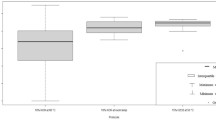
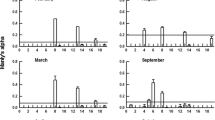
Abstract
Harsh physical conditions in the intertidal zone are the cause of an ample amount of dead macroinvertebrates, which constitute a food source for carrion-feeders. In the European Wadden Sea, this trophic guild includes decapod crustaceans and fish when the tide is in, while during nocturnal low tides the polychaete Phyllodoce mucosa is attracted in large numbers by dead mollusks, crabs or worms on the sediment surface. Within 10 s worms emerged to the surface, crawled as far as 15 m on mucus trails towards the carcass, sucked in tissue up to one-third of their own weight, and then quickly retreated to below the surface. Abundance of P. mucosa was highest in the lower intertidal zone and winter. The seaward high abundance pattern, however, did not continue into the shallow subtidal. In summer, few were attracted during daytime or when the tide was in. However, up to 447 worms aggregated at a single crushed mussel within 20 min at dusk during low-tide exposure. This study suggests that during winter carrion-feeding is an important trophic niche on cold-temperate, intertidal mud flats occupied by a phyllodocid polychaete that is segregated in feeding time from most other scavengers and benefits from cold-sensitive benthic invertebrates.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abele-Oeschger D, Oeschger R (1995) Enzymatic antioxidant protection in spawn, larvae and adult worms of Phyllodoce mucosa (Polychaeta). Ophelia 43:101–110
Ahrens MJ, Hickey CW (2002) UV-photoactivation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and the sensitivity of sediment-dwelling estuarine organisms. In: UV radiation and its effects: an update 2002. Proceedings of a workshop held in Christchurch. RSNZ miscellaneous series no. 60, Royal Society of New Zealand, Wellington, pp 63–65
Armonies W, Hellwig-Armonies M (1992) Passive settlement of Macoma balthica spat on tidal flats of the Wadden Sea and subsequent migrations of juveniles. Neth J Sea Res 29:371–378
Asmus H, Lackschewitz D, Asmus R, Scheiffarth G, Nehls G, Herrmann J-P (1998) Transporte im Nahrungsnetz eulitoraler Wattflächen des Sylt-Rømø Wattenmeeres. In: Gätje C, Reise K (eds) Ökosystem Wattenmeer—Austausch-, Transport- und Stoffumwandlungsprozesse. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 393–420
Austen I (1994) The surface sediments of Königshafen variations over the past 50 years. Helgol Meeresunters 48:163–171
Baretta JW, Ruardy P (eds) (1988) Tidal flat estuaries. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Beukema JJ (1979) Biomass and species richness of the macrobenthic animals living on a tidal flat area in the Dutch Wadden Sea: effects of a severe winter. Neth J Sea Res 13:203–223
Beukema JJ (1991) Changes in composition of bottom fauna of a tidal-flat area during a period of eutrophication. Mar Biol 111:293–301
Beukema JJ (1992) Dynamics of juvenile shrimp Crangon crangon in a tidal-flat nursery of the Wadden Sea after mild and cold winters. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 83:157–165
Beukema JJ (1993) Successive changes in distribution patterns as an adaptive strategy in the bivalve Macoma balthica (L.) in the Wadden Sea. Helgol Meeresunters 47:287–304
Black KP, Oldman JW (1999) Wave mechanisms responsible for grain sorting and non-uniform ripple distribution across two moderate-ebergy, sandy continental shelves. Mar Geol 162:121–132
Britton JC, Morton B (1994) Marine carrion and scavengers. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 32:369–434
Brown AC (1961) Physiological–ecological studies on two sandy-beach Gastropoda from South Africa: Bullia digitalis Meuschen and Bullia laevissima (Gmelin). Z Morphol Oekol Tiere 49:629–657
Brown AC (1982) The biology of sandy-beach whelks of the genus Bullia (Nassariidae). Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 20: 309–361
Cohen JE (1978) Food webs and niche space. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Creutzberg F, Fonds M (1971) The seasonal variation in the distribution of some demersal fish species in the Dutch Wadden Sea. Thalassia Jugosl 7:13–23
Crisp DJ (ed) (1964) The effects of the severe winter of 1962–63 on marine life in Britain. J Anim Ecol 33:165–210
Eriksson S, Tallmark B (1974) The influence of environmental factors on the diurnal rhythm of the prosobranch gastropod Nassarius reticulatus (L.) from a non-tidal area. Zoon 2:135–142
Eriksson S, Evans S, Tallmark B (1975a) On the coexistence of scavengers on shallow, sandy bottoms in Gullmar Fjord (Sweden): adaptations to substratum, temperature, and salinity. Zoon 3:65–70
Eriksson S, Evans S, Tallmark B (1975b) On the coexistence of scavengers on shallow, sandy bottoms in Gullmar Fjord (Sweden): activity patterns and feeding activity. Zoon 3:121–124
Farke H, Wilde PAWJ de, Berghuis EM (1979) Distribution of juvenile and adult Arenicola marina on a tidal mud flat and the importance of nearshore areas for recruitment. Neth J Sea Res 13:354–361
Fauchald K, Jumars PA (1979) The diet of worms: a study of polychaete feeding guilds. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 17:193–284
Fenske C (1997) The importance of intraspecific competition in a Littorina littorea population in the Wadden Sea. Hydrobiologia 355:29–39
Gillandt L (1979) Zur Systematik, Autökologie und Biologie der Polychaeten des Helgoländer Felslitorals. Mitt Hambg Zool Mus Inst 76:19–73
Gravier C (1896) Recherches sur les phyllodociens. Bull Sci Fr Belg 294
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1986) Oxygen free radicals and iron in relation to biology and medicine: some problems and concepts. Arch Biochem Biophys 246:501–514
Hartmann-Schröder G (1996) Annelida, Borstenwürmer, Polychaeta. Die Tierwelt Deutschlands,vol 58. Fischer, Jena
Hauser RN (1973) Bestandsänderungen der Macrofauna an einer Station im ostfriesischen Watt. Jahresber Forschstn Norderney 24:171–203
Hayes FR (1929) Contributions to the study of marine gastropods. III. Development, growth and behaviour of Littorina. Contrib Can Biol Fish 4:415–430
Hayward PJ, Ryland JS (1990) The marine fauna of the British Isles and North-West Europe. Oxford University Press, New York
Hurd LE (1985) On the importance of carrion to reproduction in an omnivorous estuarine neogastropod, Ilyanassa obsoleta (Say). Oecologia 65:513–515
Klein-Breteler WCM (1976) Migration of the shore crab, Carcinus maenas, in the Dutch Wadden Sea. Neth J Sea Res 10:338–353
Kuipers BR, Wilde PAWJ, Creutzberg F (1981) Energy flow in a tidal flat ecosystem. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 5:215–221
McKillup SC, McKillup RV (1997) Effect of food supplementation on the growth of an intertidal scavenger. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 148:109–114
Michaelis H (1987) Bestandsaufnahme des eulitoralen Makrobenthos im Jadebusen in Verbindung mit einer Luftbild-Analyse. Jahresber Forschstn Norderney 38:13–97
Miron GY, Desrosiers GL (1990) Distributions and population structures of two intertidal estuarine polychaetes in the lower St. Lawrence Estuary, with special reference to enviromental factors. Mar Biol 105: 297–306
Morton B, Chan K (1999) Hunger rapidly overrides the risk of predation in the subtidal scavenger Nassarius siquijorensis (Gastropoda: Nassariidae): an energy budget and a comparison with the intertidal Nassarius festivus in Hong Kong. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 240:213–228
Petraitis PS (2002) Effects of intraspecific competition and scavenging on growth of the periwinkle Littorina littorea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 236:179–187
Pleijel F (1988) Phyllodoce (Polychaeta, Phyllodocidae) from northern Europe. Zool Scr 17:141–153
Reichert A, Dörjes J (1980) Die Bodenfauna des Crildumersieler Wattes (Jade, Nordsee) und ihre Veränderung nach dem Eiswinter 1978/79. Senckenb Marit 12:213–245
Reise K (1978) Experiments on epibenthic predation in the Wadden Sea. Helgol Wiss Meeresunters 31:55–101
Reise K (1979a) Spatial configurations generated by motile benthic polychaetes. Helgol Wiss Meeresunters 32:55–72
Reise K (1979b) Moderate predation on meiofauna by the macrobenthos of the Wadden Sea. Helgol Wiss Meeresunters 32:453–465
Reise K (1982) Long-term changes in the macrobenthic invertebrate fauna of the Wadden Sea: are polychaetes about to take over? Neth J Sea Res 16:29–36
Reise K (1985) Tidal flat ecology. Ecological studies, vol 54. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Reise K, Herre E, Sturm M (1994) Biomass and abundance of macrofauna in intertidal sediments of Königshafen in the northern Wadden Sea. Helgol Meeresunters 48:201–215
Reise K, Simon M, Herre E (2001) Density dependant recruitment after winter disturbance on tidal flats by the lugworm Arenicola marina. Helgol Mar Res 55:161–165
Sach G (1975) Zur Fortpflanzung des Polychaeten Anaitides mucosa. Mar Biol 31:157–160
Sach G (1977) Zur Fortpflanzung, Histogenese der Geschlechtszellen, Eireifung und frühen Larvalentwicklung von Anaitides mucosa (Polychaeta, Phyllodocidae). Diplomarbeit, Universität Kiel, Kiel, Germany
Smidt ELB (1951) Animal production in the Danish Wadden Sea. Medd Dan Fisk- Havunders1–151
Strasser M, Pieloth U (2001) Recolonization pattern of the polychaete Lanice conchilega on an intertidal sand flat following the severe winter of 1995/96. Helgol Mar Res 55:176–181
Strasser M, Reinwald T, Reise K (2001) Differential effects of the severe winter of 1995/96 on the intertidal bivalves Mytilus edulis, Cerastoderma edule and Mya arenaria in the northern Wadden Sea. Helgol Mar Res 55:190–197
Szymczak R, Waite TD (1988) Generation and decay of hydrogen peroxide in estuarine waters. Aust J Mar Freshw Res 39:298–299
Tallmark B (1980) Population dynamics of Nassarius reticulatus (Gastropoda, Prosobranchia) in Gullmar Fjord, Sweden. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 3:51–62
Thiel M, Reise K (1993) Interaction of nemertines and their prey on tidal flats. Neth J Sea Res 31:163–172
Thiel M, Nordhausen W, Reise K (1996) Nocturnal surface activity of endobenthic nemertines on tidal flats. In: Eleftheriou A, et al (eds) Biology and ecology of shallow coastal waters. Olsen and Olsen, Fredensborg, Denmark, pp 283–289
Wohlenberg E (1937) Die Wattenmeer-Lebensgemeinschaften im Königshafen von Sylt. Helgol Wiss Meeresunters 1:1–92
Yonge CM (1976) Neogastropods—scavengers and predators. In: Yonge CM, Thompson TE (eds) Living marine molluscs. Collins, London, pp 97–108
Acknowledgements
We thank W. Armonies and N. Hernandez for helpful suggestions and reading the manuscript. Financial support was provided by Korea Science and Engineering Foundation within the framework of the KOSEF–DFG Joint Research Program 2002. The experiments comply with the current laws of the country in which the experiments were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CG., Huettel, M., Hong, JS. et al. Carrion-feeding on the sediment surface at nocturnal low tides by the polychaete Phyllodoce mucosa . Marine Biology 145, 575–583 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-004-1334-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-004-1334-6