Abstract
Introduction
Giant cavernous malformations (GCM) are very large, low-flow vascular malformations, which usually have atypical imaging features and are commonly misdiagnosed preoperatively as neoplasms or vascular malformations. These lesions have mostly been reported in children. As cavernomas show different features in children compared to adults, we evaluated the imaging features of pediatric GCMs in order to help in the preoperative diagnosis of these malformations.
Methods
Brain MR studies of nine children (mean age of 4 years; 8 months–9 years) with biopsy-proven GCM were retrospectively evaluated. We defined GCMs as cavernomas of ≥4 cm. Lesions were evaluated regarding their size, location, signal characteristics, general appearance (uni/multilocular) as well as regarding the presence of mass effect, edema, and fluid–fluid levels and were classified according to the Mottolese classification of pediatric cavernomas.
Results
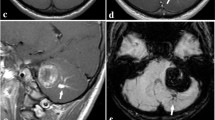
Lesion locations were parietal (n = 5), frontal (n = 2), temporal, and intraventricular. Seven lesions were in the periventricular region (with five in the periatrial region). Six patients had T1 hyperintense multilobulated lesions with “bubbles of blood” appearance and three patients had heterogeneous lesions with reticular core. All lesions had mass effect, edema (marked in four cases), and peripheral hemosiderin rim. Fluid–fluid levels were also common (n = 7). Most of our lesions (six of nine) were classified as type IIIA, two as type IIIC, and one as type IA.
Conclusion
In children, a GCM should be considered in case of very large hemorrhagic intra-axial mass with “bubbles of blood” multicystic appearance, surrounding hemosiderin ring, fluid–fluid levels, and accompanying edema–mass effect, especially in the periatrial location.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raychaudhuri R, Batjer HH, Awad IA (2005) Intracranial cavernous angioma: a practical review of clinical and biological aspects. Surg Neurol 63(4):319–328. doi:10.1016/j.surneu.2004.05.032
Moriarity JL, Clatterbuck RE, Rigamonti D (1999) The natural history of cavernous malformations. Neurosurg Clin N Am 10(3):411–417
Rigamonti D, Hadley MN, Drayer BP, Johnson PC, Hoenig-Rigamonti K, Knight JT, Spetzler RF (1988) Cerebral cavernous malformations. Incidence and familial occurrence. N Engl J Med 319(6):343–347
Robinson JR, Awad IA, Little JR (1991) Natural history of the cavernous angioma. J Neurosurg 75(5):709–714. doi:10.3171/jns.1991.75.5.0709
Mottolese C, Hermier M, Stan H, Jouvet A, Saint-Pierre G, Froment JC, Bret P, Lapras C (2001) Central nervous system cavernomas in the pediatric age group. Neurosurg Rev 24(2–3):55–71, discussion 72–53
Acciarri N, Galassi E, Giulioni M, Pozzati E, Grasso V, Palandri G, Badaloni F, Zucchelli M, Calbucci F (2009) Cavernous malformations of the central nervous system in the pediatric age group. Pediatr Neurosurg 45(2):81–104. doi:10.1159/000209283
Clatterbuck RE, Moriarity JL, Elmaci I, Lee RR, Breiter SN, Rigamonti D (2000) Dynamic nature of cavernous malformations: a prospective magnetic resonance imaging study with volumetric analysis. J Neurosurg 93(6):981–986. doi:10.3171/jns.2000.93.6.0981
Kim DS, Park YG, Choi JU, Chung SS, Lee KC (1997) An analysis of the natural history of cavernous malformations. Surg Neurol 48(1):9–17. doi:S0090301996004259, discussion 17–18
Tenti L (1954) Clinicoradiological observations on a case of giant cavernous cerebral angioma. Sist Nerv 6(1):19–27
Khosla VK, Banerjee AK, Mathuriya SN, Mehta S (1984) Giant cystic cavernoma in a child. Case report. J Neurosurg 60(6):1297–1299. doi:10.3171/jns.1984.60.6.1297
Kawagishi J, Suzuki M, Kayama T, Yoshimoto T (1993) Huge multilobular cavernous angioma in an infant: case report. Neurosurgery 32(6):1028–1030, discussion 1030–1021
Zabramski JM, Wascher TM, Spetzler RF, Johnson B, Golfinos J, Drayer BP, Brown B, Rigamonti D, Brown G (1994) The natural history of familial cavernous malformations: results of an ongoing study. J Neurosurg 80(3):422–432. doi:10.3171/jns.1994.80.3.0422
Brumblay HG, Khoshyomn S, Tranmer BI, Braff SP (2001) Giant cavernous angioma. Pediatr Neurosurg 35(6):336. doi:pne35336
Chicani CF, Miller NR, Tamargo RJ (2003) Giant cavernous malformation of the occipital lobe. J Neuroophthalmol 23(2):151–153
Thiex R, Kruger R, Friese S, Gronewaller E, Kuker W (2003) Giant cavernoma of the brain stem: value of delayed MR imaging after contrast injection. Eur Radiol 13(Suppl 4):L219–L225
Lawton MT, Vates GE, Quinones-Hinojosa A, McDonald WC, Marchuk DA, Young WL (2004) Giant infiltrative cavernous malformation: clinical presentation, intervention, and genetic analysis: case report. Neurosurgery 55(4):979–980
Gelal F, Feran H, Rezanko T, Vidinli BD (2005) Giant cavernous angioma of the temporal lobe: a case report and review of the literature. Acta Radiol 46(3):310–313
Corapcioglu F, Akansel G, Gonullu E, Yildiz K, Etus V (2006) Fatal giant pediatric intracranial cavernous angioma. Turk J Pediatr 48(1):89–92
Kim YJ, Kim JE, Kim NR, Kim HS (2007) Imaging findings of giant cavernous malformation with a focal infiltrative pattern. Pediatr Radiol 37(10):1039–1042. doi:10.1007/s00247-007-0553-7
van Lindert EJ, Tan TC, Grotenhuis JA, Wesseling P (2007) Giant cavernous hemangiomas: report of three cases. Neurosurg Rev 30(1):83–92. doi:10.1007/s10143-006-0042-8, discussion 92
Gezen F, Karatas A, Is M, Yildirim U, Aytekin H (2008) Giant cavernous haemangioma in an infant. Br J Neurosurg 22(6):787–789. doi:10.1080/02688690802108780
Kan P, Tubay M, Osborn A, Blaser S, Couldwell WT (2008) Radiographic features of tumefactive giant cavernous angiomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 150(1):49–55. doi:10.1007/s00701-007-1455-z, discussion 55
Son DW, Lee SW, Choi CH (2008) Giant cavernous malformation: a case report and review of the literature. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 43(4):198–200. doi:10.3340/jkns.2008.43.4.198
Prinzo H, Martinez F, Carminatti S (2009) Giant cerebral cavernous malformation in a child less than 1 year old: case report. Neurocirugia (Astur) 20(1):54–56
Moschovi M, Alexiou GA, Stefanaki K, Tourkantoni N, Prodromou N (2010) Propranolol treatment for a giant infantile brain cavernoma. J Child Neurol 25(5):653–655. doi:10.1177/0883073810363917
Lehnhardt FG, von Smekal U, Ruckriem B, Stenzel W, Neveling M, Heiss WD, Jacobs AH (2005) Value of gradient-echo magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of familial cerebral cavernous malformation. Arch Neurol 62(4):653–658. doi:10.1001/archneur.62.4.653
Yun TJ, Na DG, Kwon BJ, Rho HG, Park SH, Suh YL, Chang KH (2008) A T1 hyperintense perilesional signal aids in the differentiation of a cavernous angioma from other hemorrhagic masses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29(3):494–500. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A0847
Russell DS, Rubenstein LJR (1989) Pathology of tumors of the nervous system, 5th edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
McCormick WF (1966) The pathology of vascular (“arteriovenous”) malformations. J Neurosurg 24(4):807–816
Wong JH, Awad IA, Kim JH (2000) Ultrastructural pathological features of cerebrovascular malformations: a preliminary report. Neurosurgery 46(6):1454–1459
Sure U, Freman S, Bozinov O, Benes L, Siegel AM, Bertalanffy H (2005) Biological activity of adult cavernous malformations: a study of 56 patients. J Neurosurg 102(2):342–347. doi:10.3171/jns.2005.102.2.0342
Lanzino G, Spetzler RF (2008) Cavernous malformations of the brain and spinal cord. Thieme, New York
Kumar GS, Poonnoose SI, Chacko AG, Rajshekhar V (2006) Trigonal cavernous angiomas: report of three cases and review of literature. Surg Neurol 65(4):367–371. doi:10.1016/j.surneu.2005.09.015, discussion 371
Brunereau L, Leveque C, Bertrand P, Tranquart E, Cordoliani Y, Rouleau P, Labauge P (2001) Familial form of cerebral cavernous malformations: evaluation of gradient-spin-echo (GRASE) imaging in lesion detection and characterization at 1.5 T. Neuroradiology 43(11):973–979
Di Rocco C, Iannelli A, Tamburrini G (1996) Cavernomas of the central nervous system in children. A report of 22 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 138(11):1267–1274, discussion 1273–1264
Fortuna A, Ferrante L, Mastronardi L, Acqui M, d’Addetta R (1989) Cerebral cavernous angioma in children. Childs Nerv Syst 5(4):201–207
Rigamonti D, Drayer BP, Johnson PC, Hadley MN, Zabramski J, Spetzler RF (1987) The MRI appearance of cavernous malformations (angiomas). J Neurosurg 67(4):518–524. doi:10.3171/jns.1987.67.4.0518
Gomori JM, Grossman RI, Goldberg HI, Hackney DB, Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT (1986) Occult cerebral vascular malformations: high-field MR imaging. Radiology 158(3):707–713
Rapacki TF, Brantley MJ, Furlow TW Jr, Geyer CA, Toro VE, George ED (1990) Heterogeneity of cerebral cavernous hemangiomas diagnosed by MR imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 14(1):18–25
Maraire JNMD, Awad IAMDMS Intracranial cavernous malformations: Lesion behavior and management strategies. [review]. (0148-396X)
Moriarity JL, Wetzel M, Clatterbuck RE, Javedan S, Sheppard JM, Hoenig-Rigamonti K, Crone NE, Breiter SN, Lee RR, Rigamonti D (1999) The natural history of cavernous malformations: a prospective study of 68 patients. Neurosurgery 44(6):1166–1171, discussion 1172–1163
Shenkar R, Shi C, Check IJ, Lipton HL, Awad IA (2007) Concepts and hypotheses: inflammatory hypothesis in the pathogenesis of cerebral cavernous malformations. Neurosurgery 61(4):693–702. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000298897.38979.07, discussion 702–693
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozgen, B., Senocak, E., Oguz, K.K. et al. Radiological features of childhood giant cavernous malformations. Neuroradiology 53, 283–289 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-010-0783-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-010-0783-5