Abstract
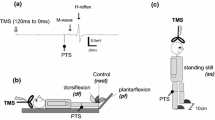
This paper contrasts responses in the soleus muscle of normal human subjects to two major inputs: the tibial nerve (TN) and the corticospinal tract. Paired transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) of the motor cortex at intervals of 10–25 ms strongly facilitated the motor evoked potential (MEP) produced by the second stimulus. In contrast, paired TN stimulation produced a depression of the reflex response to the second stimulus. Direct activation of the pyramidal tract did not facilitate a second response, suggesting that the MEP facilitation observed using paired TMS occurred in the cortex. A TN stimulus also depressed a subsequent MEP. Since the TN stimulus depressed both inputs, the mechanism is probably post-synaptic, such as afterhyperpolarization of motor neurons. Presynaptic mechanisms, such as homosynaptic depression, would only affect the pathway used as a conditioning stimulus. When TN and TMS pulses were paired, the largest facilitation occurred when TMS preceded TN by about 5 ms, which is optimal for summation of the two pathways at the level of the spinal motor neurons. A later, smaller facilitation occurred when a single TN stimulus preceded TMS by 50–60 ms, an interval that allows enough time for the sensory afferent input to reach the sensory cortex and be relayed to the motor cortex. Other work indicates that repetitively pairing nerve stimuli and TMS at these intervals, known as paired associative stimulation, produces long-term increases in the MEP and may be useful in strengthening residual pathways after damage to the central nervous system.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen R (2004) Interactions between inhibitory and excitatory circuits in the human motor cortex. Exp Brain Res 154:1–10
Chen R, Tam A, Butefisch C, Corwell B, Ziemann U, Rothwell JC, Cohen LG (1998) Intracortical inhibition and facilitation in different representations of the human motor cortex. J Neurophysiol 80:2870–2881
Chen XY, Wolpaw JR, Jakeman LB, Stokes BT (1999) Operant conditioning of H-reflex increase in spinal cord-injured rats. J Neurotrauma 16:175–186
Curtis DR, Eccles JC (1960) Synaptic action during and after repetitive stimulation. J Physiol 150:374–398
Darling WG, Wolf SL, Butler AJ (2006) Variability of motor potentials evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation depends on muscle activation. Exp Brain Res 174:376–385
Day BL, Dressler D, Maertens de Noordhout A, Marsden CD, Nakashima K, Rothwell JC, Thompson PD (1989) Electric and magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex: surface EMG and single motor unit responses. J Physiol 412:449–473
Deletis V, Schild JH, Beric A, Dimitrijevic MR (1992) Facilitation of motor evoked potentials by somatosensory afferent stimulation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 85:302–310
Deuschl G, Michels R, Berardelli A, Schenck E, Inghilleri M, Lucking CH (1991) Effects of electric and magnetic transcranial stimulation on long latency reflexes. Exp Brain Res 83:403–410
Di Lazzaro V, Oliviero A, Profice P, Meglio M, Cioni B, Tonali P, Rothwell JC (2001) Descending spinal cord volleys evoked by transcranial magnetic and electrical stimulation of the motor cortex leg area in conscious humans. J Physiol 537:1047–1058
Di Lazzaro V, Oliviero A, Pilato F, Saturno E, Dileone M, Mazzone P, Insola A, Tonali PA, Rothwell JC (2004) The physiological basis of transcranial motor cortex stimulation in conscious humans. Clin Neurophysiol 115:255–266
Di Lazzaro V, Dileone M, Pilato F, Profice P, Ranieri F, Musumeci G, Angelucci F, Sabatelli M, Tonali PA (2006) Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for ALS. A preliminary controlled study. Neurosci Lett 408:135–140
Hoffmann P (1918) Ueber die Beziehungen der Sehnenreflexe zur willkuerlichen Bewegung und zum Tonus. Zeitschrift fuer Biologie 68:351–370
Hultborn H, Illert M, Nielsen J, Paul A, Ballegaard M, Wiese H (1996) On the mechanism of the post-activation depression of the H-reflex in human subjects. Exp Brain Res 108:450–462
Jackson A, Baker SN, Fetz EE (2006) Tests for presynaptic modulation of corticospinal terminals from peripheral afferents and pyramidal tract in the macaque. J Physiol 573:107–120
Kernell D (1965) The limits of firing frequency in cat lumbosacral motoneurones possessing different time course of afterhyperpolarization. Acta Physiol Scand 65:67–100
Khaslavskaia S, Sinkjaer T (2005) Motor cortex excitability following repetitive electrical stimulation of the common peroneal nerve depends on the voluntary drive. Exp Brain Res 162:497–502
Khaslavskaia S, Ladouceur M, Sinkjaer T (2002) Increase in tibialis anterior motor cortex excitability following repetitive electrical stimulation of the common peroneal nerve. Exp Brain Res 145:309–315
Knash ME, Kido A, Gorassini M, Chan KM, Stein RB (2003) Electrical stimulation of the human common peroneal nerve elicits lasting facilitation of motor-evoked potentials. Exp Brain Res 221:366–377
Kujirai T, Caramia M, Rothwell J, Day B, Thompson P, Ferbert A, Wroe S, Asselman P, Marsden C (1993) Corticocortical inhibition in human motor cortex. J Physiol 471:501–519
Kujirai K, Kujirai T, Sinkjaer T, Rothwell JC (2006) Associative plasticity in human motor cortex during voluntary muscle contraction. J Neurophysiol 96:1337–1346
Matthews PB (1996) Relationship of firing intervals of human motor units to the trajectory of post-spike after-hyperpolarization and synaptic noise. J Physiol 492:597–628
McPhedran AM, Wuerker RB, Henneman E (1965) Properties of motor units in a homogeneous red muscle (soleus) of the cat. J Neurophysiol 28:71–84
Morita H, Baumgarten J, Petersen N, Christensen LO, Nielsen J (1999) Recruitment of extensor-carpi-radialis motor units by transcranial magnetic stimulation and radial-nerve stimulation in human subjects. Exp Brain Res 128:557–562
Mrachacz-Kersting N, Fong M, Murphy BA, Sinkjaer T (2007) Changes in excitability of the cortical projections to the human tibialis anterior after paired associative stimulation. J Neurophysiol 97:1951–1958
Nakamura H, Kitagawa H, Kawaguchi Y, Tsuji H (1997) Intracortical facilitation and inhibition after transcranial magnetic stimulation in conscious humans. J Physiol 498:817–823
Nielsen J, Petersen N, Deuschl G, Ballegaard M (1993) Task-related changes in the effect of magnetic brain stimulation on spinal neurones in man. J Physiol 471:223–243
Petersen N, Christensen LO, Morita H, Sinkjaer T, Nielsen J (1998) Evidence that a transcortical pathway contributes to stretch reflexes in the tibialis anterior muscle in man. J Physiol 512:267–276
Petersen N, Taylor JL, Gandevia SC (2002) The effect of electrical stimulation of the corticospinal tract on motor units of the human biceps brachii. J Physiol 544:277–284
Petersen NT, Pyndt HS, Nielsen JB (2003) Investigating human motor control by transcranial magnetic stimulation. Exp Brain Res 152:1–16
Pierrot-Deseilligny E, Burke D (2005) The Circuitry of the human spinal cord: its role in motor control and movement disorders. Cambridge University Press
Reis J, Swayne OB, Vandermeeren Y, Camus M, Dimyan MA, Harris-Love M, Perez MA, Ragert P, Rothwell JC, Cohen LG (2008) Contribution of transcranial magnetic stimulation to the understanding of cortical mechanisms involved in motor control. J Physiol 586:325–351
Rossi-Durand C, Jones KE, Adams S, Bawa P (1999) Comparison of the depression of H-reflexes following previous activation in upper and lower limb muscles in human subjects. Exp Brain Res 126:117–127
Roy FD, Norton JA, Gorassini MA (2007) Role of sustained excitability of the leg motor cortex after transcranial magnetic stimulation in associative plasticity. J Neurophysiol 98:657–667
Stefan K, Kunesch E, Cohen LG, Benecke R, Classen J (2000) Induction of plasticity in the human motor cortex by paired associative stimulation. Brain 123(Pt 3):572–584
Stefan K, Kunesch E, Benecke R, Cohen LG, Classen J (2002) Mechanisms of enhancement of human motor cortex excitability induced by interventional paired associative stimulation. J Physiol 543:699–708
Stein R, Thompson A (2006) Muscle reflexes in motion: how, what and why? Exerc Sport Sci Rev 34:145–153
Stein RB, Chong S, Everaert DG, Rolf R, Thompson AK, Whittaker M, Robertson J, Fung J, Preuss R, Momose K, Ihashi K (2006) A multicenter trial of a footdrop stimulator controlled by a tilt sensor. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 20:371–379
Stein RB, Everaert DG, Chong S, Thompson AK (2007) Using FES for foot drop strengthens cortico-spinal connections. 12th Annual Conference International FES Society
Stokic DS, McKay WB, Scott L, Sherwood AM, Dimitrijevic MR (1997) Intracortical inhibition of lower limb motor-evoked potentials after paired transcranial magnetic stimulation. Exp Brain Res 117:437–443
Taylor JL, Gandevia SC (2004) Noninvasive stimulation of the human corticospinal tract. J Appl Physiol 96:1496–1503
Uy J, Ridding MC, Hillier S, Thompson PD, Miles TS (2003) Does induction of plastic change in motor cortex improve leg function after stroke? Neurology 61:982–984
Wassermann EM (1998) Risk and safety of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation: report and suggested guidelines from the international workshop on the safety of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, June 5–7, 1996. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 108:1–16
Windhorst U (1996) On the role of recurrent inhibitory feedback in motor control. Prog Neurobiol 49:517–587
Zehr EP, Stein RB (1999) Interaction of the Jendrássik maneuver with segmental presynaptic inhibition. Exp Brain Res 124:474–480
Acknowledgments
The research presented here was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Christopher and Dana Reeve Foundation. We thank Dr. Parveen Bawa for helpful comments and discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poon, D.E., Roy, F.D., Gorassini, M.A. et al. Interaction of paired cortical and peripheral nerve stimulation on human motor neurons. Exp Brain Res 188, 13–21 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1334-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1334-8