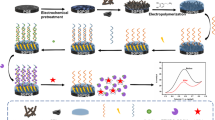
Abstract
A label-free electrochemical immunosensor has advantages of real-time and rapid detection, but it is weak in detection of small molecular toxins such as aflatoxin B1 (AFB1). The greatest obstacle to achieving this is that small molecules bound to a common immunosensing interface cannot interfere with electron transfer effectively and the detection signal is so weak. Therefore, a sensitive electrochemical immunosensing interface for small molecules is urgently needed. Here, we employed functionalized black phosphorene (BP) as electrode modification materials and anti-AFB1 nanobody (Nb) as a biorecognition element to construct a very sensitive immunosensing interface towards small molecular AFB1. The BP functionalized by carboxylic multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs-COOH) via P–C bonding behaved with a satisfactory stability and good catalytic performance for the ferricyanide/ferrocyanide probe, while the small-sized Nb showed good compatibility with the functionalized BP and also had less influence on electron transfer than monoclonal antibody (mAb). Expectedly, the as-prepared immunosensing interface was very sensitive to AFB1 detection by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) in a redox probe system. Under optimized conditions, a linear range from 1.0 pM to 5.0 nM and an ultralow detection limit of 0.27 pM were obtained. Additionally, the fabricated immunosensor exhibited satisfactory stability, specificity, and reproducibility. The strategy proposed here provides a more reliable reference for label-free sensing of small molecules in food samples.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marin S, Ramos AJ, Cano-Sancho G, Sanchis V. Mycotoxins: occurrence, toxicology, and exposure assessment. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;60:218–37.
Zhou S, Xu L, Kuang H, Xiao J, Xu C. Immunoassays for rapid mycotoxin detection: state of the art. Analyst. 2020;145(22):7088–102.
Xing K-Y, Shan S, Liu D-F, Lai W-H. Recent advances of lateral flow immunoassay for mycotoxins detection. Trac-Trends Anal Chem. 2020;133:116087.
He T, Wang Y, Li P, Zhang Q, Lei J, Zhang Z, et al. Nanobody-based enzyme immunoassay for aflatoxin in agro-products with high tolerance to cosolvent methanol. Anal Chem. 2014;86(17):8873–80.
Su L, Tong P, Zhang L, Luo Z, Fu C, Tang D, et al. Photoelectrochemical immunoassay of aflatoxin B 1 in foodstuff based on amorphous TiO2 and CsPbBr 3 perovskite nanocrystals. Analyst. 2019;144(16):4880–6.
Yan C, Wang Q, Yang Q, Wu W. Recent advances in aflatoxins detection based on nanomaterials. Nanomaterials. 2020;10(9):1626.
Wang X, Niessner R, Tang D, Knopp D. Nanoparticle-based immunosensors and immunoassays for aflatoxins. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;912:10–23.
Felix FS, Angnes L. Electrochemical immunosensors – a powerful tool for analytical applications. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;102:470–8.
Zhou Q, Tang D. Recent advances in photoelectrochemical biosensors for analysis of mycotoxins in food. TrAC, Trends Analyt Chem. 2020;124:115814.
Catanante G, Rhouati A, Hayat A, Marty JL. An overview of recent electrochemical immunosensing strategies for mycotoxins detection. Electroanalysis. 2016;28(8):1750–63.
Haab BB. Methods and applications of antibody microarrays in cancer research. Proteomics. 2003;3(11):2116–22.
Daniels JS, Pourmand N. Label-free impedance biosensors: opportunities and challenges. Electroanalysis. 2007;19(12):1239–57.
Wang D, Hu W, Xiong Y, Xu Y, Li CM. Multifunctionalized reduced graphene oxide-doped polypyrrole/pyrrolepropylic acid nanocomposite impedimetric immunosensor to ultra-sensitively detect small molecular aflatoxin B-1. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;63:185–9.
Kunene K, Weber M, Sabela M, Voiry D, Kanchi S, Bisetty K, et al. Highly-efficient electrochemical label-free immunosensor for the detection of ochratoxin A in coffee samples. Sens Actuators B-Chemical. 2020;305:127438.
Huang Y, Zhu F, Guan J, Wei W, Zou L. Label-free amperometric immunosensor based on versatile carbon nanofibers network coupled with Au nanoparticles for aflatoxin B1 detection. Biosensors (Basel). 2021;11(1):5.
Schedin F, Geim AK, Morozov SV, Hill EW, Blake P, Katsnelson MI, et al. Detection of individual gas molecules adsorbed on graphene. Nat Mater. 2007;6(9):652–5.
Mao S, Chen J. Graphene-based electronic biosensors. J Mater Res. 2017;32(15):2954–65.
Wang Y-H, Huang K-J, Wu X. Recent advances in transition-metal dichalcogenides based electrochemical biosensors: a review. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;97:305–16.
Sofer Z, Sedmidubsky D, Huber S, Luxa J, Bousa D, Boothroyd C, et al. Layered black phosphorus: strongly anisotropic magnetic, electronic, and electron-transfer properties. Angew Chem-Int Ed. 2016;55(10):3382–6.
Xiang Y, Belen Camarada M, Wen Y, Wu H, Chen J, Li M, et al. Simple voltammetric analyses of ochratoxin A in food samples using highly-stable and anti-fouling black phosphorene nanosensor. Electrochim Acta. 2018;282:490–8.
Ge X, Xia Z, Guo S. Recent advances on black phosphorus for biomedicine and biosensing. Adv Func Mater. 2019;29(29):1900318.
Peng J, Lai Y, Chen Y, Xu J, Sun L, Weng J. Sensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen using stability-limited few-layer black phosphorus as an electron donor and a reservoir. Small. 2017;13(15):1603589.
Abate Y, Akinwande D, Gamage S, Wang H, Snure M, Poudel N, et al. Recent progress on stability and passivation of black phosphorus. Adv Mater. 2018;30(29):1704749.
Thurakkal S, Zhang X. Recent advances in chemical functionalization of 2D black phosphorous nanosheets. Adv Sci. 2020;7(2):1902359.
Chen X, Zhang J, Huang C, Wu Q, Wu J, Xia L, et al. Modification of black phosphorus nanosheets with a Ni-containing carbon layer as efficient and stable hydrogen production electrocatalysts. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(49):54619–26.
WalzMitra KL, Chang CH, Hanrahan MP, Yang J, Tofan D, Holden WM, et al. Surface functionalization of black phosphorus with nitrenes: identification of P=N bonds by using isotopic labeling. Angew Chem-Int Ed. 2021;60(16):9127–34.
Jakóbczyk P, Jakobczyk P, Kowalski M, Brodowski M, Dettlaff A, Dec B, et al. Low-power microwave-induced fabrication of functionalised few-layer black phosphorus electrodes: a novel route towards Haemophilus Influenzae pathogen biosensing devices. Appl Surf Sci. 2021;539:148286.
Krah S, Schroeter C, Zielonka S, Empting M, Valldorf B, Kolmar H. Single-domain antibodies for biomedical applications. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2016;38(1):21–8.
Muyldermans S, Baral TN, Retarnozzo VC, De Baetselier P, De Genst E, Kinne J, et al. Camelid immunoglobulins and nanobody technology. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2009;128(1–3):178–83.
Li C, Tang Z, Hu Z, Wang Y, Yang X, Mo F, et al. Natural single-domain antibody-nanobody: a novel concept in the antibody field. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2018;14(1):1–19.
Bever CS, Dong J-X, Vasylieva N, Barnych B, Cui Y, Xu Z-L, et al. VHH antibodies: emerging reagents for the analysis of environmental chemicals. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408(22):5985–6002.
De Meyer T, Muyldermans S, Depicker A. Nanobody-based products as research and diagnostic tools. Trends Biotechnol. 2014;32(5):263–70.
Zhang C, Wu X, Li D, Hu J, Wan D, Zhang Z, et al. Development of nanobody-based flow-through dot ELISA and lateral-flow immunoassay for rapid detection of 3-phenoxybenzoic acid. Anal Methods. 2021;13(14):1757–65.
Liu X, Wang D, Chu J, Xu Y, Wang W. Sandwich pair nanobodies, a potential tool for electrochemical immunosensing serum prostate-specific antigen with preferable specificity. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018;158:361–9.
Liu X, Wen Y, Wang W, Zhao Z, Han Y, Tan K, et al. Nanobody-based electrochemical competitive immunosensor for the detection of AFB(1) through AFB(1)-HCR as signal amplifier. Microchim Acta. 2020;187(6):352.
Saerens D, Saerens D, Frederix F, Reekmans G, Conrath K, Jans K, et al. Engineering camel single-domain antibodies and immobilization chemistry for human prostate-specific antigen sensing. Anal Chem. 2005;77(23):7547–55.
Pan D, Li G, Hu H, Xue H, Zhang M, Zhu M, et al. Direct immunoassay for facile and sensitive detection of small molecule aflatoxin B 1 based on nanobody. Chem Eur J. 2018;24(39):9869–76.
Mann FA, Lv Z, Grosshans J, Opazo F, Kruss S. Nanobody-conjugated nanotubes for targeted near-infrared in vivo imaging and sensing. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2019;58(33):11469–73.
Kang J, Wood JD, Wells SA, Lee J-H, Liu X, Chen K-S, et al. Solvent exfoliation of electronic-grade, two-dimensional black phosphorus. ACS Nano. 2015;9(4):3596–604.
Su S, Xu B, Ding J, Yu H. Large-yield exfoliation of few-layer black phosphorus nanosheets in liquid. New J Chem. 2019;43(48):19365–71.
Hanlon D, Backes C, Doherty E, Cucinotta CS, Berner NC, Boland C, et al. Liquid exfoliation of solvent-stabilized few-layer black phosphorus for applications beyond electronics. Nat Commun. 2015;6(1):8563.
Cai J, Gou X, Sun B, Li W, Li D, Liu J, et al. Porous graphene-black phosphorus nanocomposite modified electrode for detection of leptin. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;137:88–95.
Xue T, Sheng Y, Xu J, Li Y, Lu X, Zhu Y, et al. In-situ reduction of Ag+ on black phosphorene and its NH2-MWCNT nanohybrid with high stability and dispersibility as nanozyme sensor for three ATP metabolites. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;145:111716.
Erande MB, Pawar MS, Late DJ. Humidity sensing and photodetection behavior of electrochemically exfoliated atomically thin-layered black phosphorus nanosheets. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(18):11548–56.
Zhang X, Du J, Wu D, Long X, Wang D, Xiong J, et al. Anchoring metallic MoS2 quantum dots over MWCNTs for highly sensitive detection of postharvest fungicide in traditional Chinese medicines. ACS Omega. 2021;6(2):1488–96.
Cao D-M, Xu Y, Tu Z, Li Y-P, Xiong L, Fu J-H. One-step enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for detection of aflatoxin B-1 using a nanobody-alkaline phosphatase fusion protein. Chin J Anal Chem. 2016;44(7):1085–91.
Karaman C, Karaman O, Yola BB, Ulker I, Atar N, Yola ML. A novel electrochemical aflatoxin B1 immunosensor based on gold nanoparticle-decorated porous graphene nanoribbon and Ag nanocube-incorporated MoS2 nanosheets. New J Chem. 2021;45(25):11222–33.
Wang H, Zhang Y, Chu Y, Ma H, Li Y, Wu D, et al. Disposable competitive-type immunoassay for determination of aflatoxin B1 via detection of copper ions released from Cu-apatite. Talanta. 2016;147:556–60.
Lin Y, Zhou Q, Tang D. Dopamine-loaded liposomes for in-situ amplified photoelectrochemical immunoassay of AFB(1) to enhance photocurrent of Mn2-doped Zn-3(OH)(2)V2O7 nanobelts. Anal Chem. 2017;89(21):11803–10.
Costa MP, Frias IAM, Andrade CAS, Oliveira MDL. Impedimetric immunoassay for aflatoxin B1 using a cysteine modified gold electrode with covalently immobilized carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta. 2017;184(9):3205–13.
Solanki PR, Singh J, Rupavali B, Tiwari S, Malhotra BD. Bismuth oxide nanorods based immunosensor for mycotoxin detection. Mater Sci Eng, C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;70:564–71.
Bhardwaj H, Marquette CA, Dutta P, Rajesh, Sumana G. Integrated graphene quantum dot decorated functionalized nanosheet biosensor for mycotoxin detection. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020;412(25):7029–41.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31660492, 32060575, 32160602, 31860260) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20192ACBL20019, 20181BAB204017, 20171BAB214038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Xue Zhang and Xiaoning Liao contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Liao, X., Wu, Y. et al. A sensitive electrochemical immunosensing interface for label-free detection of aflatoxin B1 by attachment of nanobody to MWCNTs-COOH@black phosphorene. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 1129–1139 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03738-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03738-1