Abstract
Introduction
The most significant factors leading to restenosis are yet to be described in the literature. The purpose of our study was to identify the incidence of restenosis in our patients with carotid artery stenting (CAS) for carotid atherosclerotic disease and to identify risk factors that are significantly responsible or related to the restenosis.
Methods
In this retrospective analysis of patients who underwent CAS for atherosclerotic disease between years 2002 and 2006, we studied various demographic, clinical, and medical factors, plaque characteristics, and technical aspects of CAS. All patients were followed up with carotid Doppler ultrasound at baseline (after 2 to 4 weeks of CAS) and then with Doppler ultrasound and clinically for various intervals of time. The restenosis was classified based on carotid Doppler ultrasound results. Clinically, restenosis was classified as symptomatic or asymptomatic. Pearson correlation coefficient was used to assess the statistical correlation of the different factors with the incidence of restenosis.
Results
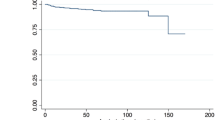
We had a total of 105 patients, with a total of 204.6 patient-year follow-up (mean, 1.95 years; range, 0–7.3 years). The overall incidence of restenosis was 26.7 % (n = 28): mild, 7.6 % (n = 8); moderate, 10.5 % (asymptomatic, 11; symptomatic, 0); and severe, 8.6 % (asymptomatic, 5; symptomatic, 4). Overall, 14.3 % (n = 4) patients with restenosis were symptomatic and 7.1 % (n = 2) underwent retreatment. Post-stenting residual stenosis greater than either 30 % (p = 0.016) or 50 % (p = 0.05) were significant for long-term restenosis. Plaques longer than 20 mm were significantly related to restenosis (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
The most important factor to explain restenosis was the immediate post-CAS residual stenosis and length of the plaque.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biller J, Feinberg WM, Castaldo JE, Whittemore AD, Harbaugh RE, Dempsey RJ et al (1998) Guidelines for carotid endarterectomy: a statement for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the Stroke Council, Am Heart Association. Stroke 29:554–562
Gupta A, Bhatia A, Ahuja A, Shalev Y, Bajwa T (2000) Carotid stenting in patients older than 65 years with inoperable carotid artery disease: a single-center experience. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 50:1–8
Paniagua D, Howell M, Strickman N, Velasco J, Dougherty K, Skolkin M et al (2001) Outcomes following extracranial carotid artery stenting in high-risk patients. J Invasive Cardiol 13:375–381
Hobson RW, Lal BK, Chakhtoura E, Goldstein J, Haser PB, Kubicka R et al (2003) Carotid artery stenting: analysis of data for 105 patients at high risk. J Vasc Surg 37:1234–1239
Maleux G, Bernaerts P, Thijs V, Vaninbroukx J, Daenens K, Fourneau I et al (2003) Extracranial carotid artery stenting in surgically high-risk patients using the Carotid Wallstent endoprosthesis: midterm clinical and ultrasound follow-up results. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 26:340–346
Brott TG, Hobson RW 2nd, Howard G, Roubin GS, Clark WM, Brooks W et al (2010) CREST Investigators. Stenting versus endarterectomy for treatment of carotid-artery stenosis. N Engl J Med 363:11–23
Frericks H, Kievit J, van Baalen JM, van Bockel JH (1998) Carotid recurrent stenosis and risk of ipsilateral stroke: a systematic review of the literature. Stroke 29:244–250
Moore WS, Kempczinski RF, Nelson JJ, Toole JF (1998) Recurrent carotid stenosis: results of the Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Study. Stroke 29:2018–2025
Christiaans MH, Ernst JM, Suttorp MJ, van den Berg JC, Overtoom TT, Kelder JC et al (2003) Restenosis after carotid angioplasty and stenting: a follow-up study with duplex ultrasonography. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 26:141–144
Khan MA, Liu MW, Chio FL, Roubin GS, Iyer SS, Vitek JJ (2003) Predictors of restenosis after successful carotid artery stenting. Am J Cardiol 92:895–897
Berkefeld J, Turowski B, Dietz A, Lanfermann H, Sitzer M, Schmitz-Rixen T et al (2002) Recanalization results after carotid stent placement. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:113–120
Chakhtoura EY, Hobson RW, Goldstein J, Simonian GT, Lal BK, Haser B et al (2001) In-stent restenosis after carotid angioplasty-stenting: incidence and management. J Vasc Surg 33:220–225
Setacci C, Pula G, Baldi I, de Donato G, Setacci F, Cappelli A et al (2003) Determinants of in-stent restenosis after carotid angioplasty: a case–control study. J Endovasc Ther 10:1031–1038
Willfort-Ehringer A, Ahmadi R, Gschwandtner ME, Haumer M, Lang W, Minar E (2002) Single-center experience with carotid stent restenosis. J Endovasc Ther 9:299–307
Gröschel K, Riecker A, Schulz JB, Ernemann U, Kastrup A (2005) Systematic review of early recurrent stenosis after carotid angioplasty and stenting. Stroke 36:367–373
Skelly CL, Gallagher K, Fairman RM, Carpenter JP, Velazquez OC, Parmer SS et al (2006) Risk factors for restenosis after carotid artery angioplasty and stenting. J Vasc Surg 44:1010–1015
Younis GA, Gupta K, Mortazavi A, Strickman NE, Krajcer Z, Perin E et al (2007) Predictors of carotid stent restenosis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 69:673–682
Van Laanen J, Hendriks JM, Van Sambeek MR (2008) Factors influencing restenosis after carotid artery stenting. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 49:743–747
Shin SH, Stout CL, Richardson AI, DeMasi RJ, Shah RM, Panneton JM (2009) Carotid angioplasty and stenting in anatomically high-risk patients: safe and durable except for radiation-induced stenosis. J Vasc Surg 50:762–767, discussion 767–8
Eskandari MK, Usman AA, Garcia-Toca M, Matsumura JS, Kibbe MR, Morasch MD et al (2010) Eight-year institutional review of carotid artery stenting. J Vasc Surg 51:1145–1151
Lal BK, Hobson RW, Tofighi B, Kapadia I, Cuadra S et al (2008) Duplex ultrasound velocity criteria for the stented carotid artery. J Vasc Surg 47:63–73
Silver FL, Mackey A, Clark WM, Brooks W, Timaran CH, Chiu D, Goldstein LB, Meschia JF, Ferguson RD, Moore WS, Howard G, Brott TG (2011) CREST Investigators. Safety of stenting and endarterectomy by symptomatic status in the Carotid Revascularization Endarterectomy Versus Stenting Trial (CREST). Stroke 42(3):675–680
Willfort-Ehringer A, Ahmadi R, Gschwandtner ME, Haumer A, Heinz G, Lang W et al (2003) Healing of carotid stents: a prospective duplex ultrasound study. J Endovasc Ther 10:636–642
Toma N, Matsushima S, Murao K, Kawaguchi K, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Yoshida T et al (2003) Histopathological findings in a human carotid artery after stent implantation. Case report. J Neurosurg 98:199–204
Lattimer CR, Burnand KG (1997) Recurrent carotid stenosis after carotid endarterectomy. Br J Surg 84:1206–1219
van den Bouwhuijsen QJ, Vernooij MW, Hofman A, Krestin GP, van der Lugt A, Witteman JC (2012) Determinants of magnetic resonance imaging detected carotid plaque components: the Rotterdam Study. Eur Heart J 33:221–229
Tartari S, Rizzati R, Righi R, Deledda A, Capello K, Soverini R et al (2011) High-resolution MRI of carotid plaque with a neurovascular coil and contrast-enhanced MR angiography: one-stop shopping for the comprehensive assessment of carotid atherosclerosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196:1164–1171
Pierce DS, Rosero EB, Modrall JG, Adams-Huet B, Valentine RJ, Clagett GP et al (2009) Open-cell versus closed-cell stent design differences in blood flow velocities after carotid stenting. J Vasc Surg 49:602–606, discussion 606
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jai Jai Shiva Shankar and Jingwen Zhang are joint first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shankar, J.J.S., Zhang, J., dos Santos, M. et al. Factors affecting long-term restenosis after carotid stenting for carotid atherosclerotic disease. Neuroradiology 54, 1347–1353 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1031-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1031-y