Abstract
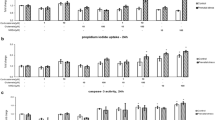
The principal glucocorticoid in rats, corticosterone, interacts with neurons in the limbic system and leads to morphological and behavioral changes. Putative corticosterone-triggered mediators are neurotrophins. In the present study we investigated the effects of early postnatal corticosterone treatment in rats on neurotrophic factors of the nerve growth factor (NGF) family and their receptors. Newborn rats were treated with corticosterone-containing polymers until postnatal day 12. The mRNA and protein levels of the neurotrophins of the NGF family (NGF, BDNF, NT-3 and NT-4/5) and their receptors (trkA, trkB, trkC and p75) were quantified in septum and hippocampus using RT-PCR. In the septal region, we found an unchanged mRNA expression after corticosterone treatment, whereas in the hippocampus there was a general increase in mRNA. Particularly, the gene expression of NGF, NT-3, and the high affinity receptors trkA, trkB and trkC increased significantly. Quantification of the neurotrophin protein levels using an ELISA revealed significant treatment effects for NGF and NT-4/5 in the hippocampus. The present study of corticosterone treatment in young rats demonstrates interactions of steroid hormones with neurotrophic factors and their receptors in the septo-hippocampal system during the first two postnatal weeks.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbany G, Persson H (1992) Regulation of neurotrophin mRNA expression in the rat brain by glucocorticoids. Eur J Neurosci 4:396–403
Chao HM, McEwen BS (1994) Glucocorticoids and the expression of mRNAs for neurotrophins, their receptors and GAP-43 in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 26:271–276
Ebendal T (1989) NGF in CNS: experimental data and clinical implications. Prog Growth Factor Res 1:143–159
Erhard PB, Ganter U, Stalder A, Bauer J, Otten U (1993) Expression of functional trk-proto-oncogene in human monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:5423–5427
Ernfors P, Wetmore C, Olson L, Persson H (1990) Identification of cells in rat brain and peripheral tissues expressing mRNA for members of the nerve growth factor family. Neuron 5:511–526
Gage FH, Chen KS, Buzsaki G, Armstrong D (1988) Experimental approaches to age-related cognitive impairments. Neurobiol Aging 9:645–655
Gerlach JL, McEwen BS (1972) Rat brain binds adrenal steroid hormone: radioautography of hippocampus with corticosterone. Science 175:1133–1136
Haik-Creguer KL, Dunbar GL, Sabel BA, Schroeder U (1998) Small drug sample fabrication of controlled release polymers using the microextrusion method. J Neurosci Methods 80:37–40
Henning SJ (1978) Plasma concentrations of total and free corticosterone during development in the rat. Am J Physiol 235:E451–E456
Ip NY, Ibanez CF, Nye SH, McClain J, Jones PF, Gies DR, Belluscio L, Le Beau MM, Espinosa 3rd R, Squinto SP (1992) Mammalian neurotrophin-4: structure, chromosomal localization, tissue distribution, and receptor specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:3060–3064
Jamieson PM, Chapman KE, Seckl JR (1999) Tissue- and temporal-specific regulation of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 by glucocorticoids in vivo. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 68:245–250
Joels M, Vreugdenhil E (1998) Corticosteroids in the brain. Cellular and molecular actions. Mol Neurobiol 17:87–108
Knizley Jr H (1972) The hippocampus and septal area as primary target sites for corticosterone. J Neurochem 19:2737–2745
Lambert JJ, Belelli D, Hill-Venning C, Peters JA (1995) Neurosteroids and GABAA receptor function. Trends Pharmacol Sci 16:295–303
Linke R, Soriano E, Frotscher M (1994) Transient dendritic appendages on differentiating septohippocampal neurons are not the sites of synaptogenesis. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 83:67–78
Lipp HP, Schwegler H, Crusio WE, Wolfer DP, Leisinger-Trigona MC, Heimrich B, Driscoll P (1989) Using genetically-defined rodent strains for the identification of hippocampal traits relevant for two-way avoidance behavior: a non-invasive approach. Experientia 45:845–859
Lüesse HG, Roskoden T, Linke R, Otten U, Heese K, Schwegler H (1998) Modulation of mRNA expression of the neurotrophins of the nerve growth factor family and their receptors in the septum and hippocampus of rats after transient postnatal thyroxine treatment. I. Expression of nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neurotrophin-3, and neurotrophin 4 mRNA. Exp Brain Res 119:1–8
Majewska MD (1992) Neurosteroids: endogenous bimodal modulators of the GABAA receptor. Mechanism of action and physiological significance. Prog Neurobiol 38:379–395
McEwen BS (1999) Stress and hippocampal plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci 22:105–122
McEwen BS, MacEwen BS, Weiss JM (1970) The uptake and action of corticosterone: regional and subcellular studies on rat brain. Prog Brain Res 32:200–212
Milner TA, Loy R, Amaral DG (1983) An anatomical study of the development of the septohippocampal projection in the rat. Dev Brain Res 8:343–371
Minkwitz HG (1976a) Zur Entwicklung der Neuronenstruktur des Hippokampus während der prä- und postnatalen Ontogenese der Albinoratte. I. Mitteilung: Neurohistologische Darstellung der Entwicklung langaxoniger Neurone aus den Regionen CA3 und CA4 [Development of the neuronal structure of the hippocampus during pre- and post-natal ontogenesis in the albino rat. I. Neurohistological demonstration of the development of lung-axonal neurons in the CA3 and CA4 regions]. J Hirnforsch 17:213–231
Minkwitz HG (1976b) Zur Entwicklung der Neuronenstruktur des Hippokampus während der prä- und postnatalen Ontogenese der Albinoratte. II. Mitteilung: Neurohistologische Darstellung der Entwicklung von Interneuronen und des Zusammenhanges lang- und kurzaxoniger Neurone [Development of neuronal structure in the hippocampus during pre- and post-natal ontogenesis in the albino rat. II. Neurohistological demonstration of the development of interneurons and of the relationship between long- and short-axonal neurons]. J Hirnforsch 17:233–253
Minkwitz HG (1976c) Zur Entwicklung der Neuronenstruktur des Hippokampus während der prä- und postnatalen Ontogenese der Albinoratte. III. Mitteilung: morphometrische Erfassung der ontogenetischen Veränderungen in Dendritenstruktur und Spinebesatz an Pyramidenneuronen (CA1) des Hippocampus [Development of neuronal structure in the hippocampus during pre- and post-natal ontogenesis in the albino rat. III. Morphometric determination of ontogenetic changes in dendrite structure and spine distribution on pyramidal neurons (CA1) of the hippocampus]. J Hirnforsch 17:255–275
Minkwitz HG, Holz L (1975) Die ontogenetische Entwicklung von Pyramidenneuronen aus dem Hippocampus (CA1) der Ratte [The ontogenetic development of pyramidal neurons in the hippocampus (CA1) of the rat]. J Hirnforsch 16:37–54
Mizoguchi K, Kunishita T, Chui DH, Tabira T (1992) Stress induces neuronal death in the hippocampus of castrated rats. Neurosci Lett 138:157–160
Packan DR, Sapolsky RM (1990) Glucocorticoid endangerment of the hippocampus: tissue, steroid and receptor specificity. Neuroendocrinology 51:613–618
Patchev VK, Montkowski A, Rouskova D, Koranyi L, Holsboer F, Almeida OFX (1997) Neonatal treatment of rats with the neuroactive steroid tetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone (THDOC) abolishes the behavioral and neuroendocrine consequences of adverse early life events. J Clin Invest 99:962–966
Pfaff DW, Gerlach JL, McEwen BS, Ferin M, Carmel P, Zimmerman EA (1976) Autoradiographic localization of hormone-concentrating cells in the brain of the female rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 170:279–293
Rhees RW, Grosser BI, Stevens W (1975) Effect of steroid competition and time on the uptake of (3H)corticosterone in the rat brain; an autoradiographic study. Brain Res 83:293–300
Roskoden T, Heese K, Otten U, Schwegler H (1999) Modulation of mRNA expression of the neurotrophins of the nerve-growth-factor family and their receptors in the septum and hippocampus of rats after transient postnatal thyroxine treatment. II. Effects on p75 and trk receptor expression. Exp Brain Res 127:307–313
Sapolsky RM, McEwen BS, Rainbow TC (1983) Quantitative autoradiography of [3H]corticosterone receptors in rat brain. Brain Res 271:331–334
Sapolsky RM, Krey LC, McEwen BS (1985) Prolonged glucocorticoid exposure reduces hippocampal neuron number: implications for aging. J Neurosci 5:1222–1227
Scaccianoce S, Catalani A, Lombardo K, Consoli C, Angelucci L (2001) Maternal glucocorticoid hormone influences nerve growth factor expression in the developing rat brain. Neuroreport 12:2881–2884
Schaaf MJ, Hoetelmans RW, de Kloet ER, Vreugdenhil E (1997) Corticosterone regulates expression of BDNF and trkB but not NT-3 and trkC mRNA in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci Res 48:334–341
Schwegler H (1995) Transient postnatal thyroxine treatment leads to an increased number of cholinergic neurons in the medial septum and to a higher density of cholinergic fibers in hippocampal CA3 in rats. Neurosci Lett 198:197–200
Schwegler H, Crusio WE, Lipp HP, Brust I, Mueller GG (1991) Early postnatal hyperthyroidism alters hippocampal circuitry and improves radial-maze learning in adult mice. J Neurosci 11:2102–2106
Scully JL, Otten U (1995) Neurotrophin expression modulated by glucocorticoids and oestrogen in immortalized hippocampal neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 31:158–164
Smith MA, Makino S, Kvetnansky R, Post RM (1995) Stress and glucocorticoids affect the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 mRNAs in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 15:1768–1777
Stöhr T, Schulte Wermeling D, Szuran T, Pliska V, Domeney A, Welzl H, Weiner I, Feldon J (1998) Differential effects of prenatal stress in two inbred strains of rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 59:799–805
Takahashi LK (1998) Prenatal stress: consequences of glucocorticoids on hippocampal development and function. Int J Dev Neurosci 16:199–207
Tizabi Y, Gilad VH, Gilad GM (1989) Effects of chronic stressors or corticosterone treatment on the septohippocampal cholinergic system of the rat. Neurosci Lett 105:177–182
Watanabe Y, Gould E, McEwen BS (1992) Stress induces atrophy of apical dendrites of hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons. Brain Res 588:341–345
Wetmore C, Ernfors P, Persson H, Olson L (1990) Localization of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA to neurons in the brain by in situ hybridization. Exp Neurol 109:141–152
Woolley CS, Gould E, McEwen BS (1990) Exposure to excess glucocorticoids alters dendritic morphology of adult hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Brain Res 531:225–231
Wrange O, Yu ZY (1983) Mineralcorticoid receptor in rat kidney and hippocampus: characterization and quantitation by isoelectric focusing. Endocrinology 113:243–250
Zimmer J (1978) Development of the hippocampus and the fascia dentata. In: Corner MA, Baker RE, van de Poll NE, Swaab DF, Uyling HBM (eds) Maturation of the nervous system (Prog Brain Res 48). Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 171–189
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roskoden, T., Otten, U. & Schwegler, H. Early postnatal corticosterone administration regulates neurotrophins and their receptors in septum and hippocampus of the rat. Exp Brain Res 154, 183–191 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-003-1656-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-003-1656-5