Abstract
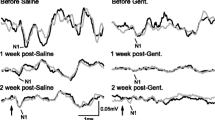
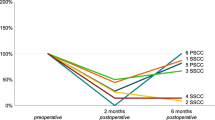
This study provides the first systematic examination of the effects of intratympanic gentamicin instillation on vestibulo-ocular responses of guinea pigs during both Earth-vertical yaw axis and off-vertical axis rotation. A scleral search coil was sutured to the right eye of pigmented female guinea pigs prior to trans-bullar instillation of a 0.2-ml bolus of either 20 mg/ml or 40 mg/ml of gentamicin (1) into the right middle ear (unilateral treatment groups) or (2) into both ears (bilateral treatment groups). Two weeks later, eye movement responses were tested during yaw axis sinusoidal rotation at 7 frequencies (0.02, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1 and 2 Hz, 40 deg/s peak velocity) and during off-vertical axis rotation at five constant velocities (20, 40, 60, 80 and 100 deg/s), tilted 30 deg relative to the earth-vertical axis. The main result was that unilateral trans-bullar gentamicin instillation produced almost exclusively unidirectional deficits in horizontal angular vestibulocular reflex (HVOR) responses and modulation and bias responses to off-vertical axis rotation (OVAR). The HVOR gain was reduced during rotation toward the injected ear in a dose-dependent manner for frequencies of 1 Hz and lower, but there was no effect on responses during rotation toward the intact ear. Further, the modulation and bias responses to OVAR were reduced profoundly in a dose-dependent manner during rotation toward the treated ear. It is suggested that these effects indicate selective cytotoxic and/or physiologic effects of gentamicin intoxication in the inner ear or, possibly, the vestibular nerve and central nervous system.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison RS, Eizenmen M, Tomlinson RD, Nedzelski J, Sharpe JA (1997) Vestibulo-ocular reflex deficits to rapid head turns following intratypmanic gentamicin instillation. J Vestib Res 7:369–380
Andrews JC, Li J, Koyama S, Hoffman LF (1997) Vestibular and optokinetic function in the normal guinea pig. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 106:838–847
Angelaki DE, Hess BJ (1996) Three-dimensional organization of otolith-ocular reflexes in rhesus monkeys. I. Linear acceleration responses during off-vertical axis rotation. J Neurophysiol 75:2405–424
Angelaki DE, Perachio AA (1993) Contribution of irregular semicircular canal afferents to the horizontal vestibulo-ocular responses during constant velocity rotation. J Neurophysiol 69:996–999
Angelaki DE, Perachio AA, Mustari MJ, Strunk CL (1992) Role of irregular otolith afferents in the steady-state nystagmus during off-vertical axis rotation. J Neurophysiol 68:1895–1900
Aran JM, Erre JP, Guilhaume A, Aurousseau C (1982) The comparative ototoxicities of gentamicin, tobramycin and dibekacin in the guinea pig. A functional and morphological cochlear and vestibular study. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 390:1–30
Bareggi R, Grill V, Narducci P, Zweyer M, Tesei L, Russolo M (1990) Gentamicin ototoxicity: histological and ultrastructural alterations after transtympanic administration. Pharmacol Res 22:635–644
C J (1952) Living without a balancing mechanism. N Engl J Med 246:458–460
Chin KW, Lopez I, Lee SC, Honrubia V (1999) Glutamate-like immunoreactivity during hair cell recovery after gentamicin exposure in the chinchilla vestibular sensory periphery. Laryngoscope 109:1037–1044
Curthoys IS (1982) The response of primary horizontal canal neurons in the rat and the guinea pig to angular acceleration. Exp Brain Res 47:286–294
Curthoys IS, Curthoys EJ, Blanks RHI, Markham CH (1975) The orientation of the semicircular canals in the guinea pig. Acta Otolaryngol 80:197–205
Darlot C, Denise P (1988) Nystagmus induced by off-vertical axis rotation in the cat. Exp Brain Res 73:78–90
Escudero M, de Waele C, Vibert N, Berthoz A, Vidal PP (1993) Saccadic eye movements and the horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflexes in the intact guinea-pig. Exp Brain Res 97:254–262
Forge A, Li L, Nevill G (1998) Hair cell recovery in the vestibular sensory epithelia of mature guinea pigs. J Comp Neurol 397:69–88
Furman JM, Cass SP (1999) Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. N Engl J Med 341:1590–1596
Gilchrist DP, Curthoys IS, Cartwright AD, Burgess AM, Topple AN, Halmagyi M (1998) High acceleration impulsive rotations reveal severe long-term deficits of the horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex in the guinea pig. Exp Brain Res 123:242–254
Harada Y, Sera K, Ohya T, Tagashira N, Suzuki M, Takumida M (1991) Effect of gentamicin on vestibular ganglion. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) Suppl 481:135–138
Hess BJ, Dieringer N (1990) Spatial organization of the maculo-ocular reflex of the rat: Responses during off-vertical axis rotation. Eur J Neurosci 2:909–919
Hess BJ, Dieringer N (1991) Spatial organization of linear vestibuloocular reflexes of the rat: responses during horizontal and vertical linear acceleration. J Neurophysiol 66:1805–1818
Hirsch BE, Kamerer DB (1997) Role of chemical labyrinthectomy in the treatment of Meniere's disease. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 30:1039–1049
Hoffer ME, Balough B, Henderson J, DeCicco M, Wester D, O'Leary MJ, Kopke R (1997) Use of sustained release vehicles in the treatment of Meniere's disease. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 30: 1159–1066
Jackson GG, Arcieri G (1971) Ototoxicity of gentamicin in man: a survey and controlled analysis of clinical experience in the United States. J Infect Dis Suppl 124:124–130
Lopez I, Honrubia V, Lee SC, Schoeman G, Beykirch K (1997) Quantification of the process of hair cell loss and recovery in the chinchilla crista ampullaris after gentamicin treatment. Int J Dev Neurosci 15:447–461
Lopez I, Honrubia V, Lee S C, Chung WH, Li G, Beykirch K, Micevych P (1999) The protective effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor after gentamicin ototoxicity. Am J Otol 20:317–324
Maruta J, Simpson JI, Raphan T, Cohen B (2001) Orienting otolith-ocular reflexes in the rabbit during static and dynamic tilts and off-vertical axis rotation. Vision Res 41:3255–3270
Minor LB (1999) Intratympanic gentamicin for control of vertigo in Meniere's disease: vestibular signs that specify completion of therapy. Am J Otol 20:209–219
Minor LB, Goldberg JM (1991) Vestibular-nerve inputs to the vestibulo-ocular reflex: a functional-ablation study in the squirrel monkey. J Neurosci 11:1636–1648
Murofushi T, Halmagyi GM, Yavor RA (1997) Intratympanic gentamicin in Meniere's disease: results of therapy. Am J Otol 18:52–57
Parnes LS, Riddell D (1993) Irritative spontaneous nystagmus following intratympanic gentamicin for Meniere's disease. Laryngoscope 103:745–749
Pettorossi VE, Bamonte F, Errico P, Ongini E, Draicchio F, Sabetta F (1986) Vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) in guinea pigs: impairment induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) Suppl 101:378–388
Pfleiderer AG (1998) The current role of local intratympanic gentamicin therapy in the management of unilateral Meniere's disease. Clin Otolaryngol 23:34–41
Pyykko I, Ishizaki H, Kaasinen S, Aalto H (1994) Intratympanic gentamicin in bilateral Meniere's disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 110:162–167
Robinson DA (1963) A method of measuring eye movement using a scleral search coil in a magnetic field. IEEE Trans Bio-Med Engng 10:137–145
Rosen JH, Thompson GC, Hill Britton B, Thompson AM (1998) Neurodegenerative changes in the guinea pig brainstem after intratympanic injection of gentamicin. Brain Res 813:177–180
Sera K, Harada Y, Tagashira N, Suzuki M, Hirakawa K, Ohya T (1987) Morphological changes in the vestibular epithelia and ganglion induced by ototoxic drug. Scanning Microsc 1:1191–1197
Smith PF, Curthoys IS (1989) Mechanisms of recovery following unilateral labyrinthectomy: a review. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 14:155–180
Stover T, Yagi M, Raphael Y (2000) Transduction of the contralateral ear after adenovirus-mediated cochlear gene transfer. Gene Ther 7:377–383
Takumida M, Popa R, Anniko M (1999) Free radicals in the guinea pig inner ear following gentamicin exposure. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 61:63–70
Tjernstrom O, Denneberg T, Harris S, Nordstrom L, Toremalm N G (1982) Ototoxicity of netilmicin. Acta Otolaryngol 94:421–429
Vibert G, de Waele C, Escudero M, Vidal PP (1993) The horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex in the hemilabyrinthectomized guinea-pig. Exp Brain Res 97:263–273
Warchol ME, Lambert PR, Goldstein BJ, Forge A, Corwin JT (1993) Regenerative proliferation in inner ear sensory epithelia from adult guinea pigs and humans. Science 259: 1619–1622
Watanuki K, Stupp HF, Gottesberge AMZ (1972) Toxic effects of gentamycin upon the peripheral vestibular sensory organs. Laryngoscope 82:363–371
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Robert H. Schor, Ph.D., for computer programming assistance and helpful comments on an earlier version of the manuscript. The Office of Naval Research supported this research with ongoing funding of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones, G.E.G., Balaban, C.D., Jackson, R.L. et al. Effect of trans-bullar gentamicin treatment on guinea pig angular and linear vestibulo-ocular reflexes. Exp Brain Res 152, 293–306 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-003-1531-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-003-1531-4