Abstract
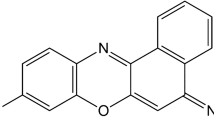
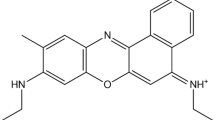
The vibronic absorption spectrum of Azure C (AC) in an aqueous solution is calculated using the time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT). The results of calculations are analyzed using all published hybrid functionals supported by Gaussian16, the 6–31 + + G(d,p) basis set, and the IEFPCM and SMD solvent models. The solvent model IEFPCM gave significantly underestimated values of λmax in comparison with the experiment. This is a manifestation of the TD-DFT "cyanine failure". However, the SMD model made it possible to obtain a good agreement between the calculation results and experimental data. The best fit was achieved using the X3LYP functional. According to our calculations, the shoulder in the visible absorption spectrum of AC has a vibronic origin. The dipole moments and atomic charges of the ground and excited states of the AC molecule have been calculated. Photoexcitation leads to an increase in the dipole moment of the dye molecule. An insignificant photoinduced electron transfer was found in the central ring of the chromophore of the dye molecule. Following our results, the absorption peak of the AC solution in the visible region of the spectrum is due to the π → π* type electronic transition. Vibronic coupling plays a significant role in the absorption spectra of AC.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marshall PN (1976) The composition of stains produced by the oxidation of methylene blue. Histochem J 8:431–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01003831
Penney DP, Powers JM, Frank M, Willis C, Churukian C (2002) Analysis and testing of biological stains - the biological stain commission procedures. Biotech Histochem 77:237–275. https://doi.org/10.1080/bih.77.5-6.237.275
Jana AK, Bhowmik BB (1999) Enhancement in power output of solar cells consisting of mixed dyes. J Photochem Photobiol A 122:53–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(98)00467-5
Orak I, Turut A, Toprak M (2015) The comparison of electrical characterizations and photovoltaic performance of Al/p-Si and Al/Azure C/p-Si junctions devices. Synth Met 200:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2014.12.023
Nakaminami T, Kuwabata S, Yoneyama H (1997) Electrochemical oxidation of cholesterol catalyzed by cholesterol oxidase with use of an artificial electron mediator. Anal Chem 69:2367–2372
Bandyopadhyay P, Basu R, Das S, Bhar DS, Manchanda R, Nandy P (2017) Enhancement of quantum efficiency of a dye-sensitized electrochemical cell by using triturated zinc oxide mixed with two organic dyes, azure c and rose bengal. Int J High Dilution Res 16:1–6
Gowda AT, Gowda NMM, Gowda HS, Rangappa KS (1985) Application of azure C for the extractive spectrophotometric determination of microgram amounts of penicillin. J Pharm Methods 13:275–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/0160-5402(85)90028-2
Gowda AT, Gowda NMM, Rangappa KS (1984) Spectrophotometric determination of saccharin in soft drinks and pharmaceuticals. Anal Lett 17:2129–2140. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032718408077203
Das S, Islam M, Jana GC, Patra A, Jha PK, Hossain M (2017) Molecular binding of toxic phenothiazinium derivatives, azures to bovine serum albumin: a comparative spectroscopic, calorimetric, and in silico study. J Mol Recognit. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmr.2609
AlRammahi DY, Waheeb AZ (2016) Removal of azure C dye from aqueous solution using natural clay adsorbent. Int J Sci Res 5:1110–1113
Narband N, Uppal M, Dunnill CW, Hyett G, Wilson M, Parkin IP (2009) The interaction between gold nanoparticles and cationic and anionic dyes: enhanced UV-visible absorption. Phys Chem Chem Phys 11:10513–10518. https://doi.org/10.1039/B909714G
N. Narband, Nanoparticles and photosensitisers; their interactions and antibacterial properties, PhD Thesis, University College London, 2009.
Chakraborty A, Ali M, Saha SK (2010) Molecular interaction of organic dyes in bulk and confined media. Spectrochim Acta A 75:1577–1583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2010.02.022
Marbán G, Vu TT, Valdés-Solís T (2011) A simple visible spectrum deconvolution technique to prevent the artefact induced by the hypsochromic shift from masking the concentration of methylene blue in photodegradation experiments. Appl Catal A 402:218–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2011.06.009
AlShamsi HAH, Hamza AT (2015) Degradation of thiazine dyes azure B and C by sonolysis, sonophotolysis and sonocatalysis. Asian J Chem. https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2015.18842
Mills A, Hazafy D, Parkinson J, Tuttle T, Hutchings MG (2011) Effect of alkali on methylene blue (CI Basic Blue 9) and other thiazine dyes. Dyes Pigments 88:149–155
Havelcova M, Kubat P, Nemcova I (2000) Photophysical properties of thiazine dyes in aqueous solution and in micelles. Dyes Pigments 44:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-7208(99)00070-4
Bertolotti SG, Previtali CM (1999) The excited states quenching of phenothiazine dyes by p-benzoquinones in polar solvents. Dyes Pigments 41:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-7208(98)00063-1
McKamey MR, Spitznagle LA (1975) Chromatographic, mass spectral, and visible light absorption characteristics of toluidine blue O and related dyes. J Pharm Sci 64:1456–1462. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.2600640907
Baiardi A, Bloino J, Barone V (2013) General time dependent approach to vibronic spectroscopy including franck-condon, herzberg-teller, and duschinsky effects. J Chem Theory Comput 9:4097–4115. https://doi.org/10.1021/ct400450k
Condon EU (1928) Nuclear motions associated with electron transitions in diatomic molecules. Phys Rev 32:858–872. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.32.858
Herzberg G, Teller E (1933) Schwingungsstruktur der Elektronenubergange bei mehratomigen Molekulen. Z Phys Chem 21:410–446
Santoro F, Lami A, Improta R, Bloino J, Barone V (2008) Effective method for the computation of optical spectra of large molecules at finite temperature including the Duschinsky and Herzberg-Teller effect: The Qx band of porphyrin as a case study. J Chem Phys 128:224311. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2929846
Improta R, Barone V, Scalmani G, Frisch MJ (2006) A state–specific polarizable continuum model time dependent density functional method for excited state calculations in solution. J Chem Phys 125:054103. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2222364
Marenich AV, Cramer CJ, Truhlar DG (2009) Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J Phys Chem B 113:6378–6396. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp810292n
M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, G. A. Petersson, H. Nakatsuji, X. Li, M. Caricato, A. V. Marenich, J. Bloino, B. G. Janesko, R. Gomperts, B. Mennucci, H. P. Hratchian, J. V. Ortiz, A. F. Izmaylov, J. L. Sonnenberg, D. Williams–Young, F. Ding, F. Lipparini, F. Egidi, J. Goings, B. Peng, A. Petrone, T. Henderson, D. Ranasinghe, V. G. Zakrzewski, J. Gao, N. Rega, G. Zheng, W. Liang, M. Hada, M. Ehara, K. Toyota, R. Fukuda, J. Hasegawa, M. Ishida, T. Nakajima, Y. Honda, O. Kitao, H. Nakai, T. Vreven, K. Throssell, J. A. Montgomery, Jr., J. E. Peralta, F. Ogliaro, M. J. Bearpark, J. J. Heyd, E. N. Brothers, K. N. Kudin, V. N. Staroverov, T. A. Keith, R. Kobayashi, J. Normand, K. Raghavachari, A. P. Rendell, J. C. Burant, S. S. Iyengar, J. Tomasi, M. Cossi, J. M. Millam, M. Klene, C. Adamo, R. Cammi, J. W. Ochterski, R. L. Martin, K. Morokuma, O. Farkas, J. B. Foresman, and D. J. Fox, Gaussian 16, Revision C.01, Inc., Wallingford CT, 2016.
R. Dennington, T.A. Keith, J.M. Millam, GaussView, Version 6.1, Semichem Inc., Shawnee Mission KS, 2016.
Dierksen M, Grimme S (2004) The vibronic structure of electronic absorption spectra of large molecules: a time-dependent density functional study on the influence of “Exact” hartree-fock exchange. J Phys Chem A 108:10225–10237. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp047289h
Charaf-Eddin A, Planchat A, Mennucci B, Adamo C, Jacquemin D (2013) Choosing a functional for computing absorption and fluorescence band shapes with TD–DFT. J Chem Theory Comput 9:2749–2760. https://doi.org/10.1021/ct4000795
Kantchev EAB, Norsten TB, Sullivan MB (2012) Time–dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) modelling of Pechmann dyes: from accurate absorption maximum prediction to virtual dye screening. Org Biomol Chem 10:6682–6692. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2OB25806D
Jacquemin D, Brémond E, Ciofini I, Adamo C (2012) Impact of vibronic couplings on perceived colors: two anthraquinones as a working example. J Phys Chem Lett 3:468–471. https://doi.org/10.1021/jz201552x
Jacquemin D, Zhao Y, Valero R, Adamo C, Ciofini I, Truhlar DG (2012) Verdict: time-dependent density functional theory “not guilty” of large errors for cyanines. J Chem Theory Comput 8:1255–1259. https://doi.org/10.1021/ct200721d
Le Guennic B, Jacquemin D (2015) Taking up the cyanine challenge with quantum tools. Acc Chem Res 48:530–537. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar500447q
Zhou P (2018) Why the lowest electronic excitations of rhodamines are overestimated by time–dependent density functional theory. Int J Quantum Chem 118:e25780. https://doi.org/10.1002/qua.25780
Fleming S, Mills A, Tuttle T (2011) Predicting the UV-vis spectra of oxazine dyes. Beilstein J Org Chem 7:432–441. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjoc.7.56
Reichardt C (1994) Solvatochromic dyes as solvent polarity indicators. Chem Rev 94:2319–2358. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00032a005
Kostjukov VV, Khomytova NM, Hernandez Santiago AA, Licona Ibarra R, Davies DB, Evstigneev MP (2011) Calculation of the electrostatic charges and energies for intercalation of aromatic drug molecules with DNA. Int J Quantum Chem 111:711–721
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LOK: Software. SVL: Visualisation. VVK: Conceptualization, Writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any Conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.






Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostjukova, L.O., Leontieva, S.V. & Kostjukov, V.V. Vibronic absorption spectrum and electronic properties of azure C in aqueous solution: TD-DFT study. Theor Chem Acc 140, 114 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-021-02808-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-021-02808-y