Abstract
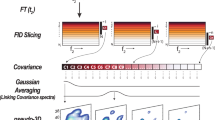
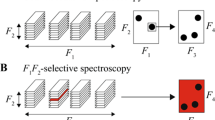
To eliminate the effects of complex background signals and to enhance the accuracy of the diffusion coefficient measurement, derivative NMR spectroscopy with negligible loss of the spectral quality is introduced based on the customized Savitzky-Golay method and used to construct diffusion-ordered NMR spectroscopy (DOSY). The criterion of the method was established by simulations. The application of this method on mouse urine and serum showed that the accuracy and precision of diffusion coefficient measurements in a complex background were improved to enhance the identification of molecules.

Diffusion-ordered NMR spectroscopy is a powerful tool for analyzing complex mixtures. To improve the accuracy of diffusion coefficient measurement, the magnitude of complex derivative spectra is introduced as a post-processing method to eliminate the effects of background signals, broad signals, or distorted baseline. And thus, accurate estimate of the diffusion coefficient is ensured to enhance the molecule identification.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morris KF, Johnson CS. Diffusion-ordered two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc. 1992;114(8):3139–41.
Morris KF, Johnson CS. Resolution of discrete and continuous molecular size distributions by means of diffusion-ordered 2D NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc. 1993;115(10):4291–9.
Stilbs P. Molecular self-diffusion coefficients in Fourier transform nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometric analysis of complex mixtures. Anal Chem. 1981;53(13):2135–7.
Yuan B, Ding Y, Kamal GM, Shao L, Zhou Z, Jiang B, et al. Reconstructing diffusion ordered NMR spectroscopy by simultaneous inversion of Laplace transform. J Magn Reson. 2017;278:1–7.
Colbourne AA, Morris GA, Nilsson M. Local covariance order diffusion-ordered spectroscopy: a powerful tool for mixture analysis. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133(20):7640–3.
Liu ML, Nicholson JK, London JC. High-resolution diffusion and relaxation edited one- and two-dimensional H-1 NMR spectroscopy of biological fluids. Anal Chem. 1996;68(19):3370–6.
Liu ML, Tang HR, Nicholson JK, Lindon JC. Use of H-1 NMR-determined diffusion coefficients to characterize lipoprotein fractions in human blood plasma. Magn Reson Chem. 2002;40:S83–S8.
Du YY, Lan WX, Ji ZS, Zhang X, Jiang B, Zhou X, et al. NMR spectroscopic approach reveals metabolic diversity of human blood plasma associated with protein-drug interaction. Anal Chem. 2013;85(18):8601–8.
Evans R, Day IJ. Matrix-assisted diffusion-ordered spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2016;6(52):47010–22.
Caldarelli S. Chromatographic NMR. Annu Rep NMR Spectrosc. 2011;73:159–73.
Barhoum S, Palit S, Yethiraj A. Diffusion NMR studies of macromolecular complex formation, crowding and confinement in soft materials. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2016;94:1–10.
Peresada S, Tonielli A, Morici R, Johnson CS. Diffusion ordered nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: principles and applications. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 1999;34(3):203–56.
Lin MF, Shapiro MJ. Mixture analysis in combinatorial chemistry. Application of diffusion-resolved NMR spectroscopy. J Organomet Chem. 1996;61(21):7617–9.
Leon M, Smith ADM, Cloarec O, et al. Statistical correlation and projection methods for improved information recovery from diffusion-edited NMR spectra of biological samples. Anal Chem. 2007;79:5682–9.
Morris GA. Diffusion-ordered spectroscopy. In: Morris GA, Emsley JW, editors. Multidimensional NMR methods for the solution state; 2010. p. 515–32.
Nilsson M, Gil AM, Delgadillo I, Morris GA. Improving pulse sequences for 3D DOSY: COSY-IDOSY. Chem Commun. 2005;13:1737–9.
Nilsson M, Gil AM, Delgadillo I, Morris GA. Improving pulse sequences for 3D diffusion-ordered NMR spectroscopy: 2DJ-IDOSY. Anal Chem. 2004;76(18):5418–22.
Vitorge B, Jeanneat D. NMR diffusion measurements in complex mixtures using constant-time-HSQC-IDOSY and computer-optimized spectral aliasing for high resolution in the carbon dimension. Anal Chem. 2006;78(15):5601–6.
Viel S, Caldarelli S. Improved 3D DOSY-TOCSY experiment for mixture analysis. Chem Commun. 2008;17:2013–5.
Jerschow A, Müller N. 3D diffusion-ordered TOCSY for slowly diffusing molecules. J Magn Reson Ser A. 1996;123(2):222–5.
Pudakalakatti SM, Chandra K, Thirupathi R, Atreya HS. Rapid characterization of molecular diffusion by NMR spectroscopy. Chem Eur J. 2014;20(48):15719–22.
Stilbs P, Paulsen K, Griffiths PC. Global least-squares analysis of large, correlated spectral data sets: application to component-resolved FT-PGSE NMR spectroscopy. J Phys Chem. 1996;100(20):8180–9.
Nilsson M, Morris GA. Speedy component resolution: an improved tool for processing diffusion-ordered spectroscopy data. Anal Chem. 2008;80(10):3777–82.
Stilbs P. RECORD processing – a robust pathway to component-resolved HR-PGSE NMR diffusometry. J Magn Reson. 2010;207(2):332–6.
Stilbs P. Automated CORE, RECORD, and GRECORD processing of multi-component PGSE NMR diffusometry data. Eur Biophys J. 2013;42(1):25–32.
Colbourne AA, Meier S, Morris GA, Nilsson M. Unmixing the NMR spectra of similar species - vive la différence. Chem Commun. 2013;49(89):10510–2.
Windig W, Antalek B. Direct exponential curve resolution algorithm (DECRA): a novel application of the generalized rank annihilation method for a single spectral mixture data set with exponentially decaying contribution profiles. Chemom Intell Lab Syst. 1997;37(2):241–54.
Antalek B, Windig W. Generalized rank annihilation method applied to a single multicomponent pulsed gradient spin echo NMR data set. J Am Chem Soc. 1996;118(42):10331–2.
Huo R, Wehrens R, Buydens LMC. Improved DOSY NMR data processing by data enhancement and combination of multivariate curve resolution with non-linear least square fitting. J Magn Reson. 2004;169(2):257–69.
Van Gorkom LCM, Hancewicz TM. Analysis of DOSY and GPC-NMR experiments on polymers by multivariate curve resolution. J Magn Reson. 1998;130(1):125–30.
Zhong J, DiDonato N, Hatcher PG. Independent component analysis applied to diffusion-ordered spectroscopy: separating nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of analytes in mixtures. J Chemom. 2012;26(5):150–7.
Toumi I, Torresani B, Caldarelli S. Effective processing of pulse field gradient NMR of mixtures by blind source separation. Anal Chem. 2013;85(23):11344–51.
Yin PH, Sun YC, Xin J. A geometric blind source separation method based on facet component analysis. SIViP. 2016;10(1):19–28.
Zhang X, Li CG, Ye CH, Liu ML. Determination of molecular self-diffusion coefficient using multiple spin-echo NMR spectroscopy with removal of convection and background gradient artifacts. Anal Chem. 2001;73(15):3528–34.
Pelantová H, Bugáňová M, Anýž J, Železná B, Maletínská L, Novák D, et al. Strategy for NMR metabolomic analysis of urine in mouse models of obesity-- from sample collection to interpretation of acquired data. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015;115:225–35.
Beumers P, Engel D, Brands T, Koß HJ, Bardow A. Robust analysis of spectra with strong background signals by first-derivative indirect hard modeling (FD-IHM). Chemom Intell Lab Syst. 2018;172:1–9.
Rohnisch HE, Eriksson J, Mullner E, Agback P, Sandstrom C, Moazzami AA. AQuA: an automated quantification algorithm for high-throughput NMR-based metabolomics and its application in human plasma. Anal Chem. 2018;90(3):2095–102.
Tardivel PJC, Canlet C, Lefort G, Tremblay-Franco M, Debrauwer L, Concordet D, et al. ASICS: an automatic method for identification and quantification of metabolites in complex 1D 1H NMR spectra. Metabolomics. 2017;13(10):109.
Hao J, Astle W, De Iorio M, Ebbels TMD. BATMAN--an R package for the automated quantification of metabolites from nuclear magnetic resonance spectra using a Bayesian model. Bioinformatics. 2012;28(15):2088–90.
Ravanbakhsh S, Liu P, Bjordahl TC, Mandal R, Grant JR, Wilson M, et al. Accurate, fully-automated NMR spectral profiling for metabolomics. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0124219.
Bradley SA, Smitka TA, Russell DJ, Krishnamurthy K. Quantitative NMR analysis of complex mixtures using CRAFT (complete reduction to amplitude frequency table) method. Current Metabolomics. 2015;3(1):21–31.
Verhoeven A, Slagboom E, Wuhrer M, Giera M, Mayboroda OA. Automated quantification of metabolites in blood-derived samples by NMR. Anal Chim Acta. 2017;976:52–62.
Filntisi A, Fotakis C, Asvestas P, Matsopoulos GK, Zoumpoulakis P, Cavouras D. Automated metabolite identification from biological fluid H-1 NMR spectra. Metabolomics. 2017;13(12).
Jung Y-S, Hyeon J-S, Hwang G-S. Software-assisted serum metabolite quantification using NMR. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;934:194–202.
Mercier P, Lewis MJ, Chang D, Baker D, Wishart DS. Towards automatic metabolomic profiling of high-resolution one-dimensional proton NMR spectra. J Biomol NMR. 2011;49(3):307–23.
Weljie AM, Newton J, Mercier P, Carlson E, Slupsky CM. Targeted profiling: quantitative analysis of 1H NMR metabolomics data. Anal Chem. 2006;78:4430–42.
Tiainen M, Soininen P, Laatikainen R. Quantitative quantum mechanical spectral analysis (qQMSA) of 1H NMR spectra of complex mixtures and biofluids. J Magn Reson 2014;242(0):67–78.
Barak P. Smoothing and differentiation by an adaptive-degree polynomial filter. Anal Chem. 1995;67(17):2758–62.
Pearce JT, Athersuch TJ, Ebbels TM, et al. Robust algorithms for automated chemical shift calibration of 1D 1H NMR spectra of blood serum. Anal Chem. 2008;80:7158–62.
Bao Q, Feng J, Chen L, Chen F, Liu Z, Jiang B, et al. A robust automatic phase correction method for signal dense spectra. J Magn Reson. 2013;234:82–9.
Li YL, Ding YQ, Li T. Nonlinear diffusion filtering for peak-preserving smoothing of a spectrum signal. Chemom Intell Lab Syst. 2016;156:157–65.
Shao XG, Ma CX. A general approach to derivative calculation using wavelet transform. Chemom Intell Lab Syst. 2003;69(1–2):157–65.
Stickel JJ. Data smoothing and numerical differentiation by a regularization method. Comput Chem Eng. 2010;34(4):467–75.
Bustacara-Medina C, Florez-Valencia L. Comparison and evaluation of first derivatives estimation. In: Chmielewski LJ, Datta A, Kozera R, Wojciechowski K, editors. Computer vision and graphics, Iccvg 2016. Lecture notes in computer science. 99722016. p. 121–33.
Luo JW, Ying K, He P, Bai J. Properties of Savitzky-Golay digital differentiators. Digit Signal Prog. 2005;15(2):122–36.
Wu DH, Chen AD, Johnson CS. An improved diffusion-ordered spectroscopy experiment incorporating bipolar-gradient pulses. J Magn Reson Ser A. 1995;115(2):260–4.
Nilsson M. The DOSY toolbox: a new tool for processing PFG NMR diffusion data. J Magn Reson. 2009;200(2):296–302.
Liu M, Nicholson JK, Lindon JC. High-resolution diffusion and relaxation edited one- and two-dimensional 1H NMR spectroscopy of biological fluids. Anal Chem. 1996;68(19):3370–6.
Zhang Y, Li W, Sun J, Zhang R, Wu B, Zhang X, et al. NMR-based metabolic profiling for serum of mouse exposed to source water. Ecotoxicology. 2011;20(5):1065–70.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Liming Zhang for providing the mouse urine and serum samples for the experiment.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0704002, 2018YFE0202300, 2017YFA0505400), National Natural Science Foundation of China (21735007, 21675170, 21475146), CAS Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences (QYZDJ-SSW-SLH027), and K.C. Wong Educational Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 655 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, B., Zhang, X., Kamal, G.M. et al. Accurate estimation of diffusion coefficient for molecular identification in a complex background. Anal Bioanal Chem 412, 4519–4525 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02693-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02693-7