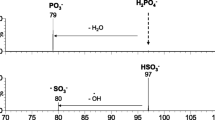
Abstract
This study describes a highly efficient method for the selective precipitation of phosphoproteins by trivalent europium, terbium, and erbium metal ions. These metal cations belong to the group of lanthanides and are known to be hard acceptors with an overwhelming preference for oxygen-containing anions such as phosphates to which they form very tight ionic bonds. The method could be successfully applied to specifically precipitate phosphoproteins from complex samples including milk and egg white by forming solid metal–protein complexes. Owing to the low solubility product of the investigated lanthanide salts, the produced metal–protein complexes showed high stability. The protein pellets were extensively washed to remove nonphosphorylated proteins and contaminants. For the analysis of proteins the pellets were first dissolved in 30 % formic acid and subjected to matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization–time of flight (MALDI-TOF) MS. For peptide mass-fingerprint analysis the precipitated phosphoproteins were enzymatically digested using microwave-assisted digestion. The method was found to be highly specific for the isolation and purification of phosphoproteins. Protein quantification was performed by colorimetric detection of total precipitated phosphoproteins and revealed more than 95 % protein recovery for each lanthanide salt.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S (2002) The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 298(5600):1912
Delom F, Chevet E (2006) Phosphoprotein analysis: from proteins to proteomes. Proteome Science 4(1):15
Mann M, Ong SE, Grønborg M, Steen H, Jensen ON, Pandey A (2002) Analysis of protein phosphorylation using mass spectrometry: deciphering the phosphoproteome. Trends Biotechnol 20(6):261–268
Mann M, Jensen ON (2003) Proteomic analysis of post-translational modifications. Nat Biotechnol 21(3):255–261
Porath J, Carlsson J, Olsson I, Belfrage G (1975) Metal chelate affinity chromatography, a new approach to protein fractionation. Nature 258:598–599
Moser K, White FM (2006) Phosphoproteomic analysis of rat liver by high capacity IMAC and LC-MS/MS. J Proteome Res 5(1):98–104
Posewitz MC, Tempst P (1999) Immobilized gallium(III) affinity chromatography of phosphopeptides. Anal Chem 71(14):2883–2892
Pearson RG (1963) Hard and soft acids and bases. J Am Chem Soc 85(22):3533–3539
Ficarro S, Chertihin O, Westbrook VA, White F, Jayes F, Kalab P, Marto JA, Shabanowitz J, Herr JC, Hunt DF (2003) Phosphoproteome analysis of capacitated human sperm. J Biol Chem 278(13):11579–11589
Wolschin F, Wienkoop S, Weckwerth W (2005) Enrichment of phosphorylated proteins and peptides from complex mixtures using metal oxide/hydroxide affinity chromatography (MOAC). Proteomics 5(17):4389–4397
Larsen MR, Thingholm TE, Jensen ON, Roepstorff P, Jørgensen TJD (2005) Highly selective enrichment of phosphorylated peptides from peptide mixtures using titanium dioxide microcolumns. Mol Cell Proteomics 4(7):873–886
Kweon HK, Håkansson K (2006) Selective zirconium dioxide-based enrichment of phosphorylated peptides for mass spectrometric analysis. Anal Chem 78(6):1743–1749
Leitner A (2010) Phosphopeptide enrichment using metal oxide affinity chromatography. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 29(2):177–185
Li Y, Lin H, Deng C, Yang P, Zhang X (2008) Highly selective and rapid enrichment of phosphorylated peptides using gallium oxide–coated magnetic microspheres for MALDI–TOF–MS and nano–LC–ESI–MS/MS/MS analysis. Proteomics 8(2):238–249
Lee A, Yang HJ, Lim ES, Kim J, Kim Y (2008) Enrichment of phosphopeptides using bare magnetic particles. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22(16):2561–2564
Ficarro SB, Parikh JR, Blank NC, Marto JA (2008) Niobium(V) oxide (Nb2O5): application to phosphoproteomics. Anal Chem 80(12):4606–4613
Rivera JG, Choi YS, Vujcic S, Wood TD, Colón LA (2009) Enrichment/isolation of phosphorylated peptides on hafnium oxide prior to mass spectrometric analysis. Analyst 134(1):31–33
Qi D, Lu J, Deng C, Zhang X (2009) Development of core-shell structure Fe3O4@Ta2O5 microspheres for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides for mass spectrometry analysis. J Chromatogr A 1216(29):5533–5539
Bodenmiller B, Mueller LN, Mueller M, Domon B, Aebersold R (2007) Reproducible isolation of distinct, overlapping segments of the phosphoproteome. Nat Methods 4(3):231–237
Thingholm TE, Jensen ON, Robinson PJ, Larsen MR (2008) SIMAC (sequential elution from IMAC), a phosphoproteomics strategy for the rapid separation of monophosphorylated from multiply phosphorylated peptides. Mol Cell Proteomics 7(4):661–671
Thingholm TE, Jensen ON, Larsen MR (2009) Enrichment and separation of mono-and multiply phosphorylated peptides using sequential elution from IMAC prior to mass spectrometric analysis. Methods Mol Biol 527:67–78
Yu YQ, Fournier J, Gilar M, Gebler JC (2009) Phosphopeptide enrichment using microscale titanium dioxide solid phase extraction. J Sep Sci 32(8):1189–1199
Sugiyama N, Masuda T, Shinoda K, Nakamura A, Tomita M, Ishihama Y (2007) Phosphopeptide enrichment by aliphatic hydroxy acid-modified metal oxide chromatography for nano-LC-MS/MS in proteomics applications. Mol Cell Proteomics 6(6):1103–1109
Mazanek M, Mituloviæ G, Herzog F, Stingl C, Hutchins JRA, Peters JM, Mechtler K (2006) Titanium dioxide as a chemo-affinity solid phase in offline phosphopeptide chromatography prior to HPLC-MS/MS analysis. Nat Protoc 2(5):1059–1069
Jensen SS, Larsen MR (2007) Evaluation of the impact of some experimental procedures on different phosphopeptide enrichment techniques. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 21(22):3635–3645
Zhang X, Ye J, Jensen ON, Roepstorff P (2007) Highly efficient phosphopeptide enrichment by calcium phosphate precipitation combined with subsequent IMAC enrichment. Mol Cell Proteomics 6(11):2032–2042
Xia Q, Cheng D, Duong DM, Gearing M, Lah JJ, Levey AI, Peng J (2008) Phosphoproteomic analysis of human brain by calcium phosphate precipitation and mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res 7(7):2845–2851
Ruse CI, McClatchy DB, Lu B, Cociorva D, Motoyama A, Park SK, Yates Iii JR (2008) Motif-specific sampling of phosphoproteomes. J Proteome Res 7(5):2140–2150
Chang MF, White JL, Nail SL, Hem SL (1997) Role of the electrostatic attractive force in the adsorption of proteins by aluminum hydroxide adjuvant. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol 51(1):25–29
Iyer S, HogenEsch H, Hem SL (2003) Effect of the degree of phosphate substitution in aluminum hydroxide adjuvant on the adsorption of phosphorylated proteins. Pharm Dev Technol 8(1):81–86
Dubrovska A, Souchelnytskyi S (2005) Efficient enrichment of intact phosphorylated proteins by modified immobilized metal–affinity chromatography. Proteomics 5(18):4678–4683
Pandey A, Fernandez MM, Steen H, Blagoev B, Nielsen MM, Roche S, Mann M, Lodish HF (2000) Identification of a novel immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif-containing molecule, STAM2, by mass spectrometry and its involvement in growth factor and cytokine receptor signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 275(49):38633–38639
Grønborg M, Kristiansen TZ, Stensballe A, Andersen JS, Ohara O, Mann M, Jensen ON, Pandey A (2002) A mass spectrometry-based proteomic approach for identification of serine/threonine-phosphorylated proteins by enrichment with phospho-specific antibodies. Mol Cell Proteomics 1(7):517–527
Pink M, Verma N, Polato F, Bonn GK, Baba HA, Rettenmeier AW, Schmitz-Spanke S (2011) Precipitation by lanthanum ions: a straightforward approach to isolating phosphoproteins. J Proteomics 75(2):375–83
Polato F, Rainer M, Gjerde D, Bonn GK (2011) Method and device for the isolation of phosphoproteins, glycoproteins and fragments thereof. US Patent Application US 13/270,148, 11 October 2011
Liu X, Byrne RH (1997) Rare earth and yttrium phosphate solubilities in aqueous solution. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61(8):1625–1633
Jensen RG (1995) Handbook of milk composition. Academic, London
Mine Y (1995) Recent advances in the understanding of egg white protein functionality. Trends Food Sci Technol 6(7):225–232
Guerin-Dubiard C, Pasco M, Hietanen A, Quiros del Bosque A, Nau F, Croguennec T (2005) Hen egg white fractionation by ion-exchange chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1090(1–2):58–67
Aisen P, Aasa R, Redfield AG (1969) The chromium, manganese, and cobalt complexes of transferrin. J Biol Chem 244(17):4628
Harris WR, Yang B, Abdollahi S, Hamada Y (1999) Steric restrictions on the binding of large metal ions to serum transferrin. J Inorg Biochem 76(3–4):231–242
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Austrian Science Foundation (FWF), SFB-Project 021 (Vienna, Austria).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 260 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Güzel, Y., Rainer, M., Mirza, M.R. et al. Highly efficient precipitation of phosphoproteins using trivalent europium, terbium, and erbium ions. Anal Bioanal Chem 403, 1323–1331 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-5917-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-5917-7