Abstract
Background/objective
Little is known about the relationship between proton pump inhibitors use and pyogenic liver abscess. The objective of this study was to evaluate the correlation between proton pump inhibitors use and pyogenic liver abscess in Taiwan.
Methods
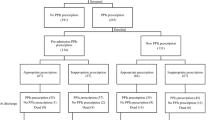
This was a population-based case-control study using the database of the Taiwan National Health Insurance Program since 2000 to 2011. Subjects aged 20 to 84 who experienced their first episode of pyogenic liver abscess were enrolled as the case group (n = 1372). Randomly selected subjects aged 20 to 84 without pyogenic liver abscess were enrolled as the control group (n = 1372). Current use, early use, and late use of proton pump inhibitors was defined as subjects whose last one tablet for proton pump inhibitors was noted ≤30 days, between 31 to 90 days and ≥91 days before the date of admission for pyogenic liver abscess. Subjects who never received a prescription for proton pump inhibitors were defined as nonusers of proton pump inhibitors. A multivariable unconditional logistic regression model was used to measure the odds ratio and 95% confidence interval to evaluate the correlation between proton pump inhibitors use and pyogenic liver abscess.
Results
After adjusting for confounders, the adjusted odds ratio of pyogenic liver abscess was 7.59 for subjects with current use of proton pump inhibitors (95% confidence interval 5.05, 11.4), when compared with nonusers.
Conclusions
Current use of proton pump inhibitors is associated with a greater risk of pyogenic liver abscess.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blum RA (1996) Lansoprazole and omeprazole in the treatment of acid peptic disorders. Am J Health-Syst Pharm 53(12):1401–1415
Shin JM, Besancon M, Prinz C, Simon A, Sachs G (1994) Continuing development of acid pump inhibitors: site of action of pantoprazole. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 8(Suppl 1):11–23
Kahrilas PJ, Shaheen NJ, Vaezi MF (2008) American Gastroenterological Association Institute technical review on the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 135(4):1392–1413
Fraser LA, Leslie WD, Targownik LE, Papaioannou A, Adachi JD (2013) The effect of proton pump inhibitors on fracture risk: report from the Canadian Multicenter Osteoporosis Study. Osteoporos Int 24:1161–1168
Khalili H, Huang ES, Jacobson BC, Camargo CA Jr, Feskanich D, Chan AT (2012) Use of proton pump inhibitors and risk of hip fracture in relation to dietary and lifestyle factors: a prospective cohort study. Br Med J 344:e372
Jena AB, Sun E, Goldman DP (2012) Confounding in the association of proton pump inhibitor use with risk of community-acquired pneumonia. J Gen Med 28(2):223–230
de Jager CP, Wever PC, Gemen EF, van Oijen MG, van Gageldonk-Lafeber AB, Siersema PD et al (2012) Proton pump inhibitor therapy predisposes to community-acquired Streptococcus pneumoniae pneumonia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 36:941–949
Johnstone J, Nerenberg K, Loeb M (2010) Meta-analysis: proton pump inhibitor use and the risk of community-acquired pneumonia. 31:1165–77
Campbell MS, Obstein K, Reddy KR, Yang YX (2008) Association between proton pump inhibitor use and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Dig Dis Sci 53:394–398
Bajaj JS, Zadvornova Y, Heuman DM, Hafeezullah M, Hoffmann RG, Sanyal AJ et al (2009) Association of proton pump inhibitor therapy with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic patients with ascites. Am J Gastroenterol 104:1130–1134
Lai SW, Liao KF, Lai HC, Lin CL, Sung FC (2013 Jun) Use of proton pump inhibitors correlates with increased risk of colorectal cancer in Taiwan. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 9(2):192–193. doi:10.1111/ajco.12054
Lai S-W, Sung F-C, Lin C-L, Liao K-F (2014) Use of proton pump inhibitors correlates with increased risk of pancreatic cancer: a case-control study in Taiwan. Kuwait Med J 46:44–48
McDonald MI, Corey GR, Gallis HA, Durack DT (1984) Single and multiple liver abscess. Medicine 63:291–302
Frey CF, Zhu Y, Suzuki M, Isaji S (1989) Liver abscesses. Surg Clin N Am 69:259–271
Kendal G, Marcon NE (1984) Pyogenic liver abscess: new concepts of an old disease. Am J Gastroenterol 79:65–71
Greenstein AJ, Lowenthal D, Hammer GS, Schaffner F, Aufses AH (1984) Continuing changing patterns of disease in pyogenic liver abscess: a study of 38 patients. Am J Gastroenterol 79:217–225
Wang JH, Liu YC, Lee SJ, Yen MY, Chen YS, Wang JH (1998) Primary liver abscess due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in Taiwan. Clin Infect Dis 26:1434–1438
Chang FY, Chou MY, Fan RL, Shaio MF (1988) A clinical study of Klebsiella liver abscesses. J Formos Med Assoc 87:282–287
Chang FY, Chou MY (1995) Comparison of pyogenic liver abscesses caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae and non-K.pneumoniae pathogens. J Formos Med Assoc 94:232–237
Yang CC, Chen CY, Lin XZ, Chang TT, Shin JS, Lin CY (1993) Pyogenic liver abscess in Taiwan: emphasis on gas-forming liver abscess in diabetics. Am J Gastroenterol 88:1911–1915
National Health Insurance Research Database. Taiwan. http://nhird.nhri.org.tw/en/index.html [cited in March 1, 2017, English version]
Lai SW, Liao KF, Liao CC, Muo CH, Liu CS, Sung FC (2010) Polypharmacy correlates with increased risk for hip fracture in the elderly: a population-based study. Medicine (Baltimore) 89:295–299
Hung SC, Liao KF, Lai SW, Li CI, Chen WC (2011) Risk factors associated with symptomatic cholelithiasis in Taiwan: a population-based study. BMC Gastroenterol 11:111
Lai SW, Chen PC, Liao KF, Muo CH, Lin CC, Sung FC (2012) Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in diabetic patients and risk reduction associated with anti-diabetic therapy: a population-based cohort study. Am J Gastroenterol 107:46–52
Chen HY, Lai SW, Muo CH, Chen PC, Wang IJ (2012) Ethambutol-induced optic neuropathy: a nationwide population-based study from Taiwan. Br J Ophthalmol 96:1368–1371
Lai HC, Chang SN, Lin CC, Chen CC, Chou JW, Peng CY et al (2013) Does diabetes mellitus with or without gallstones increase the risk of gallbladder cancer? Results from a population-based cohort study. J Gastroenterol 48:856–865
Hung SC, Lai SW, Tsai PY, Chen PC, Wu HC, Lin WH et al (2013) Synergistic interaction of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostatitis on prostate cancer risk. Br J Cancer 108:1778–1783
Lai HC, Tsai IJ, Chen PC, Muo CH, Chou JW, Peng CY et al (2013) Gallstones, a cholecystectomy, chronic pancreatitis, and the risk of subsequent pancreatic cancer in diabetic patients: a population-based cohort study. J Gastroenterol 48:721–727
Lai HC, Lin CC, Cheng KS, Kao JT, Chou JW, Peng CY et al (2014) Increased incidence of gastrointestinal cancers among patients with pyogenic liver abscess: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology 146:129–137
Kuo SC, Lai SW, Hung HC, Muo CH, Hung SC, Liu LL et al (2015) Association between comorbidities and dementia in diabetes mellitus patients: population-based retrospective cohort study. J Diabetes Complicat 29:1071–1076
Yang SP, Muo CH, Wang IK, Chang YJ, Lai SW, Lee CW et al (2015) Risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in female breast cancer patients treated with morphine: a retrospective population-based time-dependent cohort study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 110:285–290
Cheng KC, Chen YL, Lai SW, Tsai PY, Sung FC (2012) Risk of esophagus cancer in diabetes mellitus: a population-based case-control study in Taiwan. BMC Gastroenterol 12:177
Chen YL, Cheng KC, Lai SW, Tsai IJ, Lin CC, Sung FC et al (2013) Diabetes and risk of subsequent gastric cancer: a population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Gastric Cancer 16:389–396
Wang YP, Liu CJ, Chen TJ, Lin YT, Fung CP (2015) Proton pump inhibitor use significantly increases the risk of cryptogenic liver abscess: a population-based study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 41:1175–1181
Lo WK, Chan WW (2013) Proton pump inhibitor use and the risk of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: a meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 11:483–490
Sarkar M, Hennessy S, Yang YX (2008) Proton-pump inhibitor use and the risk for community-acquired pneumonia. Ann Intern Med 149:391–398
Aybay C, Imir T, Okur H (1995) The effect of omeprazole on human natural killer cell activity. Gen Pharmacol 26:1413–1418
Yoshida N, Yoshikawa T, Tanaka Y, Fujita N, Kassai K, Naito Y et al (2000) A new mechanism for anti-inflammatory actions of proton pump inhibitors-inhibitory effects on neutrophil-endothelial cell interactions. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 14:74–81
Zedtwitz-Liebenstein K, Wenisch C, Patruta S, Parschalk B, Daxbock F, Graninger W (2002) Omeprazole treatment diminishes intra- and extracellular neutrophil reactive oxygen production and bactericidal activity. Crit Care Med 30:1118–1122
Cheng KC, Chen YL, Lai SW, Mou CH, Tsai PY, Sung FC (2012) Patients with chronic kidney disease are at an elevated risk of dementia: a population-based cohort study in Taiwan. BMC Nephrol 13:129
Lai SW, Liao KF, Lai HC, Lin CL, Sung FC (2013) Proton pump inhibitors and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma : a case-control study in Taiwan. Acta Gastro-Enterol Belg 76:348–350
Lai SW, Liao KF, Lai HC, Tsai PY, Sung FC, Chen PC (2013) Kidney cancer and diabetes mellitus: a population-based case-control study in Taiwan. Ann Acad Med Singap 42:120–124
Lai SW, Liu JC, Tseng CH, Muo CH, Liao KF (2013) Chronic osteomyelitis and hepatocellular carcinoma: an observation in Taiwan. Kuwait Med J 45:159–160
Liao K-F, Lin C-L, Lai S-W (2015) Schizophrenia correlates with increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in men: a cohort study in Taiwan. Int Med J 22
Lai S-W, Lin C-L, Liao K-F, Lin C-M (2015) Parkinson’s disease and hepatocellular carcinoma in older people: a population-based case-control study in Taiwan. Int Med J 22
Hung SC, Hung SR, Lin CL, Lai SW, Hung HC (2015) Use of celecoxib correlates with increased relative risk of acute pancreatitis: a case-control study in Taiwan. Am J Gastroenterol 110:1490–1496
Lai SW, Lai HC, Lin CL, Liao KF (2015) Splenectomy correlates with increased risk of pyogenic liver abscess: a nationwide cohort study in Taiwan. J Epidemiol 25:561–566
Cheng KC, Lin WY, Liu CS, Lin CC, Lai HC, Lai SW (2016) Association of different types of liver disease with demographic and clinical factors. BioMedicine-Taiwan 6:16–22
Liao KF, Cheng KC, Lin CL, Lai SW (2017) Etodolac and the risk of acute pancreatitis. BioMedicine-Taiwan 7:25–29
Shen ML, Liao KF, Tsai SM, Lin CL, Lai SW (2016) Herpes zoster correlates with pyogenic liver abscesses in Taiwan. BioMedicine-Taiwan 6:24–29
Lai SW (2016) Risks and benefits of zolpidem use in Taiwan: a narrative review. BioMedicine-Taiwan 6:9–11
Lin HF, Lai SW, Lin WY, Liu CS, Lin CC, Chang CM (2016) Prevalence and factors of elevated alanine aminotransferase in central Taiwan—a retrospective study. BioMedicine-Taiwan 6:25–30
Acknowledgements
This study is supported in part by Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare Clinical Trial Center (MOHW106-TDU-B-212-113004). This funding agency did not influence the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hsien-Feng Lin initiated the draft of the article and revised the article.
Kuan-Fu Liao, Ching-Mei Chang, and Cheng-Li Lin conducted the data analysis and revised the article.
Shih-Wei Lai planned and conducted this study. He contributed to the conception of the article, initiated the draft of the article, and revised the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, HF., Liao, KF., Chang, CM. et al. Correlation between proton pump inhibitors and risk of pyogenic liver abscess. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 73, 1019–1025 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-017-2256-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-017-2256-9