Abstract
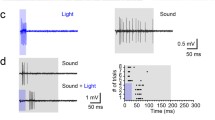
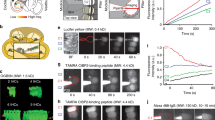
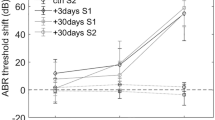
We have used the perfused guinea-pig temporal-bone preparation to study the sound-evoked efflux of aspartate and glutamate, which are putative afferent transmitters in the cochlea. The cochlea was stimulated with white noise at 89, 95, and 101 dB SPL. Cochlear function was monitored by recording the endocochlear potential, the cochlear microphonic, and the summating potential. In silence, there was a low basal efflux of both amino acids. A significant and intensity dependent sound-evoked efflux of aspartate was observed at all levels, whereas a significant efflux of glutamate was found only at the 101 dB SPL level. Immunohistochemistry of sections from the organ of corti showed an ubiquitous distribution of glutamate-like immunoreactivity in the sensory organ and ganglion, whereas aspartate-like immunoreactivity was found in the region of the inner hair cells and in the spiral ganglion. In view of these findings, we suggest that not only glutamate, but also aspartate may have a neurotransmitter role in the afferent pathway of the cochlea.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 7 November 1997 / Accepted: 3 March 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jäger, W., Goiny, M., Herrera-Marschitz, M. et al. Sound-evoked efflux of excitatory amino acids in the guinea-pig cochlea in vitro. Exp Brain Res 121, 425–432 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210050477
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210050477