Eckert T, Tang C, Ma Y, Brown N, Lin T, Frucht S, Feigin A, Eidelberg D (2008) Abnormal metabolic networks in atypical parkinsonism. Mov Disord 23:727–733. doi:10.1002/mds.21933
Poston KL, Tang CC, Eckert T, Dhawan V, Frucht S, Vonsattel JP, Fahn S, Eidelberg D (2012) Network correlates of disease severity in multiple system atrophy. Neurology 78:1237–1244. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e318250d7fd
Niethammer M, Tang CC, Feigin A, Allen PJ, Heinen L, Hellwig S, Amtage F, Hanspal E, Vonsattel JP, Poston KL, Meyer PT, Leenders KL, Eidelberg D (2014) A disease-specific metabolic brain network associated with corticobasal degeneration. Brain 137:3036–3046. doi:10.1093/brain/awu256
Spetsieris PG, Eidelberg D (2011) Scaled subprofile modeling of resting state imaging data in Parkinson’s disease: methodological issues. NeuroImage 54:2899–2914. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.10.025
Tang CC, Poston KL, Eckert T, Feigin A, Frucht S, Gudesblatt M, Dhawan V, Lesser M, Vonsattel J-P, Fahn S, Eidelberg D (2010) Differential diagnosis of parkinsonism: a metabolic imaging study using pattern analysis. Lancet Neurol 9:149–158. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70002-8
Tripathi M, Tang CC, Feigin A, De Lucia I, Nazem A, Dhawan V, Eidelberg D (2016) Automated differential diagnosis of early parkinsonism using metabolic brain networks: a validation study. J Nucl Med 57:60–66. doi:10.2967/jnumed.115.161992
Eidelberg D (2009) Metabolic brain networks in neurodegenerative disorders: a functional imaging approach. Trends Neurosci 32:548–557. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2009.06.003
Wu P, Wang J, Peng S, Ma Y, Zhang H, Guan Y, Zuo C (2013) Metabolic brain network in the Chinese patients with Parkinson’s disease based on 18F-FDG PET imaging. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 19:622–627. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2013.02.013
Teune LK, Renken RJ, Mudali D, De Jong BM, Dierckx RA, Roerdink JBTM, Leenders KL (2013) Validation of parkinsonian disease-related metabolic brain patterns. Mov Disord 28:547–551. doi:10.1002/mds.25361
Holtbernd F, Ma Y, Peng S, Schwartz F, Timmermann L, Kracht L, Fink GR, Tang CC, Eidelberg D, Eggers C (2015) Dopaminergic correlates of metabolic network activity in Parkinson’s disease. Hum Brain Mapp 36:3575–3585. doi:10.1002/hbm.22863
Poston KL, Eidelberg D (2009) Network biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of movement disorders. Neurobiol Dis 35:141–147. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2008.09.026
Gibb WR, Lees AJ (1988) Occasional review: the relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:745–752. doi:10.1136/jnnp.51.6.745
Feigin A, Fukuda M, Dhawan V, Przedborski S, Jackson-Lewis V, Mentis MJ, Moeller JR, Eidelberg D (2001) Metabolic correlates of levodopa response in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 57:2083–2088. doi:10.1212/WNL.57.11.2083
Moeller JR, Nakamura T, Mentis MJ, Dhawan V, Spetsieres P, Antonini A, Missimer J, Leenders KL, Eidelberg D (1999) Reproducibility of regional metabolic covariance patterns: comparison of four populations. J Nucl Med 40:1264–1269. doi:10.1016/B978-012161340-2/50039-1
Ma Y, Huang C, Dyke JP, Pan H, Alsop D, Feigin A, Eidelberg D (2010) Parkinson’s disease spatial covariance pattern: noninvasive quantification with perfusion MRI. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:505–509. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2009.256
Moeller JR, Ishikawa T, Dhawan V, Spetsieris P, Mandel F, Alexander GE, Grady C, Pietrini P, Eidelberg D (1996) The metabolic topography of normal aging. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:385–398. doi:10.1097/00004647-199605000-00005
Peng S, Ma Y, Spetsieris PG, Mattis P, Feigin A, Dhawan V, Eidelberg D (2014) Characterization of disease-related covariance topographies with SSMPCA toolbox: effects of spatial normalization and PET scanners. Hum Brain Mapp 35:1801–1814. doi:10.1002/hbm.22295
Eckert T, Van Laere K, Tang C, Lewis DE, Edwards C, Santens P, Eidelberg D (2007) Quantification of Parkinson’s disease-related network expression with ECD SPECT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 34:496–501. doi:10.1007/s00259-006-0261-9
Holtbernd F, Gagnon J-F, Postuma RB, Ma Y, Tang CC, Feigin A, Dhawan V, Vendette M, Soucy J-P, Eidelberg D, Montplaisir J (2014) Abnormal metabolic network activity in REM sleep behavior disorder. Neurology 82:620–627. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000000130
Wu P, Yu H, Peng S, Dauvilliers Y, Wang J, Ge J, Zhang H, Eidelberg D, Ma Y, Zuo C (2014) Consistent abnormalities in metabolic network activity in idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder. Brain 137:3122–3128. doi:10.1093/brain/awu290
Ko JH, Spetsieris P, Ma Y, Dhawan V, Eidelberg D (2014) Quantifying significance of topographical similarities of disease-related brain metabolic patterns. PLoS One 9:e88119. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0088119
Ma Y, Peng S, Spetsieris PG, Sossi V, Eidelberg D, Doudet DJ (2012) Abnormal metabolic brain networks in a nonhuman primate model of parkinsonism. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:633–642. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2011.166
Peng S, Ma Y, Flores J, Cornfeldt M, Mitrovic B, Eidelberg D, Doudet DJ (2016) Modulation of abnormal metabolic brain networks by experimental therapies in a nonhuman primate model of Parkinson’s disease: an application to human retinal pigment epithelial (hRPE) cell implantation. J Nucl Med 57:1591–1598
Borghammer P, Hansen SB, Eggers C, Chakravarty M, Vang K, Aanerud J, Hilker R, Heiss WD, Rodell A, Munk OL, Keator D, Gjedde A (2012) Glucose metabolism in small subcortical structures in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand 125:303–310. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2011.01556.x
Eggers C, Hilker R, Burghaus L, Schumacher B, Heiss WD (2009) High resolution positron emission tomography demonstrates basal ganglia dysfunction in early Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 276:27–30. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2008.08.029
Mitchell IJ, Clarke CE, Boyce S, Robertson RG, Peggs D, Sambrook MA, Crossman AR (1989) Neural mechanisms underlying parkinsonian symptoms based upon regional uptake of 2-deoxyglucose in monkeys exposed to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Neuroscience 32:213–226
Guigoni C, Li Q, Aubert I, Dovero S, Bioulac BH, Bloch B, Crossman AR, Gross CE, Bezard E (2005) Involvement of sensorimotor, limbic, and associative basal ganglia domains in L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine-induced dyskinesia. J Neurosci 25:2102–2107
Carlson JD, Pearlstein RD, Buchholz J, Iacono RP, Maeda G (1999) Regional metabolic changes in the pedunculopontine nucleus of unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine Parkinson’s model rats. Brain Res 828:12–19
Goetz CG, Stebbins GT, Tilley BC (2012) Calibration of unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale scores to Movement Disorder Society-unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale scores. Mov Disord 27:1239–1242. doi:10.1002/mds.25122
Wichmann T, DeLong MR (2007) Anatomy and physiology of the basal ganglia: relevance to Parkinson’s disease and related disorders. Handb Clin Neurol 83:1–18. doi:10.1016/S0072-9752(07)83001-6
Melzer TR, Watts R, MacAskill MR, Pearson JF, Rüeger S, Pitcher TL, Livingston L, Graham C, Keenan R, Shankaranarayanan A, Alsop DC, Dalrymple-Alford JC, Anderson TJ (2011) Arterial spin labelling reveals an abnormal cerebral perfusion pattern in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 134:845–855. doi:10.1093/brain/awq377
Asllani I, Habeck C, Scarmeas N, Borogovac A, Brown TR, Stern Y (2008) Multivariate and univariate analysis of continuous arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI in Alzheimer’s disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:725–736. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600570
Wu T, Ma Y, Zheng Z, Peng S, Wu X, Eidelberg D, Chan P (2015) Parkinson’s disease-related spatial covariance pattern identified with resting-state functional MRI. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 35:1764–1770. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2015.118
Bergfield KL, Hanson KD, Chen K, Teipel SJ, Hampel H, Rapoport SI, Moeller JR, Alexander GE (2010) Age-related networks of regional covariance in MRI gray matter: reproducible multivariate patterns in healthy aging. NeuroImage 49:1750–1759. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.09.051
Brickman AM, Habeck C, Ramos MA, Scarmeas N, Stern Y (2008) A forward application of age associated gray and white matter networks. Hum Brain Mapp 29:1139–1146. doi:10.1002/hbm.20452
Alexander GE, Chen K, Aschenbrenner M, Merkley TL, Santerre-Lemmon LE, Shamy JL, Skaggs WE, Buonocore MH, Rapp PR, Barnes CA (2008) Age-related regional network of magnetic resonance imaging gray matter in the rhesus macaque. J Neurosci 28:2710–2718. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1852-07.2008
M. Niethammer, A. Feigin, D. Eidelberg (2012) Functional neuroimaging in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2 doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a009274
Dickson DW, Fujishiro H, Orr C, DelleDonne A, Josephs KA, Frigerio R, Burnett M, Parisi JE, Klos KJ, Ahlskog JE (2009) Neuropathology of non-motor features of Parkinson disease. Park Relat Disord 15:S1–S5. doi:10.1016/S1353-8020(09)70769-2
Pletnikova O, West N, Lee MK, Rudow GL, Skolasky RL, Dawson TM, Marsh L, Troncoso JC (2005) Abeta deposition is associated with enhanced cortical alpha-synuclein lesions in Lewy body diseases. Neurobiol Aging 26:1183–1192. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.10.006
Hilker R, Thomas AV, Klein JC, Weisenbach S, Kalbe E, Burghaus L, Jacobs AH, Herholz K, Heiss WD (2005) Dementia in Parkinson disease: functional imaging of cholinergic and dopaminergic pathways. Neurology 65:1716–1722. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000191154.78131.f6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by the Slovenian Research Agency (L3-4255). The work of YM, SP, VD and DE was supported by the NIH Morris K Udall Center of Excellence for Parkinson’s Disease Research (P50 NS071675).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Slovenian Medical Ethics Committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomše, P., Jensterle, L., Grmek, M. et al. Abnormal metabolic brain network associated with Parkinson’s disease: replication on a new European sample. Neuroradiology 59, 507–515 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1821-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1821-3