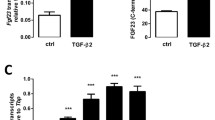
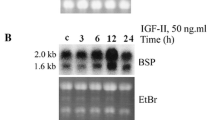
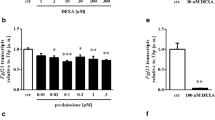
Transforming growth factors-beta (TGF-b1, -b2, and -b3) is secreted from osteoblasts and act as an anabolic factor through its influence of osteoblast proliferation and differentiation and on the synthesis of bone matrix. The ability of progestins to promote bone formation is attributed to their ability to act upon osteoblasts. In the present studies, we observed the effects of progesterone on three TGF-b isoforms (b1, b2, and b3) expression in culture of normal human osteoblast-like cells (hOB). mRNA levels were determined by Northern blot analysis, and TGF-b1, -b2, and -b3 concentrations in conditioned media were determined by ELISA, After 12–24 hours of treatment, progesterone at 10-9 M increased TGF-b1, -b2, and -b3 mRNA levels and protein production in cultures of hOB, treatment with increasing dose of progesterone caused a dose-dependent increase in the expression of TGF-b1, -b2, and -b3 mRNA and protein by hOB. The data suggest that a direct action of progesterone on osteoblasts may be mediated by up-regulated TGF-b isoforms production.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, XH., Liao, EY. & Su, X. Progesterone Upregulates TGF-b Isoforms (b1, b2, and b3) Expression in Normal Human Osteoblast-Like Cells . Calcif Tissue Int 71, 335–343 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-001-2129-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-001-2129-0