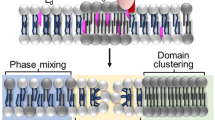
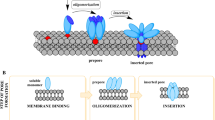
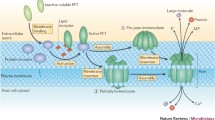
Abstract
Pore-forming proteins/toxins (PFPs/PFTs) are the distinct class of membrane-damaging proteins. They act by forming oligomeric pores in the plasma membranes. PFTs and PFPs from diverse organisms share a common mechanism of action, in which the designated pore-forming motifs of the membrane-bound protein molecules insert into the membrane lipid bilayer to create the water-filled pores. One common characteristic of these pore-forming motifs is that they are amphipathic in nature. In general, the hydrophobic sidechains of the pore-forming motifs face toward the hydrophobic core of the membranes, while the hydrophilic residues create the lining of the water-filled pore lumen. Interestingly, pore-forming motifs of the distinct subclass of PFPs/PFTs share very little sequence similarity with each other. Therefore, the common guiding principle that governs the sequence-to-structure paradigm in the mechanism of action of these PFPs/PFTs still remains an enigma. In this article, we discuss this notion using the examples of diverse groups of membrane-damaging PFPs/PFTs.
Graphic Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakrac B, Gutierrez-Aguirre I, Podlesek Z, Sonnen AF, Gilbert RJ, Macek P, Lakey JH, Anderluh G (2008) Molecular determinants of sphingomyelin specificity of a eukaryotic pore-forming toxin. J Biol Chem 283:18665–18677
Bayly-Jones C, Bubeck D, Dunstone MA (2017). The mystery behind membrane insertion: a review of the complement membrane attack complex. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 372
Bischofberger M, Iacovache I, van der Goot FG (2012) Pathogenic pore-forming proteins: function and host response. Cell Host Microbe 12:266–275
Brauning B, Groll M (2018) Structural and mechanistic features of ClyA-like alpha-pore-forming toxins. Toxins (Basel) 10
Brauning B, Bertosin E, Praetorius F, Ihling C, Schatt A, Adler A, Richter K, Sinz A, Dietz H, Groll M (2018) Structure and mechanism of the two-component alpha-helical pore-forming toxin YaxAB. Nat Commun 9:1806
Dal Peraro M, van der Goot FG (2016) Pore-forming toxins: ancient, but never really out of fashion. Nat Rev Microbiol 14:77–92
De S, Olson R (2011) Crystal structure of the Vibrio cholerae cytolysin heptamer reveals common features among disparate pore-forming toxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:7385–7390
Degiacomi MT, Iacovache I, Pernot L, Chami M, Kudryashev M, Stahlberg H, van der Goot FG, Dal Peraro M (2013) Molecular assembly of the aerolysin pore reveals a swirling membrane-insertion mechanism. Nat Chem Biol 9:623–629
Fleishman SJ, Ben-Tal N (2006) Progress in structure prediction of alpha-helical membrane proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol 16:496–504
Gonzalez MR, Bischofberger M, Pernot L, van der Goot FG, Freche B (2008) Bacterial pore-forming toxins: the (w)hole story? Cell Mol Life Sci 65:493–507
Gutierrez-Aguirre I, Barlic A, Podlesek Z, Macek P, Anderluh G, Gonzalez-Manas JM (2004) Membrane insertion of the N-terminal alpha-helix of equinatoxin II, a sea anemone cytolytic toxin. Biochem J 384:421–428
Heuck AP, Tweten RK, Johnson AE (2001) Beta-barrel pore-forming toxins: intriguing dimorphic proteins. Biochemistry 40:9065–9073
Heuck AP, Moe PC, Johnson BB (2010) The cholesterol-dependent cytolysin family of gram-positive bacterial toxins. Subcell Biochem 51:551–577
Hunt S, Green J, Artymiuk PJ (2010) Hemolysin E (HlyE, ClyA, SheA) and related toxins. Adv Exp Med Biol 677:116–126
Iacovache I, De Carlo S, Cirauqui N, Dal Peraro M, van der Goot FG, Zuber B (2016) Cryo-EM structure of aerolysin variants reveals a novel protein fold and the pore-formation process. Nat Commun 7:12062
Jiang J, Pentelute BL, Collier RJ, Zhou ZH (2015) Atomic structure of anthrax protective antigen pore elucidates toxin translocation. Nature 521:545–549
Koster S, van Pee K, Hudel M, Leustik M, Rhinow D, Kuhlbrandt W, Chakraborty T, Yildiz O (2014) Crystal structure of listeriolysin O reveals molecular details of oligomerization and pore formation. Nat Commun 5:3690
Kristan K, Viero G, Macek P, Dalla Serra M, Anderluh G (2007) The equinatoxin N-terminus is transferred across planar lipid membranes and helps to stabilize the transmembrane pore. FEBS J 274:539–550
Kristan KC, Viero G, Dalla Serra M, Macek P, Anderluh G (2009) Molecular mechanism of pore formation by actinoporins. Toxicon 54:1125–1134
Kundu N, Tichkule S, Pandit SB, Chattopadhyay K (2017) Disulphide bond restrains the C-terminal region of thermostable direct hemolysin during folding to promote oligomerization. Biochem J 474:317–331
Law RH, Lukoyanova N, Voskoboinik I, Caradoc-Davies TT, Baran K, Dunstone MA, D'Angelo ME, Orlova EV, Coulibaly F, Verschoor S, Browne KA, Ciccone A, Kuiper MJ, Bird PI, Trapani JA, Saibil HR, Whisstock JC (2010) The structural basis for membrane binding and pore formation by lymphocyte perforin. Nature 468:447–451
Liu Z, Wang C, Yang J, Zhou B, Yang R, Ramachandran R, Abbott DW, Xiao TS (2019) Crystal structures of the full-length murine and human gasdermin D reveal mechanisms of autoinhibition, lipid binding, and oligomerization. Immunity 51(43–49):e4
Los FC, Randis TM, Aroian RV, Ratner AJ (2013) Role of pore-forming toxins in bacterial infectious diseases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77:173–207
Lovelace LL, Cooper CL, Sodetz JM, Lebioda L (2011) Structure of human C8 protein provides mechanistic insight into membrane pore formation by complement. J Biol Chem 286:17585–17592
Mancheno JM, Martin-Benito J, Martinez-Ripoll M, Gavilanes JG, Hermoso JA (2003) Crystal and electron microscopy structures of sticholysin II actinoporin reveal insights into the mechanism of membrane pore formation. Structure 11:1319–1328
Mechaly AE, Bellomio A, Morante K, Gonzalez-Manas JM, Guerin DM (2009) Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of fragaceatoxin C, a pore-forming toxin from the sea anemone Actinia fragacea. Acta Crystallogr Sect F 65:357–360
Mondal AK, Chattopadhyay K (2020) Taking toll on membranes: curious cases of bacterial beta-barrel pore-forming toxins. Biochemistry 59:163–170
Mondal AK, Sreekumar A, Kundu N, Kathuria R, Verma P, Gandhi S, Chattopadhyay K (2018) Structural basis and functional implications of the membrane pore-formation mechanisms of bacterial pore-forming toxins. Adv Exp Med Biol 1112:281–291
Morante K, Caaveiro JM, Tanaka K, Gonzalez-Manas JM, Tsumoto K (2015) A pore-forming toxin requires a specific residue for its activity in membranes with particular physicochemical properties. J Biol Chem 290:10850–10861
Mueller M, Grauschopf U, Maier T, Glockshuber R, Ban N (2009) The structure of a cytolytic alpha-helical toxin pore reveals its assembly mechanism. Nature 459:726–730
Olson R, Gouaux E (2005) Crystal structure of the Vibrio cholerae cytolysin (VCC) pro-toxin and its assembly into a heptameric transmembrane pore. J Mol Biol 350:997–1016
Olson R, Nariya H, Yokota K, Kamio Y, Gouaux E (1999) Crystal structure of staphylococcal LukF delineates conformational changes accompanying formation of a transmembrane channel. Nat Struct Biol 6:134–140
Parker MW, Postma JP, Pattus F, Tucker AD, Tsernoglou D (1992) Refined structure of the pore-forming domain of colicin A at 2.4 A resolution. J Mol Biol 224:639–657
Paul K, Chattopadhyay K (2014) Pre-pore oligomer formation by Vibrio cholerae cytolysin: insights from a truncated variant lacking the pore-forming pre-stem loop. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 443:189–193
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera–a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612
Podobnik M, Savory P, Rojko N, Kisovec M, Wood N, Hambley R, Pugh J, Wallace EJ, McNeill L, Bruce M, Liko I, Allison TM, Mehmood S, Yilmaz N, Kobayashi T, Gilbert RJ, Robinson CV, Jayasinghe L, Anderluh G (2016) Crystal structure of an invertebrate cytolysin pore reveals unique properties and mechanism of assembly. Nat Commun 7:11598
Podobnik M, Kisovec M, Anderluh G (2017). Molecular mechanism of pore formation by aerolysin-like proteins. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 372
Rai AK, Chattopadhyay K (2014) Trapping of Vibrio cholerae cytolysin in the membrane-bound monomeric state blocks membrane insertion and functional pore formation by the toxin. J Biol Chem 289:16978–16987
Ramirez-Carreto S, Miranda-Zaragoza B, Rodriguez-Almazan C (2020). Actinoporins: from the structure and function to the generation of biotechnological and therapeutic tools. Biomolecules 10
Reboul CF, Whisstock JC, Dunstone MA (2016) Giant MACPF/CDC pore forming toxins: a class of their own. Biochim Biophys Acta 1858:475–486
Robert X, Gouet P (2014) Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucl Acids Res 42:W320–W324
Rojko N, Dalla Serra M, Macek P, Anderluh G (2016) Pore formation by actinoporins, cytolysins from sea anemones. Biochim Biophys Acta 1858:446–456
Ros U, Rodriguez-Vera W, Pedrera L, Valiente PA, Cabezas S, Lanio ME, Garcia-Saez AJ, Alvarez C (2015) Differences in activity of actinoporins are related with the hydrophobicity of their N-terminus. Biochimie 116:70–78
Rosado CJ, Kondos S, Bull TE, Kuiper MJ, Law RH, Buckle AM, Voskoboinik I, Bird PI, Trapani JA, Whisstock JC, Dunstone MA (2008) The MACPF/CDC family of pore-forming toxins. Cell Microbiol 10:1765–1774
Rossjohn J, Feil SC, McKinstry WJ, Tweten RK, Parker MW (1997) Structure of a cholesterol-binding, thiol-activated cytolysin and a model of its membrane form. Cell 89:685–692
Ruan J, Xia S, Liu X, Lieberman J, Wu H (2018) Cryo-EM structure of the gasdermin A3 membrane pore. Nature 557:62–67
Savinov SN, Heuck AP (2017). Interaction of cholesterol with perfringolysin O: what have we learned from functional analysis? Toxins (Basel) 9
Savva CG, Fernandes da Costa SP, Bokori-Brown M, Naylor CE, Cole AR, Moss DS, Titball RW, Basak AK (2013) Molecular architecture and functional analysis of NetB, a pore-forming toxin from Clostridium perfringens. J Biol Chem 288:3512–3522
Savva CG, Clark AR, Naylor CE, Popoff MR, Moss DS, Basak AK, Titball RW, Bokori-Brown M (2019) The pore structure of Clostridium perfringens epsilon toxin. Nat Commun 10:2641
Shi J, Gao W, Shao F (2017) Pyroptosis: gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends Biochem Sci 42:245–254
Song L, Hobaugh MR, Shustak C, Cheley S, Bayley H, Gouaux JE (1996) Structure of staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin, a heptameric transmembrane pore. Science 274:1859–1866
Sonnen AF, Plitzko JM, Gilbert RJ (2014) Incomplete pneumolysin oligomers form membrane pores. Open Biol 4:140044
Spicer BA, Conroy PJ, Law RHP, Voskoboinik I, Whisstock JC (2017) Perforin-A key (shaped) weapon in the immunological arsenal. Semin Cell Dev Biol 72:117–123
Tavares J, Amino R, Menard R (2014) The role of MACPF proteins in the biology of malaria and other apicomplexan parasites. Subcell Biochem 80:241–253
Tweten RK (2005) Cholesterol-dependent cytolysins, a family of versatile pore-forming toxins. Infect Immun 73:6199–6209
Valeva A, Palmer M, Hilgert K, Kehoe M, Bhakdi S (1995) Correct oligomerization is a prerequisite for insertion of the central molecular domain of staphylococcal alpha-toxin into the lipid bilayer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1236:213–218
van Pee K, Neuhaus A, D'Imprima E, Mills DJ, Kuhlbrandt W, Yildiz O (2017). CryoEM structures of membrane pore and prepore complex reveal cytolytic mechanism of Pneumolysin. Elife 6
Waldispuhl J, Berger B, Clote P, Steyaert JM (2006) Predicting transmembrane beta-barrels and interstrand residue interactions from sequence. Proteins 65:61–74
White SH, Ladokhin AS, Jayasinghe S, Hristova K (2001) How membranes shape protein structure. J Biol Chem 276:32395–32398
Wimley WC (2002) Toward genomic identification of beta-barrel membrane proteins: composition and architecture of known structures. Protein Sci 11:301–312
Wimley WC, Hristova K, Ladokhin AS, Silvestro L, Axelsen PH, White SH (1998) Folding of beta-sheet membrane proteins: a hydrophobic hexapeptide model. J Mol Biol 277:1091–1110
Yamada T, Yoshida T, Kawamoto A, Mitsuoka K, Iwasaki K, Tsuge H (2020) Cryo-EM structures reveal translocational unfolding in the clostridial binary iota toxin complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol 27:288–296
Yamashita D, Sugawara T, Takeshita M, Kaneko J, Kamio Y, Tanaka I, Tanaka Y, Yao M (2014) Molecular basis of transmembrane beta-barrel formation of staphylococcal pore-forming toxins. Nat Commun 5:4897
Funding
We acknowledge funding under the Centre of Excellence (COE) in the Frontier Areas of Science and Technology (FAST) program of the Ministry of Human Resource Development, Govt. of India, in the area of protein science, design, and engineering. We also thank Indian Institute of Science Education and Research Mohali for support; Research fellowships from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India (to A.K.M. and K.L.), University Grants Commission, India (to P.V. and S.C.), and Department of Biotechnology, India (to M.S.) are also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that there is no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mondal, A.K., Verma, P., Lata, K. et al. Sequence Diversity in the Pore-Forming Motifs of the Membrane-Damaging Protein Toxins. J Membrane Biol 253, 469–478 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-020-00141-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-020-00141-2