Abstract.
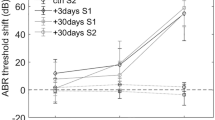
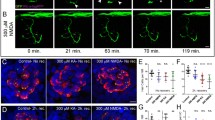
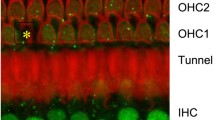
Aspartate and glutamate were monitored in the scala tympani of the guinea pig cochlea using in vivo microdialysis before and during noise exposure. Moderate level broad band noise [105 dB sound pressure level (SPL), 30 min] neither altered the levels of aspartate or glutamate, nor auditory brainstem response (ABR) thresholds. High level noise exposure (135 dB SPL, 30 min) caused a large increase in aspartate (330%), a smaller increase in glutamate (150%), and a permanent ABR threshold shift of 60–75 dB between 2.0 and 12.5 kHz. Morphological analysis of the cochlea revealed a collapse of supporting structures, swelling of the afferent dendrites under the inner hair cells, and outer hair cell loss. Pretreatment with the NMDA antagonist, MK 801 (1 mg/kg body weight, i.p.) 1 h before noise exposure protected the afferent dendrites from swelling but did not protect the collapse of supporting structures, outer hair cell loss, or auditory thresholds. In conclusion, the noise-induced increase in aspartate and glutamate release in the cochlea and the protective effect of NMDA antagonism suggest that these two neurotransmitters are involved in noise-induced hearing loss.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jäger, W., Goiny, M., Herrera-Marschitz, M. et al. Noise-induced aspartate and glutamate efflux in the guinea pig cochlea and hearing loss. Exp Brain Res 134, 426–434 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210000470
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210000470