Abstract
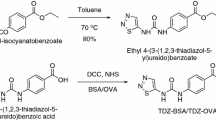
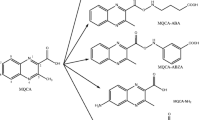
The development and characterization of one rat monoclonal antibody (mAb) for 2,4-dinitroaniline and of two rat mAbs for 2,6-dinitroaniline are described. With the immunization of rats with 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl-glycylglycine–keyhole limpet hemocyanine (KLH) conjugate one mAb (PK 5H6) has been developed and formatted into a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). This assay no. 1 is very sensitive for 2,4-dinitroaniline with a test midpoint of 0.24 ± 0.06 μg L−1 (n = 19) in 40 mM phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). A second hapten, 3-(4-amino-2,6-dinitrophenyl)propionic acid, which was also conjugated to KLH and used for the immunization of rats, led to two sensitive ELISAs for 2,6-dinitroaniline in 40 mM PBS with test midpoints of 0.61 ± 0.08 μg L−1 (n = 15; mAb DNT4 3C6; assay no. 2) and 0.94 ± 0.29 μg L−1 (n = 17; mAb DNT4 1A7, assay no. 3). Selectivities of all mAbs were checked with more than 20 compounds, including nitroaromatic compounds, 2,6-dinitroaniline pesticides, and other substituted derivatives of aniline. As very noticeable cross-reactivities, all mAbs recognize 2-chloro-4,6-dinitroaniline, 4-chloro-2,6-dinitroaniline and 2-bromo-4,6-dinitroaniline, the last of these being a major metabolite of the azo dye Disperse Blue 79. As first demonstrations of applications, two ELISAs (assays no. 1 and 2) were used for the analysis of 2,4- or 2,6-dinitroaniline in spiked water and soil samples. Recovery data were determined and the majority of these data were in the range of 90–120%. These assays can contribute to a very cost-effective and environmentally friendly immunochemical surveillance monitoring of environmental samples for contaminations with these compounds. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, these are the first antibodies described for 2,4-dinitroaniline and for 2,6-dinitroaniline.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4-DNA:
-
2,4-dinitroaniline
- 2,6-DNA:
-
2,4-dinitroaniline
- DNP:
-
dinitrophenyl
- 2-ADNT:
-
2-amino-4,6-dinitrotoluene
- 4-ADNT:
-
4-amino-2,6-dinitrotoluene
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- CR:
-
cross-reactivity
- D:
-
dalton
- ECD:
-
electron capture detector
- ELISA:
-
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- GC:
-
gas chromatography
- HMX:
-
1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetraazacyclooctane
- H2O2 :
-
hydrogen peroxide
- HRP:
-
horseradish peroxidase
- IC50 :
-
inhibitory concentration 50%, test midpoint of standard curve
- IgG:
-
immunoglobulin G
- KLH:
-
keyhole limpet hemocyanine
- mAb:
-
monoclonal antibody
- LC:
-
liquid chromatography
- MW:
-
molecular weight
- NPD:
-
nitrogen phosphorus detector
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- RDX:
-
1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazacyclohexane
- TMB:
-
3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine
- TNP:
-
trinitrophenyl
- TNT:
-
2,4,6-trinitrotoluene
References
Windholz M (1983) The Merck index, 10th edn. Merck, Rahway, NJ p 3275
Keum Y-S, Li QX (2004) Chemospere 54:255
EPA Method 8131 (1996) http://www.epa.gov/sw-846/pdfs/8131.pdf. Accessed 28 Apr 2008
Riggin RM, Cole TF, Billets S (1983) Anal Chem 55:1862
Krämer PM, Kremmer E, Weber CM, Ciumasu IM, Forster S, Kettrup AA (2005) Anal Bioanal Chem 382:1919
Whelan JP, Kusterbeck AW, Wemhoff GA, Bredehorst R, Ligler FS (1993) Anal Chem 65:3561
Zeck A, Weller MG, Niessner R (1999) Fresenius J Anal Chem 364:113
Altstein M, Bronshtein A, Glattstein B, Zeichner A, Tamiri T, Almog J (2001) Anal Chem 73:2461
Hegedüs G, Bélai I, Székács A (2000) Anal Chim Acta 421:121
Park K-M, Yoon I, Lee SS, Choi G, Lee JS (2002) Dyes Pigments 54:155
Köhler G, Milstein C (1975) Nature 256:495
Whitaker JR, Granum PE (1980) Anal Biochem 109:156
Guigues N, Behro C, Roy S, Foucher J-C, Fouillac A-M (2007) TrAC 26:268
Krämer PM (1998) Anal Chim Acta 376:3
Weber EJ, Adams RL (1995) Environ Sci Technol 29:1163
Krämer PM, Baumann BA, Stoks PG (1997) Anal Chim Acta 347:187
Tschmelak J, Proll G, Gauglitz G (2005) Talanta 65:313
Tschmelak J, Proll G, Riedt J, Kaiser J, Kraemmer P, Barzaga L, Wilkinson JS, Hua P, Hole JP, Nudd R, Jackson M, Abuknesha R, Barceló D, Rodriguez-Mozaz S, López de Alda MJ, Sacher F, Stien J, Slobodník J, Oswald P, Kozmenko H, Korenková E, Tóthová L, Krascsenits Z, Gauglitz G (2005) Biosens Bioelectron 20:1499
Tschmelak J, Proll G, Riedt J, Kaiser J, Kraemmer P, Barzaga L, Wilkinson JS, Hua P, Hole JP, Nudd R, Jackson M, Abuknesha R, Barceló D, Rodriguez-Mozaz S, López de Alda MJ, Sacher F, Stien J, Slobodník J, Oswald P, Kozmenko H, Korenková E, Tóthová L, Krascsenits Z, Gauglitz G (2005) Biosens Bioelectron 20:1509
Krämer PM, Weber CM, Kremmer E, Räuber C, Martens D, Forster S, Stanker LH, Rauch P, Shiundu PM, Mulaa FJ (2007) In: Kennedy IR et al (ed) Rational environmental management of agrochemicals, risk assessment, monitoring, and remedial action. ACS Symposium Series 966, Washington, DC, USA
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Norbert Hertkorn (IEC, HMGU) for the confirmation of NMR data of the hapten 3-(4-amino-2,6-dinitrophenyl)propionic acid. Dr. Ioan Manuel Ciumasu, Dr. Cristina Weber and Ms Sabine Rottmüller (all formerly IEC, HMGU) and Ms Melanie Keß (IEC, HMGU) are acknowledged for their dedicated commitment in laboratory work and technical assistance. SWIFT water samples were kindly provided within the EU project SWIFT-WFD (SSPI-CT-2003–502492). Part of this research was funded by the BMBF (Federal Ministry of Education and Research, FKZ 02WU0102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krämer, P.M., Forster, S. & Kremmer, E. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for the sensitive analysis of 2,4-dinitroaniline and 2,6-dinitroaniline in water and soil. Anal Bioanal Chem 391, 1821–1835 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2146-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2146-1