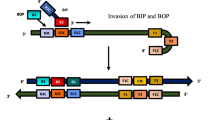
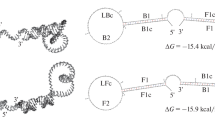
Abstract
Since RNA is an important biomarker of many infectious pathogens, RNA detection of pathogenic organisms is crucial for disease diagnosis and environmental and food safety. By simulating the base mismatch during DNA replication, this study presents a novel three-way junction structure-mediated reverse transcription-free exponential amplification reaction (3WJ-RTF-EXPAR) for the rapid and sensitive detection of pathogen RNA. The target RNA served as a switch to initiate the reaction by forming a three-way junction (3WJ) structure with the ex-trigger strand and the ex-primer strand. The generated trigger strand could be significantly amplified through EXPAR to open the stem-loop structure of the molecular beacon to emit fluorescence signal. The proofreading activity of Vent DNA polymerase, in combination with the unique structure of 2+1 bases at the 3′-end of the ex-primer strand, could enhance the role of target RNA as a reaction switch to reduce non-specific amplification and ensure excellent specificity to differentiate target pathogen from those causing similar symptoms. Furthermore, detection of target RNA showed a detection limit of 1.0×104 copies/mL, while the time consumption was only 20 min, outperforming qRT-LAMP and qRT-PCR, the most commonly used RNA detection methods in clinical practice. All those indicates the great application prospects of this method in clinical diagnostic.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Browne DJ, Brady JL, Waardenberg AJ, Loiseau C, Doolan DL. An analytically and diagnostically sensitive RNA extraction and RT-qPCR protocol for peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Front Immunol. 2020;11:402. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00402.
Li Y, Zheng Q, Bao C, Li S, Guo W, Zhao J, et al. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: a promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015;25:981–4. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2015.82.
Várallyay É, Burgyán J, Havelda Z. MicroRNA detection by Northern blotting using locked nucleic acid probes. Nat Protoc. 2008;3:190–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.528.
Nolan T, Hands RE, Bustin SA. Quantification of mRNA using real-time RT-PCR. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:1559–82. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.236.
Kenzelmann M, Maertens S, Hergenhahn M, Kueffer S, Hotz-Wagenblatt A, Li L, et al. Microarray analysis of newly synthesized RNA in cells and animals. Proc Nat Acad Sci. 2007;104:6164–9. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0610439104.
Franz O, Bruchhaus I, Roeder T. Verification of differential gene transcription using virtual Northern blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;27:e3. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/27.11.e3.
Hiley SL, Jackman J, Babak T, Trochesset M, Morris QD, Phizicky E, et al. Detection and discovery of RNA modifications using microarrays. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:e2–e2. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gni002.
Hong M, Tao S, Zhang L, Diao LT, Huang X, Huang S, et al. RNA sequencing: new technologies and applications in cancer research. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13:166. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-01005-x.
Alcoba-Florez J, González-Montelongo R, Íñigo-Campos A, de Artola DG, Gil-Campesino H. The microbiology technical support T, et al. Fast SARS-CoV-2 detection by RT-qPCR in preheated nasopharyngeal swab samples. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;97:66–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.099.
Jenkins HH, Lopez AAT, Tarantini FS, Tomlin H, Scales D, Lee IN, et al. Performance evaluation of a non-invasive one-step multiplex RT-qPCR assay for detection of SARS-CoV-2 direct from saliva. Sci Rep. 2022;12:11553. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-15616-6.
Sarkar MMH, Naser SR, Chowdhury SF, Khan MS, Habib MA, Akter S, et al. M gene targeted qRT-PCR approach for SARS-CoV-2 virus detection. Sci Rep. 2023;13:16659. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-43204-9.
Li Y, Zhang X, Liao Y, Shi C, Wang Y, Mu X, et al. Engineering of a chimeric template triggers rNase H-based isothermal amplification approach for sensitive detection of pathogen RNA. Anal Chem. 2023;95:18249–57. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.3c04098.
Sharma A, Balda S, Apreja M, Kataria K, Capalash N, Sharma P. COVID-19 diagnosis: current and future techniques. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;193:1835–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.11.016.
Colbert AJ, Lee DH, Clayton KN, Wereley ST, Linnes JC, Kinzer-Ursem TL. PD-LAMP smartphone detection of SARS-CoV-2 on chip. Anal Chim Acta. 2022;1203:339702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2022.339702.
Van Ness J, Van Ness LK, Galas DJ. Isothermal reactions for the amplification of oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:4504–9. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0730811100.
Qian J, Zhang Q, Liu M, Wang Y, Lu M. A portable system for isothermal amplification and detection of exosomal microRNAs. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;196:113707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113707.
Zhang Y, Zhang CY. Sensitive detection of microRNA with isothermal amplification and a single-quantum-dot-based nanosensor. Anal Chem. 2012;84:224–31. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac202405q.
Mittal S, Thakur S, Mantha AK, Kaur H. Bio-analytical applications of nicking endonucleases assisted signal-amplification strategies for detection of cancer biomarkers -DNA methyl transferase and microRNA. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;124–125:233–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.10.001.
Kim HY, Song J, Park HG. Ultrasensitive isothermal method to detect microRNA based on target-induced chain amplification reaction. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021;178:113048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113048.
Wei S, Chen G, Jia X, Mao X, Chen T, Mao D, et al. Exponential amplification reaction and triplex DNA mediated aggregation of gold nanoparticles for sensitive colorimetric detection of microRNA. Anal Chim Acta. 2020;1095:179–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.10.020.
Wang K, Zhang K, Lv Z, Zhu X, Zhu L, Zhou F. Ultrasensitive detection of microRNA with isothermal amplification and a time-resolved fluorescence sensor. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;57:91–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.01.058.
Reid MS, Paliwoda RE, Zhang H, Le XC. Reduction of background generated from template-template hybridizations in the exponential amplification reaction. Anal Chem. 2018;90:11033–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b02788.
Qian J, Ferguson TM, Shinde DN, Ramirez-Borrero AJ, Hintze A, Adami C, et al. Sequence dependence of isothermal DNA amplification via EXPAR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:e87. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks230.
Zhang Q, Chen F, Xu F, Zhao Y, Fan C. Target-triggered three-way junction structure and polymerase/nicking enzyme synergetic isothermal quadratic DNA machine for highly specific, one-step, and rapid microRNA detection at attomolar level. Anal Chem. 2014;86:8098–105. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac501038r.
Chen F, Fan C, Zhao Y. Inhibitory impact of 3′-terminal 2′-O-methylated small silencing RNA on target-primed polymerization and unbiased amplified quantification of the RNA in Arabidopsis thaliana. Anal Chem. 2015;87:8758–64. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b01683.
Wang X, Wang H, Liu C, Wang H, Li Z. A three-way junction structure-based isothermal exponential amplification strategy for sensitive detection of 3′-terminal 2’-O-methylated plant microRNA. Chem Commun (Camb). 2017;53:1124–7. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cc08726d.
Xu Y, Wang Y, Liu S, Yu J, Wang H, Guo Y, et al. Ultrasensitive and rapid detection of miRNA with three-way junction structure-based trigger-assisted exponential enzymatic amplification. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;81:236–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.02.034.
Yuan C, Fang J, Luo X, Zhang Y, Huang G, Zeng X, et al. One-step isothermal amplification strategy for microRNA specific and ultrasensitive detection based on nicking-assisted entropy-driven DNA circuit triggered exponential amplification reaction. Anal Chim Acta. 2022;1203:339706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2022.339706.
Liu H, Tian T, Zhang Y, Ding L, Yu J, Yan M. Sensitive and rapid detection of microRNAs using hairpin probes-mediated exponential isothermal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;89:710–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.10.099.
Chen J, Zhou X, Ma Y, Lin X, Dai Z, Zou X. Asymmetric exponential amplification reaction on a toehold/biotin featured template: an ultrasensitive and specific strategy for isothermal microRNAs analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:e130. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw504.
Emaus MN, Anderson JL. Magnetic ionic liquids as microRNA extraction solvents and additives for the exponential amplification reaction. Anal Chim Acta. 2021;1181:338900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338900.
Lin Q, Cao Y, Han G, Sun W, Weng W, Chen H, et al. Programmable clostridium perfringens argonaute-based, one-pot assay for the multiplex detection of miRNAs. Anal Chem. 2023;95:13401–6. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.3c01990.
Xu Y, Li D, Cheng W, Hu R, Sang Y, Yin Y, et al. Chemiluminescence imaging for microRNA detection based on cascade exponential isothermal amplification machinery. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;936:229–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.07.007.
Yu Y, Chen Z, Shi L, Yang F, Pan J, Zhang B, et al. Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of microRNA based on an arched probe mediated isothermal exponential amplification. Anal Chem. 2014;86:8200–5. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac501505a.
Li RD, Yin BC, Ye BC. Ultrasensitive, colorimetric detection of microRNAs based on isothermal exponential amplification reaction-assisted gold nanoparticle amplification. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;86:1011–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.042.
Chen J, An T, Ma Y, Situ B, Chen D, Xu Y, et al. Isothermal amplification on a structure-switchable symmetric toehold Dumbbell-Template: a strategy enabling microRNA analysis at the single-cell level with ultrahigh specificity and accuracy. Anal Chem. 2018;90:859–65. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03713.
Carter JG, Orueta Iturbe L, Duprey JHA, Carter IR, Southern CD, Rana M, et al. Ultrarapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA using a reverse transcription-free exponential amplification reaction, RTF-EXPAR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118:e2100347118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2100347118.
Hang XM, Wang HY, Liu PF, Zhao KR, Wang L. Cas12a-assisted RTF-EXPAR for accurate, rapid and simple detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;216:114683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114683.
Huang K, Martí AA. Recent trends in molecular beacon design and applications. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012;402:3091–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5570-6.
Bellassai N, D’Agata R, Spoto G. Novel nucleic acid origami structures and conventional molecular beacon-based platforms: a comparison in biosensing applications. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021;413:6063–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03309-4.
Steitz TA. DNA polymerases: structural diversity and common mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:17395–8. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.25.17395.
Huang X, Yan Y, Zhang L, Yuan L, Tang Y, Jiang X, et al. Simple, sensitive, colorimetric detection of pyrophosphate via the analyte-triggered decomposition of metal-organic frameworks regulating their adaptive multi-color Tyndall effect. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05200-4.
Funding
We highly appreciate the financial support of the Science and Technology Benefiting the People Demonstration Project of Qingdao (22-2-7-smjk-2-nsh), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2023MC064), and the Key Project of Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation (ZR2020KH030). This work is supported by the Taishan Industrial Experts Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xinguang Zhang, Chao Jiang, Yuting Shan, and Yao Liu performed the experiments. Yang Li, Xinguang Zhang, Chao Jiang, Yuting Shan, and Yao Liu analyzed the data. Yang Li, Qing Wang, Qunqun Guo, Cuiping Ma, and Chao Shi designed the study. Yang Li and Xinguang Zhang wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to the writing of the paper, had primary responsibility for the final content, and read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The authorized Human Health and Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University approved this study (Approval No. QDU-HEC-2023260). All volunteers providing nasopharyngeal swabs signed informed consent forms. All methods were carried out in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Li, Y., Wang, Q. et al. Three-way junction structure-mediated reverse transcription-free exponential amplification reaction for pathogen RNA detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 416, 3161–3171 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05264-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05264-2