Abstract
Introduction
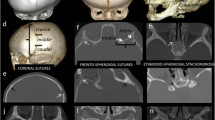
This study aims to identify the premature synostosis of “major” and “minor” sutures of the four “sutural arches” of the skull and to perform a morphometric analysis in children with syndromic craniosynostosis in order to evaluate changes in the skull base linked with premature suture synostosis.
Methods
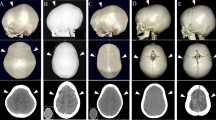
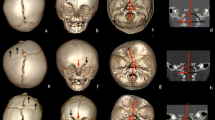
We reviewed multiplanar high-resolution CT images, implemented with 3D reconstructions, from 18 patients with complex syndromic craniosynostosis and compared them with 18 age-matched healthy subjects. We assessed the calvarial sutures and their extension to the skull base, and then we correlated specific types of synostosis with the size, shape and symmetry of the cranial fossae.
Results
We found a marked asymmetry of the skull base growth in all patients. The synostotic involvement around the coronal ring caused a reduction in the growth of the anterior and middle fossae. The size of the posterior cranial fossa was related not only to “major” but also to “minor” suture synostosis of the lambdoid and parieto-squamosal arches.
Conclusion
Changes in the skull base and craniofacial axis symmetry are due to structural and functional relationships between “major” and “minor” skull sutures, suggesting a structural and functional relationship between the neurocranium and basicranium.
The early recognition of prematurely closed skull base sutures may help clinicians and neurosurgeons to establish correct therapeutic approaches.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ursitti F, Fadda T, Papetti L, Pagnoni M, Nicita F, Iannetti G, Spalice A (2011) Evaluation and management of nonsyndromic craniosynostosis. Acta Paediatr 100(9):1185–1194. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.2011.02299.x
Reardon W (2000) Craniosynostosis. Diagnosis, evaluation and management. J Med Genet 37(9):727
Delashaw JB, Persing JA, Broaddus WC, Jane JA (1989) Cranial vault growth in craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg 70(2):159–165. doi:10.3171/jns.1989.70.2.0159
Di Rocco F, Arnaud E, Renier D (2009) Evolution in the frequency of nonsyndromic craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg Pediatr 4(1):21–25. doi:10.3171/2009.3.PEDS08355
Nagaraja S, Anslow P, Winter B (2013) Craniosynostosis. Clin Radiol 68(3):284–292. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2012.07.005
Kirmi O, Lo SJ, Johnson D, Anslow P (2009) Craniosynostosis: a radiological and surgical perspective. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 30(6):492–512
Branson HM, Shroff MM (2011) Craniosynostosis and 3-dimensional computed tomography. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 32(6):569–577. doi:10.1053/j.sult.2011.07.002
de Jong T, Maliepaard M, Bannink N, Raat H, Mathijssen IM (2012) Health-related problems and quality of life in patients with syndromic and complex craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 28(6):879–882. doi:10.1007/s00381-012-1681-4
Furuya Y, Edwards MS, Alpers CE, Tress BM, Norman D, Ousterhout DK (1984) Computerized tomography of cranial sutures. Part 2: abnormalities of sutures and skull deformity in craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg 61(1):59–70. doi:10.3171/jns.1984.61.1.0059
Schweitzer T, Bohm H, Meyer-Marcotty P, Collmann H, Ernestus RI, Krauss J (2012) Avoiding CT scans in children with single-suture craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 28(7):1077–1082. doi:10.1007/s00381-012-1721-0
de Ribaupierre S, Czorny A, Pittet B, Jacques B, Rilliet B (2007) Frontosphenoidal synostosis: a rare cause of unilateral anterior plagiocephaly. Childs Nerv Syst 23(12):1431–1438. doi:10.1007/s00381-007-0469-4
Dundulis JA, Becker DB, Govier DP, Marsh JL, Kane AA (2004) Coronal ring involvement in patients treated for unilateral coronal craniosynostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 114(7):1695–1703
Captier G, Cristol R, Montoya P, Prudhomme M, Godlewski G (2003) Prenatal organization and morphogenesis of the sphenofrontal suture in humans. Cells Tissues Organs 175(2):98–104. doi:10.1159/000073753
Calandrelli R, D'Apolito G, Gaudino S, Sciandra MC, Caldarelli M, Colosimo C (2014) Identification of skull base sutures and craniofacial anomalies in children with craniosynostosis: utility of multidetector CT. Radiol Med. doi:10.1007/s11547-014-0387-y
Monteforte F, Giannoni M (2013) Atlante TC neurocranio e splancnocranio : anatomia e varianti. Piccin, Padova
Cendekiawan T, Wong RW, Rabie ABM (2010) Relationships between cranial base synchondroses and craniofacial development: a review. Open Anat J 2:67–75
Madeline LA, Elster AD (1995) Suture closure in the human chondrocranium: CT assessment. Radiology 196(3):747–756. doi:10.1148/radiology.196.3.7644639
Bassed RB, Briggs C, Drummer OH (2010) Analysis of time of closure of the spheno-occipital synchondrosis using computed tomography. Forensic Sci Int 200(1–3):161–164. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2010.04.009
Brenner DJ, Hall EJ (2007) Computed tomography–—an increasing source of radiation exposure. N Engl J Med 357(22):2277–2284. doi:10.1056/NEJMra072149
Medina LS, Richardson RR, Crone K (2002) Children with suspected craniosynostosis: a cost-effectiveness analysis of diagnostic strategies. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179(1):215–221
Rapalino O, Kamalian S, Payabvash S, Souza LC, Zhang D, Mukta J, Sahani DV, Lev MH, Pomerantz SR (2012) Cranial CT with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction: improved image quality with concomitant radiation dose reduction. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33(4):609–615. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2826
Captier G, Leboucq N, Bigorre M, Canovas F, Bonnel F, Bonnafe A, Montoya P (2003) Plagiocephaly: morphometry of skull base asymmetry. Surg Radiol Anat 25(3–4):226–233. doi:10.1007/s00276-003-0118-x
Slater BJ, Lenton KA, Kwan MD, Gupta DM, Wan DC, Longaker MT (2008) Cranial sutures: a brief review. Plast Reconstr Surg 121(4):170e–178e. doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000304441.99483.97
Kotrikova B, Krempien R, Freier K, Muhling J (2007) Diagnostic imaging in the management of craniosynostoses. Eur Radiol 17(8):1968–1978. doi:10.1007/s00330-006-0520-y
Tartaro A, Larici AR, Antonucci D, Merlino B, Colosimo C, Bonomo L (1998) Optimization and diagnostic accuracy of computerized tomography with tridimensional spiral technique in the study of craniostenosis. Radiol Med 96(1–2):10–17
Cohen SR, Pryor L, Mittermiller PA, Meltzer HS, Levy ML, Broder KW, Ozgur BM (2008) Nonsyndromic craniosynostosis: current treatment options. Plast Surg Nurs 28(2):79–91. doi:10.1097/01.PSN.0000324781.80590.f1
Blount JP, Louis RG Jr, Tubbs RS, Grant JH (2007) Pansynostosis: a review. Childs Nerv Syst 23(10):1103–1109. doi:10.1007/s00381-007-0362-1
Bristol RE, Krieger MD, McComb JG (2011) Normally shaped heads with no sutures, normally shaped heads with abnormal sutures, and abnormally shaped heads with normal sutures. J Craniofac Surg 22(1):173–177. doi:10.1097/SCS.0b013e3181f752c2
Cedzich C, Farmand M (2003) Diagnosis and therapy of syndromic and non-syndromic craniosynostosis. HNO 51(3):198–208. doi:10.1007/s00106-002-0799-1
Sgouros S, Goldin JH, Hockley AD, Wake MJ (1996) Posterior skull surgery in craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 12(11):727–733
Cinalli G, Chumas P, Arnaud E, Sainte-Rose C, Renier D (1998) Occipital remodeling and suboccipital decompression in severe craniosynostosis associated with tonsillar herniation. Neurosurgery 42(1):66–71, discussion 71-63
Tamburrini G, Caldarelli M, Massimi L, Gasparini G, Pelo S, Di Rocco C (2012) Complex craniosynostoses: a review of the prominent clinical features and the related management strategies. Childs Nerv Syst 28(9):1511–1523. doi:10.1007/s00381-012-1819-4
Ethical standards and patient consent
We declare that all human studies have been approved by the local ethics committee and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. We declare that all patients gave informed consent prior to inclusion in this study.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calandrelli, R., D’Apolito, G., Gaudino, S. et al. Radiological assessment of skull base changes in children with syndromic craniosynostosis: role of “minor” sutures. Neuroradiology 56, 865–875 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-014-1392-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-014-1392-5