Abstract
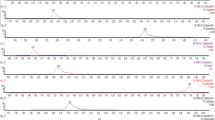
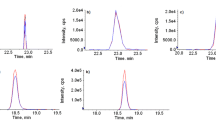
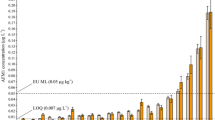
A rapid multi-analyte method has been developed for the simultaneous determination of pesticides and mycotoxins in milk by ultra high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (UHPLC–QqQ–MS/MS). A variety of methodologies has been evaluated, including solid-phase extraction (SPE), “dilute-and-shoot” (liquid–liquid extraction-based procedures), and QuEChERS (quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe)-based methods. The optimization and development process was carried out considering that the maximum residue level for aflatoxin M1 (AFM1) in milk in the European Union (EU) is set at 0.05 μg kg−1, which is the lowest tolerance in the target compounds. The selected method consisted of an extraction by SPE using C18 as sorbent and methanol as elution solvent. The final determination was performed by UHPLC–QqQ–MS/MS. Matrix-matched standard calibration was used for quantification, obtaining recoveries in the range 60–120% with relative standard deviations <25%, at three spiking levels: 0.5, 10, and 50 μg kg−1 (ten times lower for AFM1). Limits of quantification ranged from 0.20 to 0.67 μg kg−1, which were always below or equal to the established tolerance levels by the EU. Finally, the selected method was applied to different types of milk.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perseo Program, Spanish Ministry of Health and Consumption/Spanish Food Safety and Nutrition Authority (Ministerio de Sanidad y Consumo/Agencia Española de Seguridad Alimentaria y Nutrición). Available at http://www.perseo.aesan.msps.es/. Accessed on October 2010
Moss MO (2002) Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 50:137–142
MacLachlan DJ, Bhula R (2008) Aust J Exp Agric 48:589–598
Fink-Gremmels J (2008) Food Addit Contam A 25:172–180
Seccia S, Fidente P, Montesano D, Morrica P (2008) J Chromatogr A 1214:115–120
Hussein HS, Brasel JM (2001) Toxicology 167:101–134
Díaz S, Domínguez L, Prieta J, Blanco JL, Moreno MA (1995) J Agric Food Chem 43:2678–2680
Bascarán V, Hernández de Rojas A, Chouciño P, Delgado T (2007) J Chromatogr A 1167:95–101
González-Osnaya L, Soriano JM, Moltó JC, Mañes J (2008) Food Chem 108:272–276
Sørensen LK, Elbæk TH (2005) J Chromatogr B 820:183–196
Commission Regulation (EC) No 839/2008 of 31 July 2008 amending Regulation (EC) No 395/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards Annexes II, III and IV on maximum residue levels of pesticides in or on certain products. Official Journal of the European Union L234/1, 30 Aug 2008
US Food and Drug Administration (1996) Sec. 527.400 Whole milk, low fat milk, skim milk-aflatoxin M1 (CPG 7106.210). In: FDA compliance policy guides. FDA, Washington, DC, p. 219
Commission Regulation (EC) No 165/2010 of 26 February 2010 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs as regards aflatoxins. Official Journal of the European Union, L50/8, 27 Feb 2010
Chen CY, Li WJ, Peng KY (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:8474–8480
Manetta AC, Di Giuseppe L, Giammarco M, Fusaro I, Simonella A, Gramenzi A, Formigoni A (2005) J Chromatogr A 1083:219–222
Boudra H, Barnouin J, Dragacci S, Morgavi DP (2007) J Dairy Sci 90:3197–3201
Decastelli L, Lai J, Gramaglia M, Monaco A, Nachtmann C, Oldano F, Ruffier M, Sezian A, Bandirola C (2007) Food Control 18:1263–1266
Bogialli S, Curini R, Di Corcia A, Laganà A, Stabile A, Sturchio E (2006) J Chromatogr A 1102:1–10
Khay S, Abd El-Aty AM, Choi JH, Shin EH, Kim JS, Chang BJ, Lee CH, Shin SC, Jeong JY, Shim JH (2009) J Sep Sci 32:244–251
Bogialli S, Curini R, Di Corcia A, Laganà A, Nazzari M, Tonci M (2004) J Chromatogr A 1054:351–357
Dagnac T, García-Chao M, Pulleiro P, García-Jares C, Llompart M (2009) J Chromatogr A 1216:3702–3709
Zhu L, Huey Ee K, Zhao L, Kee Lee H (2002) J Chromatogr A 963:335–343
Basheer C, Kee Lee H (2004) J Chromatogr A 1047:189–194
Anastassiades M, Lehotay SJ, Stajnbaher D, Schenck FJ (2003) J AOAC Int 86:412–431
Cunha SC, Lehotay SJ, Mastovska K, Fernándes JO, Oliveira MBPP (2007) J Sep Sci 30:620–632
Romero-González R, Garrido Frenich A, Martínez Vidal JL (2008) Talanta 76:211–225
Lacina O, Urbanová J, Krplová A, Hajšlová J (2008) Chem Listy 102:s404–s405
Mol HGJ, Plaza-Bolaños P, Zomer P, de Rijk TC, Stolker AAM, Mulder PPJ (2008) Anal Chem 80:9450–9459
Frenich AG, Martínez Vidal JL, Romero-González R, Aguilera-Luiz MM (2009) Food Chem 117:705–712
Beltrán E, Ibáñez M, Sancho JV, Hernández F (2009) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 23:1801–1809
Zhang K, Wong JW, Hayward DG, Sheladia P, Krynitsky AJ, Schenck FJ, Webster MG, Ammann JA, Ebeler SE (2009) J Agric Food Chem 57:4019–4029
CEN Standard Method EN 15662: Food of plant origin-determination of pesticide residues using GC-MS and/or LC-MS/MS following acetonitrile extraction/portioning and clean-up by dispersive SPE-QuECHERS method. Available at http://www.cen.eu. Accessed on October 2010
AOAC Official Method 2007.01. Pesticide residues in foods by acetonitrile extraction and partitioning with magnesium sulphate
Lehotay SJ, Mastovska K, Yun SJ (2005) J AOAC Int 88:630–638
Commission Decision 2002/657/EEC of 12 August 2002 implementing Council Directive 92/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of the results (2002) Official Journal of the European Communities L221, 17 Aug 2002, pp 8–36
European Commission Directorate General Health and Consumer Protection, Guidance Document on Method Validation and Quality Control Procedures for Pesticide Residues Analyses in Food and Feed, SANCO/10684/2009, 01 Jan 2010
http://ec.europa.eu/sanco_pesticides/public/index.cfm. Accessed on October 2010
Cuadros-Rodríguez L, García-Campaña A, Jiménez-Linares C, Alés-Barrero F, Román-Ceba M (1995) J AOAC Int 78:471–476
British Crop Protection Council (2005–2006) The e-Pesticide Manual. Version 3.2. 13th edn. British Crop Protection Council, Hampshire
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (MICINN-FEDER) for financial support (Project Ref. AGL2006-12127-C02-01 and CTQ2009-07686). MMAL acknowledges her grant (F.P.U.) from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (Ref. AP2008-02811). PPB is grateful for personal funding through Juan de la Cierva Program (Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation-European Social Fund, SMSI-ESF). RRG is also grateful for personal funding through the Ramón y Cajal Program (SMSI-ESF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aguilera-Luiz, M.M., Plaza-Bolaños, P., Romero-González, R. et al. Comparison of the efficiency of different extraction methods for the simultaneous determination of mycotoxins and pesticides in milk samples by ultra high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 399, 2863–2875 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-4670-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-4670-7