Abstract
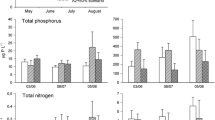
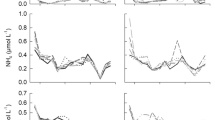
A comparative analysis of data, obtained during four indoor-mesocosm experiments with natural spring plankton communities from the Baltic Sea, was conducted to investigate whether biogeochemical cycling is affected by an increase in water temperature of up to 6 °C above present-day conditions. In all experiments, warming stimulated in particular heterotrophic bacterial processes and had an accelerating effect on the temporal development of phytoplankton blooms. This was also mirrored in the build-up and partitioning of organic matter between particulate and dissolved phases. Thus, warming increased both the magnitude and rate of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) build-up, whereas the accumulation of particulate organic carbon (POC) and phosphorus (POP) decreased with rising temperature. In concert, the observed temperature-mediated changes in biogeochemical components suggest strong shifts in the functioning of marine pelagic food webs and the ocean’s biological carbon pump, hence providing potential feedback mechanisms to Earth’s climate system.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azam F (1998) Microbial control of oceanic carbon flux: the plot thickens. Science 280:694–696
Barnett TP, Pierce DW, AchutaRao KM, Gleckler PJ, Santer BD, Gregory JM, Washington WM (2005) Penetration of human-induced warming into the world’s oceans. Science 309:284–287
Bellerby RGJ, Schulz KG, Riebesell U, Neill C, Nondal G, Johannessen T, Brown KR (2008) Marine ecosystem community carbon and nutrient uptake stoichiometry under varying ocean acidification during the PeECE III experiment. Biogeosciences 5:1517–1527
Bopp L, Monfray P, Aumont O, Dufresne J-L, Le Treut H, Madec G, Terray L, Orr JC (2001) Potential impact of climate change on marine export production. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 15:81–99
Boyd PW, Doney SC (2002) Modeling regional responses by marine pelagic ecosystems to global climate change. Geophys Res Lett 29:1806
Breithaupt P (2009) The impact of climate change on phytoplankton-bacterioplankton interactions. Dissertation, Christian-Albrechts-University, Kiel, Germany
Brock TD (1981) Calculating solar radiation for ecological models. Ecol Model 14:1–19
Chin WC, Orellana MV, Verdugo P (1998) Spontaneous assembly of marine dissolved organic matter into polymers. Nature 391:568–572
Claquin P, Probert I, Lefebvre S, Veron B (2008) Effects of temperature on photosynthetic parameters and TEP production in eight species of marine microalgae. Aquat Microb Ecol 51:1–11
Copin MG, Avril B (1993) Vertical distribution and temporal variation of dissolved organic carbon in the North-Western Mediterranean Sea. Deep-Sea Res I 40:1963–1972
Davison IR (1991) Environmental effects on algal photosynthesis: temperature. J Phycol 27:2–8
Edwards M, Richardson AJ (2004) Impact of climate change on marine pelagic phenology and trophic mismatch. Nature 430:881–884
Engel A (2004) Distribution of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in the northeast Atlantic Ocean and their potential significance for aggregation processes. Deep-Sea Res I 51:83–92
Engel A, Goldthwait S, Passow U, Alldredge AL (2002) Temporal decoupling of carbon and nitrogen dynamics in a mesocosm diatom bloom. Limnol Oceanogr 47:753–761
Engel A, Thoms S, Riebesell U, Rochelle-Newall E, Zondervan I (2004) Polysaccharide aggregation as a potential sink of marine dissolved organic carbon. Nature 428:929–932
Engel A, Händel N, Wohlers J, Lunau M, Grossart HP, Sommer U, Riebesell U (2011) Effects of sea surface warming on the production and composition of dissolved organic matter during phytoplankton blooms: results from a mesocosm study. J Plankt Res 33:357–372
Finkel ZV, Beardall J, Flynn KJ, Quigg A, Rees TAV, Raven JA (2009) Phytoplankton in a changing world: cell size and elemental stoichiometry. J Plankt Res 32:119–137
Fuhrman JA, Azam F (1982) Thymidine incorporation as a measure of heterotrophic bacterioplankton production in marine surface waters: evaluation and field results. Mar Biol 66:109–120
Gargas E (1975) A manual for phytoplankton primary production studies in the Baltic. Baltic Mar Biol 2:1–88
Hansen HP, Koroleff F (1999) Determination of nutrients. In: Grasshoff K, Kremling K, Ehrhardt M (eds) Methods of seawater analysis. Wiley VCH, Weinheim, pp 159–228
Jiao N, Herndl GJ, Hansell DA, Benner R, Kattner G, Wilhelm SW, Kirchman DL, Weinbauer MG, Luo T, Chen F, Azam F (2010) Microbial production of recalcitrant dissolved organic matter: long-term carbon storage in the global ocean. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:593–599
Kawasaki N, Benner R (2006) Bacterial release of dissolved organic matter during cell growth and decline: molecular origin and composition. Limnol Oceanogr 51:2170–2180
Kim JM, Lee K, Shin K, Yang EJ, Engel A, Karl DM, Kim HC (2011) Shifts in biogenic carbon flow from particulate to dissolved forms under high carbon dioxide and Warm Ocean conditions. Geophys Res Lett 38:L08612
Kroeker KJ, Kordas RL, Crim RN, Singh GG (2010) Meta-analysis reveals negative yet variable effects of ocean acidification on marine organisms. Ecol Lett. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2010.01518x
Kujawinski EB (2011) The impact of microbial metabolism on marine dissolved organic matter. Annu Rev Mar Sci 3:567–599
Levitus S, Antonov J, Boyer T (2005) Warming of the world ocean, 1955–1998. Geophys Res Lett 32:L02604
Lewandowska AM, Sommer U (2010) Climate change and the spring bloom: a mesocosm study on the influence of light and temperature on phytoplankton and mesozooplankton. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 405:101–111
Lewandowska AM, Breithaupt P, Hillebrand H, Hoppe HG, Jürgens K, Sommer U (2011) Responses of primary productivity to increased temperature and phytoplankton diversity. J Sea Res. doi:10.1016/j.seares.2011.10.003
López-Urrutia A, San Martin E, Harris RP, Irigoien X (2006) Scaling the metabolic balance of the oceans. Proc Nat Acad Sci 103:8739–8744
Meehl GA, Stocker TF, Collins WD, Friedlingstein P, Gaye AT, Gregory JM, Kitoh A, Knutti R, Murphy JM, Noda A, Raper SCB, Watterson IG, Weaver AJ, Zhao ZC (2007) Global climate projections. In: Solomon S, Qin MMD, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (eds) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 747–845
Morán XAG, Sebastián M, Pedrós-Alió C, Estrada M (2006) Response of Southern Ocean phytoplankton and bacterioplankton production to short-term experimental warming. Limnol Oceanogr 51:1791–1800
Morán XAG, López-Urrutia A, Calvo-Díaz A, Li WKW (2010) Increasing importance of small phytoplankton in a warmer ocean. Glob Change Biol 16:1137–1144
Müren U, Berglund J, Samuelsson K, Andersson A (2005) Potential effects of elevated sea-water temperature on pelagic food webs. Hydrobiol 545:153–166
Myklestad S, Skånøy E, Hestmann S (1997) A sensitive and rapid method for analysis of dissolved mono- and polysaccharides in seawater. Mar Chem 56:279–286
Norrman B, Zweifel UL, Hopkinson CS, Fry B (1995) Production and utilization of dissolved organic carbon during an experimental diatom bloom. Limnol Oceanogr 40:898–907
O’Connor MI, Piehler MF, Leech DM, Anton A, Bruno JF (2009) Warming and resource availability shift food web structure and metabolism. PLoS Biol 7:e1000178. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000178
Ogawa H, Amagai Y, Koike I, Kaiser K, Benner R (2001) Production of refractory dissolved organic matter by bacteria. Science 292:917–920
Passow U (2002) Transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in aquatic environments. Prog Oceanogr 55:287–333
Passow U, Alldredge AL (1995a) A dye-binding assay for the spectrophotometric measurement of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP). Limnol Oceanogr 40:1326–1335
Passow U, Alldredge AL (1995b) Aggregation of a diatom bloom in a mesocosm: the role of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP). Deep-Sea Res II 42:99–109
Qian J, Mopper K (1996) Automated high-performance, high-temperature combustion total organic carbon analyzer. Analyt Chem 68:3090–3097
Redfield AC, Ketchum BM, Richards FA (1963) The influence of organism on the composition of sea-water. In: Hill MN (ed) The sea. Wiley, New York, pp 26–77
Riebesell U, Schulz KG, Bellerby RGJ, Botros M, Fritsche P, Meyerhöfer M, Neill C, Nondal G, Oschlies A, Wohlers J, Zöllner E (2007) Enhanced biological carbon consumption in a high CO2 ocean. Nature 450:545–549
Riebesell U, Körtzinger A, Oschlies A (2009) Sensitivities of marine carbon fluxes to ocean change. Proc Nat Acad Sci 106:20602–20609
Sarmiento JL, Hughes TMC, Stouffer RJ, Manabe S (1998) Simulated response of the ocean carbon cycle to anthropogenic warming. Nature 393:245–249
Sarmiento JL, Slater R, Barber R, Bopp L, Doney SC, Hirst AC, Kleypas J, Matear R, Mikolajewicz U, Monfray P, Soldatov V, Spall SA, Stouffer R (2004) Response of ocean ecosystems to climate warming. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 18:GB3003
Schartau M, Engel A, Schröter J, Thoms S, Völker C, Wolf-Gladrow D (2007) Modelling carbon overconsumption and the formation of extracellular particulate organic carbon. Biogeosciences 4:433–454
Sharp JH (1974) Improved analysis for particulate organic carbon and nitrogen from seawater. Limnol Oceanogr 19:984–989
Sharples J, Ross ON, Scott BE, Greenstreet SPR, Fraser H (2006) Inter-annual variability in the timing of stratification and the spring bloom in the North-western North Sea. Cont Shelf Res 26:733–751
Siegenthaler U, Sarmiento JL (1993) Atmospheric carbon dioxide and the ocean. Nature 365:119–125
Simon M, Azam F (1989) Protein content and protein synthesis rates of planktonic marine bacteria. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 51:201–213
Sommer U, Lengfellner K (2008) Climate change and the timing, magnitude, and composition of the phytoplankton spring bloom. Glob Change Biol 14:1199–1208
Sommer U, Lewandowska A (2011) Climate change and the phytoplankton spring bloom: warming and overwintering zooplankton have similar effects on phytoplankton. Glob Change Biol 17:154–162
Sommer U, Aberle N, Engel A, Hansen T, Lengfellner K, Sandow M, Wohlers J, Zöllner E, Riebesell U (2007) An indoor mesocosm system to study the effect of climate change on the late winter and spring succession of Baltic Sea phyto- and zooplankton. Oecologia 150:655–667
Steemann Nielsen E (1952) The use of radioactive carbon (14C) for measuring production in the sea. J Cons Int Explor Mer 18:117–140
Stoderegger K, Herndl GJ (1998) Production and release of bacterial capsular material and its subsequent utilization by marine bacterioplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 43:877–884
Thingstad TF, Hagström Å, Rassoulzadegan F (1997) Accumulation of degradable DOC in surface waters: is it caused by a malfunctioning microbial loop? Limnol Oceanogr 42:398–404
Thornton DCO, Thake B (1998) Effect of temperature on the aggregation of Skeletonema costatum (Bacillariophyceae) and the implication for carbon flux in coastal waters. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 174:223–231
Tilzer MM, Dubinsky Z (1986) Effects of temperature and day length on the mass balance of Antarctic phytoplankton. Polar Biol 7:35–42
Van den Meersche K, Middelburg JJ, Soetaert K, van Rijswijk P, Boschker HTS (2004) Carbon-nitrogen coupling and algal-bacterial interactions during an experimental bloom: modeling a 13Ctracer experiment. Limnol Oceanogr 49:862–878
Verity PG (1981) Effects of temperature, irradiance, and daylength on the marine diatom Leptocylindrus danicus cleve. I. Photosynthesis and cellular composition. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 55:79–91
Wiltshire KH, Manly BFJ (2004) The warming trend at Helgoland Roads, North Sea: phytoplankton response. Helgol Mar Res 58:269–273
Wohlers J (2009) The impact of climate change on phytoplankton-bacterioplankton interactions. Dissertation, Christian-Albrechts-University, Kiel, Germany
Wohlers J, Engel A, Zöllner E, Breithaupt P, Jürgens K, Hoppe HG, Sommer U, Riebesell U (2009) Changes in biogenic carbon flow in response to sea surface warming. Proc Nat Acad Sci 106:7067–7072
Wohlers-Zöllner J, Breithaupt P, Walther K, Jürgens K, Riebesell U (2011) Temperature and nutrient stoichiometry interactively modulate organic matter cycling in a pelagic algal–bacterial community. Limnol Oceanogr 56:599–610
Wolfstein K, Brouwer JFC, Stal LJ (2002) Biochemical partitioning of photosynthetically fixed carbon by benthic diatoms during short-term incubations at different irradiances. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 245:21–31
Zöllner E, Hoppe HG, Sommer U, Juergens K (2009) Effect of zooplankton-mediated trophic cascades on marine microbial food web components (bacteria, nanoflagellates, ciliates). Limnol Oceanogr 54:262–275
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank A. Ludwig, N. Händel and P. Fritsche for their technical assistance in sample preparation and analysis. All members of the Kiel AQUASHIFT-team are appreciated for their help during the experiments. We are particularly grateful to E. Zöllner and the anonymous reviewers for their comments on an earlier version of this manuscript. This work was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) grant no. RI 598/2-3 to U. R. and A. E. and by the Helmholtz Association (contract no. HZ-NG-102 to A. E.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Winder.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wohlers-Zöllner, J., Biermann, A., Engel, A. et al. Effects of rising temperature on pelagic biogeochemistry in mesocosm systems: a comparative analysis of the AQUASHIFT Kiel experiments. Mar Biol 159, 2503–2518 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-1958-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-1958-x