Abstract
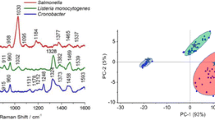
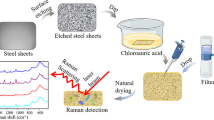
A novel method was developed to rapidly concentrate, detect, and differentiate bacteria in skimmed milk using surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) mapping on 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid (4-MPBA) functionalized silver (Ag) dendrites. The 4-MPBA functionalized Ag dendritic SERS substrate was used to capture the bacterial cells and enhance the bacterial signal. Salmonella, a significantly important food pathogen, was used as the representative strain to optimize and evaluate the developed method. The capture efficiency for Salmonella enterica subsp enterica BAA1045 (SE1045) was 84.92 ± 3.25% at 106 CFU/mL and as high as 99.65 ± 3.58% at 103 CFU/mL. Four different strains, two gram-negative and two gram-positive, can be clearly distinguished by their SERS spectra using principle component analysis. A mapping technique was utilized to automatically collect 400 spectra over an area of 60 μm × 60 μm to construct a visual image for a sensitive and statistically reliable detection within 30 min. Using this method, we were able to detect as low as 103 CFU/mL bacterial cells in 50 mM NH4HCO3 solution and 102 CFU/mL cells in both 1% casein and skimmed milk. Our results demonstrate the feasibility of using SERS mapping method coupled with 4-MPBA functionalized Ag dendrites for rapid and sensitive bacteria detection in complex liquid samples.

A novel SERS mapping method based on 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid functionalized silver (Ag) dendrites was developed to rapidly concentrate, detect, and differentiate bacteria








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hakonen A, Andersson PO, Stenbæk Schmidt M, Rindzevicius T, Käll M. Explosive and chemical threat detection by surface-enhanced Raman scattering: a review. Anal Chim Acta. 2015;893:1–13.
Zheng J, He L. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for the chemical analysis of food. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2014;13(3):317–28.
Stiles PL, Dieringer JA, Shah NC, Van Duyne RP. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Annu Rev Anal Chem. 2008;1(1):601–26.
Campion A, Kambhampati P, Campion A, Harris C. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering. 1998;27:241–50.
Kneipp K, Moskovits M, Kneipp H. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering—physics and applications. Topics in Applied Physics. 2006. 19–61 p.
Zhou H, Yang D, Ivleva NP, Mircescu NE, Schubert S, Niessner R, et al. Rapid label-free in-situ discrimination of live and dead bacteria by SERS. Anal Chem. 2015;87:6553–61.
Sengupta A, Mujacic M, Davis EJ. Detection of bacteria by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2006;386(5):1379–86.
Jarvis RM, Goodacre R. Characterisation and identification of bacteria using SERS. Chem Soc Rev. 2008;37(5):931–6.
Jarvis RM, Brooker A, Goodacre R. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering for the rapid discrimination of bacteria. Faraday Discuss. 2006;132:281–92.
Chen L, Mungroo N, Daikuara L, Neethirajan S. Label-free NIR-SERS discrimination and detection of foodborne bacteria by in situ synthesis of Ag colloids. J Nanobiotechnol BioMed Central. 2015;13:45–53.
Guicheteau J, Christesen S, Emge D, Tripathi A. Bacterial mixture identification using Raman and surface-enhanced Raman chemical imaging. J Raman Spectrosc. 2010;41(November 2009):1632–7.
Montoya JR, Armstrong RL, Smith GB. Detection of Salmonella using surfaced enhanced Raman scattering. Proc SPIE. 2003;5085:144–52.
Zhou H, Yang D, Ivleva NP, Mircescu NE, Niessner R, Haisch C. SERS detection of bacteria in water by in situ coating with Ag nanoparticles. Anal Chem. 2014;86(3):1525–33.
Wang P, Pang S, Chen J, McLandsborough L, Nugen SR, Fan M, et al. Label-free mapping of single bacterial cells using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Analyst. 2016;141(4):1356–62.
Cho I-H, Bhandari P, Patel P, Irudayaraj J. Membrane filter-assisted surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy for the rapid detection of E. coli O157:H7 in ground beef. Biosens Bioelectron Elsevier. 2014;64C:171–6.
Chen L, Razavi FS, Mumin A, Guo X, Sham T-K, Zhang J. Multifunctional nanoparticles for rapid bacterial capture, detection, and decontamination. RSC Adv. 2013;3(7):2390–7.
Chang Y-C, Yang C-Y, Sun R-L, Cheng Y-F, Kao W-C, Yang P-C. Rapid single cell detection of Staphylococcus aureus by aptamer-conjugated gold nanoparticles. Sci Rep. 2013;3:1–7.
He L, Deen DB, Pagel AH, Diez-Gonzalez F, Labuza TP. Concentration, detection and discrimination of Bacillus anthracis spores in orange juice using aptamer based surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Analyst. 2013;138(6):1657–9.
Liu T-Y, Tsai K-T, Wang H-H, Chen Y, Chen Y-H, Chao Y-C, et al. Functionalized arrays of Raman-enhancing nanoparticles for capture and culture-free analysis of bacteria in human blood. Nat Commun Nature Publ Group. 2011;2:538–46.
Wang H, Zhou Y, Jiang X, Sun B, Zhu Y, Wang H, et al. Simultaneous capture, detection, and inactivation of bacteria as enabled by a surface-enhanced Raman scattering multifunctional chip. Angew Chemie Int Ed. 2015;54(17):5132–6.
Ivnitski D, Abdel-Hamid I, Atanasov P, Wilkins E. Biosensors for detection of pathogenic bacteria. Biosens Bioelectron. 1999;14(7):599–624.
Tombelli S, Minunni M, Mascini M. Aptamers-based assays for diagnostics, environmental and food analysis. Biomol Eng. 2007;24(2):191–200.
Wu X, Xu C, Tripp RA, Huang Y, Zhao Y. Detection and differentiation of foodborne pathogenic bacteria in mung bean sprouts using field deployable label-free SERS devices. Analyst. 2013;138(10):3005–12.
He L, Lin M, Li H, Kim NJ. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy coupled with dendritic silver nanosubstrate for detection of restricted antibiotics. J Raman Spectrosc. 2010;41(7):739–44.
He LL, Rodda T, Haynes CL, Deschaines T, Strother T, Diez-Gonzalez F, et al. Detection of a foreign protein in milk using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy coupled with antibody-modified silver dendrites. Anal Chem. 2011;83(5):1510–3.
Jackson P, Attalla MI. N-Nitrosopiperazines form at high pH in post-combustion capture solutions containing piperazine: a low-energy collisional behaviour study. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2010;24(24):3567–77.
Qi D, Zhang H, Tang J, Deng C, Zhang X. Facile Synthesis of Mercaptophenylboronic acid-functionalized core-shell structure Fe3O4@C@Au magnetic microspheres for selective enrichment of glycopeptides and glycoproteins. 2010;114(20):9221–6
Khan SA, Singh AK, Senapati D, Fan Z, Ray PC. Targeted highly sensitive detection of multi-drug resistant Salmonella DT104 using gold nanoparticles. Chem Commun (Camb). 2011;47:9444–6.
Walter A, März A, Schumacher W, Rösch P, Popp J. Towards a fast, high specific and reliable discrimination of bacteria on strain level by means of SERS in a microfluidic device. Lab Chip. 2011;11(207890):1013–21.
Jarvis RM, Law N, Shadi IT, O’Brien P, Lloyd JR, Goodacre R. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering from intracellular and extracellular bacterial locations. Anal Chem. 2008;80(17):6741–6.
Acknowledgements
This study is funded by USDA-NIFA 2015-67021-22993 and USDA-NIFA hatch (MAS00491).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 1353 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Pang, S., Pearson, B. et al. Rapid concentration detection and differentiation of bacteria in skimmed milk using surface enhanced Raman scattering mapping on 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid functionalized silver dendrites. Anal Bioanal Chem 409, 2229–2238 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-0167-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-0167-8