Abstract.
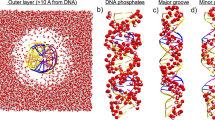
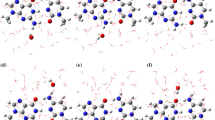
Interactions with water molecules are important for the stabilization of three-dimensional structures of nucleic acids and for their functioning. The first hydration shells of macromolecules can be considered as structural parts of nucleic acid. We performed a Monte Carlo study of systems containing a nucleic acid base or base pair with water molecules using improved potential functions. These potential functions enable experimental data on both single base–single water interaction energies and enthalpies of base hydration to be reproduced. Hydration shell structures of base pairs are dependent on the pair geometry. Structural elements of hydration shells can contribute to the pair stability and hence to the probability of mispair formation during nucleic acid biosynthesis. The distribution of water molecules around bases and base pairs is essentially nonhomogeneous.
Similar content being viewed by others
Acknowledgments.
This study was supported in part by CONACyT, Mexico, project no.35239-E, by VIEPBUAP-CONACyT, project no. II151G02 and by INTAS, project no. 97-31753.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
From the Proceedings of the 28th Congreso de Químicos Teóricos de Expresión Latina (QUITEL 2002).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González, E., Deriabina, A., Teplukhin, A. et al. Monte Carlo study of three-dimensional organization of water molecules around DNA fragments. Theor Chem Acc 110, 460–465 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-003-0502-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-003-0502-y