Abstract
Rationale
Chronic administration of D2/3 receptor agonists ropinirole or pramipexole can increase the choice of uncertain rewards in rats, theoretically approximating iatrogenic gambling disorder (iGD).
Objectives
We aimed to assess the effect of chronic ropinirole in animal models that attempt to capture critical aspects of commercial gambling, including the risk of losing rather than failing to gain, and the use of win-paired sensory stimuli heavily featured in electronic gambling machines (EGMs).
Methods
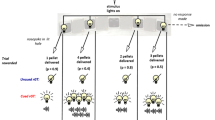
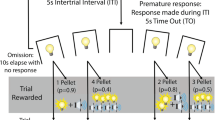
Male Long–Evans rats learned the rat gambling task (rGT; n = 24), in which animals sample between four options that differ in the magnitude and probability of rewards and time-out punishments. In the cued rGT (n = 40), reward-concurrent audiovisual cues were added that scaled in complexity with win size. Rats were then implanted with an osmotic pump delivering ropinirole (5 mg/kg/day) or saline for 28 days.
Results
Chronic ropinirole did not unequivocally increase preference for more uncertain outcomes in either the cued or uncued rGT. Ropinirole transiently increased premature responses, a measure of motor impulsivity, and this change was larger and more long-lasting in the cued task.
Conclusions
These data suggest that explicitly signaling loss prevents the increase in preference for uncertain rewards caused by D2/3 receptor agonists observed previously. The ability of win-paired cues to amplify ropinirole-induced increases in motor impulsivity may explain why compulsive use of EGMs is particularly common in iGD. These data offer valuable insight into the cognitive–behavioral mechanisms through which chronic dopamine agonist treatments may induce iGD and related impulse control disorders.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams WK, Barkus C, Ferland JN, Sharp T, Winstanley CA (2017a) Pharmacological evidence that 5-HT2C receptor blockade selectively improves decision making when rewards are paired with audiovisual cues in a rat gambling task. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 234(20):3091–3104
Adams WK, Barrus MM, Zeeb FD, Cocker PJ, Benoit J, Winstanley CA (2017b) Dissociable effects of systemic and orbitofrontal administration of adrenoceptor antagonists on yohimbine-induced motor impulsivity. Behav Brain Res 328:19–27
Adams WK, Vonder Haar C, Tremblay M, Cocker PJ, Silveira MM, Kaur S, Baunez C, Winstanley CA (2017c) Deep-brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus selectively decreases risky choice in risk-preferring rats. eNeuro 4:ENEURO.0094–ENEU17.2017
Alter A (2017) Irresistible: the rise of addictive technology and the business of keeping us hooked, 1st edn. Penguin, City of Westminster
Anastasio NC, Stutz SJ, Fink LH, Swinford-Jackson SE, Sears RM, DiLeone RJ, Rice KC, Moeller FG, Cunningham KA (2015) Serotonin (5-HT) 5-HT2A receptor (5-HT2AR):5-HT2CR imbalance in medial prefrontal cortex associates with motor impulsivity. ACS Chem Neurosci 6:1248–1258
Aston-Jones G, Cohen JD (2005) An integrative theory of locus coeruleus-norepinephrine function: adaptive gain and optimal performance. Annu Rev Neurosci 28:403–450
Azeem A, Talegaonkar S, Negi LM, Ahmad FJ, Khar RK, Iqbal Z (2012) Oil based nanocarrier system for transdermal delivery of ropinirole: a mechanistic, pharmacokinetic and biochemical investigation. Int J Pharm 422:436–444
Baarendse PJ, Winstanley CA, Vanderschuren LJ (2012) Simultaneous blockade of dopamine and noradrenaline reuptake promotes disadvantageous decision making in a rat gambling task. Psychopharmacology 225:719–731
Barrus MM, Winstanley CA (2016) Dopamine D3 receptors modulate the ability of win-paired cues to increase risky choice in a rat gambling task. J Neurosci 36:785–794
Barrus MM, Hosking JG, Zeeb FD, Tremblay M, Winstanley CA (2015) Disadvantageous decision-making is associated with increased motor impulsivity at the population level on a rodent gambling task. J Psychiatry Neurosci 40:108–117
Beaulieu JM, Sotnikova TD, Yao WD, Kockeritz L, Woodgett JR, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2004) Lithium antagonizes dopamine-dependent behaviors mediated by an AKT/glycogen synthase kinase 3 signaling cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:5099–5104
Beaulieu JM, Sotnikova TD, Marion S, Lefkowitz RJ, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2005) An Akt/beta-arrestin 2/PP2A signaling complex mediates dopaminergic neurotransmission and behavior. Cell 122:261–273
Beaulieu JM, Tirotta E, Sotnikova TD, Masri B, Salahpour A, Gainetdinov RR, Borrelli E, Caron MG (2007) Regulation of Akt signaling by D2 and D3 dopamine receptors in vivo. J Neurosci 27:881–885
Bechara A (2005) Decision making, impulse control and loss of willpower to resist drugs: a neurocognitive perspective. Nat Neurosci 8:1458–1463
Bechara A, Dolan S, Denburg N, Hindes A, Anderson SW, Nathan PE (2001) Decision-making deficits, linked to a dysfunctional ventromedial prefrontal cortex, revealed in alcohol and stimulant abusers. Neuropsychologia 39:376–389
Belin D, Mar AC, Dalley JW, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2008) High impulsivity predicts the switch to compulsive cocaine-taking. Science 320:1352–1355
Bentivoglio AR, Baldonero E, Ricciardi L, De Nigris F, Daniele A (2013) Neuropsychological features of patients with Parkinson’s disease and impulse control disorders. Neurol Sci 34:1207–1213
Bolla KI, Eldreth DA, Matochik JA, Cadet JL (2005) Neural substrates of faulty decision-making in abstinent marijuana users. Neuroimage 26:480–492
Breen RB, Zimmerman M (2002) Rapid onset of pathological gambling in machine gamblers. J Gambl Stud 18:31–43
Carli M, Robbins TW, Evenden JL, Everitt BJ (1983) Effects of lesions to ascending noradrenergic neurons on performance of a 5-choice serial reaction time task in rats—implications for theories of dorsal noradrenergic bundle function based on selective attention and arousal. Behav Brain Res 9:361–380
Chernoloz O, El Mansari M, Blier P (2011) Long-term administration of the dopamine D3/2 receptor agonist pramipexole increases dopamine and serotonin neurotransmission in the male rat forebrain. J Psychiatry Neurosci 37:113–121
Choliz M (2010) Experimental analysis of the game in pathological gamblers: effect of the immediacy of the reward in slot machines. J Gambl Stud 26:249–256
Cocker PJ, Winstanley CA (2015) Irrational beliefs, biases and gambling: exploring the role of animal models in elucidating vulnerabilities for the development of pathological gambling. Behav Brain Res 279:259–273
Cocker PJ, Hosking JG, Benoit J, Winstanley CA (2012) Sensitivity to cognitive effort mediates psychostimulant effects on a novel rodent cost/benefit decision-making task. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:1825–1837
Cocker PJ, Tremblay M, Kaur S, Winstanley CA (2017) Chronic administration of the dopamine D2/3 agonist ropinirole invigorates performance of a rodent slot machine task, potentially indicative of less distractible or compulsive-like gambling behaviour. Psychopharmacology 234:137–153
Cole BJ, Robbins TW (1989) Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the nucleus accumbens septi on performance of a 5-choice serial reaction time task in rats—implications for theories of selective attention and arousal. Behav Brain Res 33:165–179
Cunningham KA, Anastasio NC (2014) Serotonin at the nexus of impulsivity and cue reactivity in cocaine addiction. Neuropharmacology 76(Pt B):460–478
Dagher A, Robbins TW (2009) Personality, addiction, dopamine: insights from Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 61:502–510
Dalley JW, Fryer TD, Brichard L, Robinson ES, Theobald DE, Laane K, Pena Y, Murphy ER, Shah Y, Probst K, Abakumova I, Aigbirhio FI, Richards HK, Hong Y, Baron JC, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (2007) Nucleus accumbens D2/3 receptors predict trait impulsivity and cocaine reinforcement. Science 315:1267–1270
Di Ciano P, Manvich DF, Pushparaj A, Gappasov A, Hess EJ, Weinshenker D, Le Foll B (2018) Effects of disulfiram on choice behavior in a rodent gambling task: association with catecholamine levels. Psychopharmacology 235:23–35
Dixon MJ, Harrigan KA, Sandhu R, Collins K, Fugelsang JA (2010) Losses disguised as wins in modern multi-line video slot machines. Addiction 105:1819–1824
Dow Schull N (2012) Addiction by design: machine gambling in Las Vegas, 1st edn. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Eden RJ, Costall B, Domeney AM, Gerrard PA, Harvey CA, Kelly ME, Naylor RJ, Owen DA, Wright A (1991) Preclinical pharmacology of ropinirole (SK&F 101468-A) a novel dopamine D2 agonist. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 38:147–154
Endrenyi L, Tothfalusi L (2012) Metrics for the evaluation of bioequivalence of modified-release formulations. AAPS J 14:813–819
Euteneuer F, Schaefer F, Stuermer R, Boucsein W, Timmermann L, Barbe MT, Ebersbach G, Otto J, Kessler J, Kalbe E (2009) Dissociation of decision-making under ambiguity and decision-making under risk in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a neuropsychological and psychophysiological study. Neuropsychologia 47:2882–2890
Ferland J-MN, Winstanley CA (2016) Risk-preferring rats make worse decisions and show increased incubation of craving after cocaine self-administration. Addict Biol 22(4):991–1001
Fiorillo CD, Tobler PN, Schultz W (2003) Discrete coding of reward probability and uncertainty by dopamine neurons. Science 299:1898–1902
Floresco SB, St Onge JR, Ghods-Sharifi S, Winstanley CA (2008) Cortico-limbic-striatal circuits subserving different forms of cost-benefit decision making. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 8:375–389
Goudriaan AE, Oosterlaan J, de Beurs E, van den Brink W (2005) Decision making in pathological gambling: a comparison between pathological gamblers, alcohol dependents, persons with Tourette syndrome, and normal controls. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 23:137–151
Grant LD, Bowling AC (2015) Gambling attitudes and beliefs predict attentional bias in non-problem gamblers. J Gambl Stud 31:1487–1503
Grant S, Contoreggi C, London ED (2000) Drug abusers show impaired performance in a laboratory test of decision making. Neuropsychologia 38:1180–1187
Grimes CA, Jope RS (2001) The multifaceted roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in cellular signaling. Prog Neurobiol 65:391–426
Harrison A, Everitt BL, Robbins TW (1997a) Central 5-HT depletion enhances impulsive responding without affecting the accuracy of attentional performance: interactions with dopaminergic mechanisms. Psychopharmacology 133:329–342
Harrison A, Everitt BL, Robbins TW (1997b) Double dissociable effects of median- and dorsal-raphe lesions on the performance of the five-choice serial reaction time test of attention in rats. Behav Brain Res 89:135–149
Higgins GA, Enderlin M, Haman M, Fletcher PJ (2003) The 5-HT2A receptor antagonist M100,907 attenuates motor and “impulsive-like” behaviours produced by NMDA receptor antagonism. Psychopharmacology 170:309–319
Holtz NA, Tedford SE, Persons AL, Grasso SA, Napier TC (2016) Pharmacologically distinct pramipexole-mediated akinesia vs. risk-taking in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 70:77–84
Lane EL, Dunnett SB (2010) Pre-treatment with dopamine agonists influence L-dopa mediated rotations without affecting abnormal involuntary movements in the 6-OHDA lesioned rat. Behav Brain Res 213:66–72
Laties VG (1975) The role of discriminative stimuli in modulating drug action. Fed Proc 34:1880–1888
Laties VG, Weiss B (1966) Influence of drugs on behavior controlled by internal and external stimuli. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 152:388–396
Li YC, Gao WJ (2011) GSK-3beta activity and hyperdopamine-dependent behaviors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35:645–654
Li Z, Yu F, Di Z, Zhao X, Zhao S, Liu Y, Li Y, Wang Z, Gong W, Zhang H, Yang Y, Xie X, Mei X (2016) Development and uniform evaluation of ropinirole osmotic pump tablets with REQUIP XL both in vitro and in beagle dogs. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 42:12–18
Lim MS, Jocham G, Hunt LT, Behrens TE, Rogers RD (2015) Impulsivity and predictive control are associated with suboptimal action-selection and action-value learning in regular gamblers. Int Gambl Stud 15:489–505
Lonze BE, Ginty DD (2002) Function and regulation of CREB family transcription factors in the nervous system. Neuron 35:605–623
Lutri V, Soldini E, Ronzitti S, Smith N, Clerici M, Blaszczynski A, Bowden-Jones H (2018) Impulsivity and gambling type among treatment-seeking disordered gamblers: an explorative study. J Gambl Stud 34:1341–1354
Madden GJ, Johnson PS, Brewer AT, Pinkston JW, Fowler SC (2010) Effects of pramipexole on impulsive choice in male Wistar rats. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 18:267–276
Mahoney MK, Barnes JH, Wiercigroch D, Olmstead MC (2016) Pharmacological investigations of a yohimbine-impulsivity interaction in rats. Behav Pharmacol 27:585–595
Matsukawa N, Maki M, Yasuhara T, Hara K, Yu G, Xu L, Kim KM, Morgan JC, Sethi KD, Borlongan CV (2007) Overexpression of D2/D3 receptors increases efficacy of ropinirole in chronically 6-OHDA-lesioned Parkinsonian rats. Brain Res 1160:113–123
Meyer F, Latour J, Cools AR, Verheij MM (2014) Noradrenaline-induced release of newly-synthesized accumbal dopamine: differential role of alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors. Front Cell Neurosci 8:243
Moerschbaecher JM, Boren JJ, Schrot J, Fontes JC (1979) Effects of cocaine and d-amphetamine on the repeated acquisition and performance of conditional discriminations. J Exp Anal Behav 31:127–140
Nashatizadeh MM, Lyons KE, Pahwa R (2009) A review of ropinirole prolonged release in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Interv Aging 4:179–186
Obrien CP, Childress AR, Mclellan AT, Ehrman R (1992) Classical-conditioning in drug-dependent humans. Ann N Y Acad Sci 654:400–415
Pattij T, Janssen MC, Vanderschuren LJ, Schoffelmeer AN, van Gaalen MM (2007) Involvement of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the nucleus accumbens core and shell in inhibitory response control. Psychopharmacology 191:587–598
Pes R, Godar SC, Fox AT, Burgeno LM, Strathman HJ, Jarmolowicz DP, Devoto P, Levant B, Phillips PE, Fowler SC, Bortolato M (2017) Pramipexole enhances disadvantageous decision-making: lack of relation to changes in phasic dopamine release. Neuropharmacology 114:77–87
Petry NM (2001) Substance abuse, pathological gambling, and impulsiveness. Drug Alcohol Depend 63:29–38
Prikhojan A, Brannan T, Yahr MD (2000) Comparative effects of repeated administration of dopamine agonists on circling behavior in rats. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 107:1159–1164
Ramji JV, Keogh JP, Blake TJ, Broom C, Chenery RJ, Citerone DR, Lewis VA, Taylor AC, Yeulet SE (1999) Disposition of ropinirole in animals and man. Xenobiotica 29:311–325
Ravenscroft P, Chalon S, Brotchie JM, Crossman AR (2004) Ropinirole versus L-DOPA effects on striatal opioid peptide precursors in a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease: implications for dyskinesia. Exp Neurol 185:36–46
Rivalan M, Ahmed SH, Dellu-Hagedorn F (2009) Risk-prone individuals prefer the wrong options on a rat version of the Iowa Gambling Task. Biol Psychiatry 66:743–749
Rokosik SL, Napier TC (2012) Pramipexole-induced increased probabilistic discounting: comparison between a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease and controls. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:1397–1408
Scarselli M, Novi F, Schallmach E, Lin R, Baragli A, Colzi A, Griffon N, Corsini GU, Sokoloff P, Levenson R, Vogel Z, Maggio R (2001) D2/D3 dopamine receptor heterodimers exhibit unique functional properties. J Biol Chem 276:30308–30314
Schepisi C, De Carolis L, Nencini P (2013) Effects of the 5HT2C antagonist SB242084 on the pramipexole-induced potentiation of water contrafreeloading, a putative animal model of compulsive behavior. Psychopharmacology 227:55–66
Schultz W (1998) Predictive reward signal of dopamine neurons. J Neurophysiol 80:1–27
Silveira MM, Malcolm E, Shoaib M, Winstanley CA (2015) Scopolamine and amphetamine produce similar decision-making deficits on a rat gambling task via independent pathways. Behav Brain Res 281:86–95
Simon NW, Gilbert RJ, Mayse JD, Bizon JL, Setlow B (2009) Balancing risk and reward: a rat model of risky decision making. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:2208–2217
Singer BF, Scott-Railton J, Vezina P (2012) Unpredictable saccharin reinforcement enhances locomotor responding to amphetamine. Behav Brain Res 226:340–344
Stevens L, Betanzos-Espinosa P, Crunelle CL, Vergara-Moragues E, Roeyers H, Lozano O, Dom G, Gonzalez-Saiz F, Vanderplasschen W, Verdejo-Garcia A, Perez-Garcia M (2013) Disadvantageous decision-making as a predictor of drop-out among cocaine-dependent individuals in long-term residential treatment. Front Psychiatry 4:149
Tothfalusi L, Endrenyi L (2003) Estimation of Cmax and Tmax in populations after single and multiple drug administrations. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 30:363–385
Tremblay M, Silveira MM, Kaur S, Hosking JG, Adams WK, Baunez C, Winstanley CA (2017) Chronic D2/3 agonist ropinirole treatment increases preference for uncertainty in rats regardless of baseline choice patterns. Eur J Neurosci 45:159–166
Usher M, Cohen JD, Servan-Schreiber D, Rajkowski J, Aston-Jones G (1999) The role of locus coeruleus in the regulation of cognitive performance. Science 283:549–554
van den Bos R, Lasthuis W, den Heijer E, van der Harst J, Spruijt B (2006) Toward a rodent model of the Iowa gambling task. Behav Res Methods 38:470–478
van Holst RJ, Lemmens JS, Valkenburg PM, Peter J, Veltman DJ, Goudriaan AE (2012) Attentional bias and disinhibition toward gaming cues are related to problem gaming in male adolescents. J Adolesc Health 50:541–546
Verdejo-Garcia A, Bechara A (2009) A somatic marker theory of addiction. Neuropharmacology 56(Suppl 1):48–62
Verdejo-Garcia A, Lawrence AJ, Clark L (2008) Impulsivity as a vulnerability marker for substance-use disorders: review of findings from high-risk research, problem gamblers and genetic association studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32:777–810
Voon V, Thomsen T, Miyasaki JM, de Souza M, Shafro A, Fox SH, Duff-Canning S, Lang AE, Zurowski M (2007) Factors associated with dopaminergic drug-related pathological gambling in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 64:212–216
Voon V, Schoerling A, Wenzel S, Ekanayake V, Reiff J, Trenkwalder C, Sixel-Doring F (2011a) Frequency of impulse control behaviours associated with dopaminergic therapy in restless legs syndrome. BMC Neurol 11:117
Voon V, Sohr M, Lang AE, Potenza MN, Siderowf AD, Whetteckey J, Weintraub D, Wunderlich GR, Stacy M (2011b) Impulse control disorders in Parkinson disease: a multicenter case–control study. Ann Neurol 69:986–996
Wang G, Shi J, Chen N, Xu L, Li J, Li P, Sun Y, Lu L (2013) Effects of length of abstinence on decision-making and craving in methamphetamine abusers. PLoS One 8:e68791
Weintraub D (2009) Impulse control disorders in Parkinson’s disease: prevalence and possible risk factors. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 15(Suppl 3):S110–S113
Weintraub D, Nirenberg MJ (2013) Impulse control and related disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Neurodegener Dis 11:63–71
Winstanley CA, Clark L (2016) Translational models of gambling-related decision-making. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 28:93–120
Winstanley CA, Floresco SB (2016) Deciphering decision making: variation in animal models of effort- and uncertainty-based choice reveals distinct neural circuitries underlying core cognitive processes. J Neurosci 36(48):12069–12079
Winstanley CA, Theobald DE, Dalley JW, Glennon JC, Robbins TW (2004) 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor antagonists have opposing effects on a measure of impulsivity: interactions with global 5-HT depletion. Psychopharmacology 176:376–385
Winstanley CA, Eagle DM, Robbins TW (2006) Behavioral models of impulsivity in relation to ADHD: translation between clinical and preclinical studies. Clin Psychol Rev 26:379–395
Winstanley CA, Olausson P, Taylor JR, Jentsch JD (2010a) Insight into the relationship between impulsivity and substance abuse from studies using animal models. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34:1306–1318
Winstanley CA, Zeeb FD, Bedard A, Fu K, Lai B, Steele C, Wong AC (2010b) Dopaminergic modulation of the orbitofrontal cortex affects attention, motivation and impulsive responding in rats performing the five-choice serial reaction time task. Behav Brain Res 210:263–272
Worhunsky PD, Rogers RD (2018) An initial investigation of individual rate-of-play preferences and associations with EGM gambling behavior. J Gambl Stud 34:1067–1083
Zack M, Featherstone RE, Mathewson S, Fletcher PJ (2014) Chronic exposure to a gambling-like schedule of reward predictive stimuli can promote sensitization to amphetamine in rats. Front Behav Neurosci 8:36
Zalocusky KA, Ramakrishnan C, Lerner TN, Davidson TJ, Knutson B, Deisseroth K (2016) Nucleus accumbens D2R cells signal prior outcomes and control risky decision-making. Nature 531:642–646
Zeeb FD, Winstanley CA (2011) Lesions of the basolateral amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex differentially affect acquisition and performance of a rodent gambling task. J Neurosci 31:2197–2204
Zeeb FD, Winstanley CA (2013) Functional disconnection of the orbitofrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala impairs acquisition of a rat gambling task and disrupts animals’ ability to alter decision-making behavior after reinforcer devaluation. J Neurosci 33:6434–6443
Zeeb FD, Robbins TW, Winstanley CA (2009) Serotonergic and dopaminergic modulation of gambling behavior as assessed using a novel rat gambling task. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:2329–2343
Zeeb FD, Wong AC, Winstanley CA (2013) Differential effects of environmental enrichment, social-housing, and isolation-rearing on a rat gambling task: dissociations between impulsive action and risky decision-making. Psychopharmacology 225:381–395
Zeeb FD, Li Z, Fisher DC, Zack MH, Fletcher PJ (2017) Uncertainty exposure causes behavioural sensitization and increases risky decision-making in male rats: toward modelling gambling disorder. J Psychiatry Neurosci 42:404–413
Funding
This work was supported by an operating grant awarded to CAW from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research (CIHR), a pilot grant from Parkinson Society Canada, and ERA-NET NEURON (STNDBS-ICD) funding to CB and CAW. CAW also received salary support through the Michael Smith Foundation for Health Research and the CIHR New Investigator Award program. MT was supported by a CIHR Doctoral Award. MMB was supported by a Doctoral Four-Year Fellowship (4YF) provided by The University of British Columbia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
In the past 3 years, CAW has consulted for Hogan Lovells LLP and received due compensation. The authors confirm they have no other conflicts of interest or financial disclosures to make.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tremblay, M., Barrus, M.M., Cocker, P.J. et al. Increased motor impulsivity in a rat gambling task during chronic ropinirole treatment: potentiation by win-paired audiovisual cues. Psychopharmacology 236, 1901–1915 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-5173-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-5173-z