Abstract
Rationale
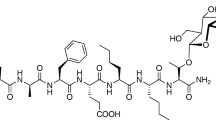
VRP26 displays mu opioid receptor agonist and delta opioid receptor antagonist activity in vitro, a pharmacological profile purported to produce reduced tolerance, dependence, and rewarding effects. We hypothesized that VRP26 would display reduced adverse effects after chronic administration as compared with the traditional opioid analgesic fentanyl.
Objective
The aim of this study is to explore the development of tolerance, dependence, and conditioned place preference of VRP26 as compared with the traditional opioid analgesic fentanyl.
Methods
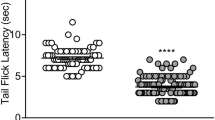
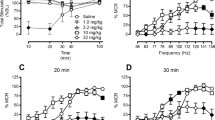
The antinociceptive effects of VRP26 and fentanyl were assessed using the mouse warm water tail withdrawal (WWTW) assay. Measurement of antinociceptive tolerance and physical dependence occurred after 7 days of continuous administration of either fentanyl (0.3 mg/kg/day) or VRP26 (10 mg/kg/day); tolerance was measured by a shift in the antinociceptive dose response curve in the WWTW assay. Physical dependence was determined by observation of withdrawal symptoms after precipitated withdrawal. Rewarding effects were measured by the ability of VRP26 or fentanyl to produce conditioned place preference.
Results
Fentanyl produced significant tolerance and dependence, as well as significant conditioned place preference. VRP26 produced neither tolerance nor physical dependence, nor did it produce significant conditioned place preference.
Conclusions
These results suggest that chronic treatment with VRP26 may produce less tolerance or physical dependence than chronic treatment with clinically available mu opioid analgesics such as fentanyl. Additionally, VRP26 produces less rewarding effects than fentanyl. This desirable in vivo profile may be due to the mixed efficacy nature of VRP26 and could provide the framework for safer opioid analgesics.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhamid EE, Sultana M, Portoghese PS, Takemori AE (1991) Selective blockage of the delta opioid receptors prevents the development of morphine tolerance and dependence in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 258:299–303
Aceto MD, Harris LS, Negus SS, Banks ML, Hughes LD, Akgun E, Portoghese PS (2012) MDAN-21: a bivalent opioid ligand containing mu-agonist and delta-antagonist pharmacophores and its effects in rhesus monkeys. Int J Med Chem 2012
Anand JP, Purington LC, Pogozheva ID, Traynor JR, Mosberg HI (2012) Modulation of opioid receptor ligand affinity and efficacy using active and inactive state receptor models. Chem Biol Drug Des 80:763–770
Anathan S, Khare NK, Saini SK, Seitz LE, Bartlett JL, Davis P, Dersch CM, Porecca F, Rothman RB, Bilsky EJ (2004) Identification of opioid ligands possessing mixed mu agonist/delta antagonist activity among pyridomorphans derived from naloxone, oxymorphone, and hydromorphone. J Med Chem 47:1400–1412
Bailey CP, Connor M (2005) Opioids: cellular mechanisms of tolerance and physical dependence. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:60–68
Balboni G, Guerrini R, Salvadori S, Bianchi C, Rizzi D, Bryant SD, Lazaruz LH (2002) Evaluation of the Dmt-Tic pharmacophore: conversion of a potent delta-opioid receptor antagonist into a potent delta agonist and ligands with mixed properties. J Med Chem 45:713–720
Ballantyne JC, LaForge KS (2007) Opioid dependence and addiction during opioid treatment of chronic pain. Pain 129:235–255
Bender AM, Griggs NW, Anand JP, Traynor JR, Jutkiewicz EM, Mosberg HI (2015) Asymmetric synthesis and in vitro and in vivo activity of tetrahydroquinolines featuring a diverse set of polar substitutions at the 6 position as mixed-efficacy mu opioid receptor/delta opioid receptorl. ACS Chem Neurosci 6:1428–1435
Breitwieser GE (2004) G protein-coupled receptor oligomerization: implications for G protein activation and cell signaling. Circ Res 94:17–27
Cahill CM, Holdridge SV, Morinville A (2007) Trafficking of the delta opioid receptors and other G protein-coupled receptors: implications for pain and analgesia. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28:23–31
Daniels DJ, Lenard NR, Etienne CL, Law PY, Roerig SC, Portoghese PS (2005) Opioid-induced tolerance and dependence in mice is modulated by the distance between pharmacophores in a bivalent ligand series. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:19208–19213
Dietis N, Guerrini R, Calo G, Salvadori S, Rowbotham DJ, Lambert DG (2009) Simultaneous targeting of multiple opioid receptors: a strategy to improve side-effect profile. Br J Anaesth 103:38–49
Fundytus ME, Schiller PW, Shapiro M, Weltrowska H, Coderre TJ (1995) Attenuation of morphine tolerance and dependence with the highly selective delta opioid receptor antagonist TIPP(psi). Eur J Pharmacol 286:105–108
Gomes I, IJzerman AP, Ye K, Maillet EL, Devi LA (2011) G protein-coupled receptor heteromerization: a role in allosteric modulation of ligand binding. Mol Pharmacol 79:1044–1052
Hanyaloglu AC, Seeber RM, Kohout TA, Lefkowitz RJ, Eidne KA (2002) Homo- and hetero-oligomerization of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) receptor subtypes. Differential regulation of beta-arrestins 1 and 2. J Biol Chem 277:50422–50430
Healy JR, Bezawada P, Shim J, Jones JW, Kane MA, Jr ADM, Coop A, Matsumoto RR (2013) Synthesis, modeling, and pharmacological evaluation of UMB 425, a mixed μ agonist/δ antagonist opioid analgesic with reduced tolerance liabilities. ACS Chem Neurosci 4:1256–1266
Hepburn MJ, Little PJ, Gringas J, Khun CM (1997) Differential effects of naltrindole on morphine-induced tolerance and physical dependence in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 281:1350–1356
Johnston LD, O’Malley PM, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE (2009) Monitoring the future: national survey results on drug use. Natl Inst Drug Abuse 1:1–721
Law P-Y, Erickzon-Herbrandson LJ, Zha QQ, Solberg J, Chu J, Sarre A, Loh HH (2005) Heterodimerization of the mu and delta opioid receptors occurs at the cell surface only and requires receptor-G protein interactions. J Biol Chem 280:11152–11164
Lenard NR, Daniels DJ, Portoghese PS, Roerig SC (2007) Absence of conditioned place preference or reinstatement with bivalent ligands containing mu-opioid receptor agonist and delta-opioid receptor antagonist pharmacophores. Eur J Pharmacol 566:75–82
Milligan G (2010) The role of dimerization in cellular trafficking of G-protein-coupled receptors. Curr Opin Pharmacol 10:23–29
Morphy R, Kay C, Rankovic Z (2004) From magic bullets to designed multiple ligands. Res Focus Rev 9:641–652
Morphy R, Rankovic Z (2009) Designing multiple ligands—medicinal chemistry strategies and challenges. Curr Pharm Des 15:587–600
Mosberg HI, Yeomans L, Anand JP, Porter V, Sobczyk-Kojiro K, Traynor JR, Jutkiewicz EM (2014) Development of a bioavailable μ opioid receptor (MOPr) agonist, δ opioid receptor (DOPr) antagonist peptide that evokes antinociception without development of acute tolerance. J Med Chem 57:3148–3153
National Research Council (2011) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. National Academies Press, Washington, D.C
Purington LC, Pohozheva ID, Traynor JR, Mosberg HI (2009) Pentapeptides displaying mu opioid receptor agonist and delta opioid receptor partial agonist/antagonist properties. J Med Chem 52:7724–7731
Purington LC, Sobczyk-Kojiro K, Pogozheva ID, Traynor JR, Mosberg HI (2011) Development and in vitro characterization of a novel bifunctional mu-agonist/delta-antagonist opioid tetrapeptide. ACS Chem Biol 6:1375–1381
Quock RM, Burkey TH, Varga E, Hosohata Y, Hosohata K, Cowell SM, Slate CA, Ehlert FJ, Roeske WR, Yamamura HI (1999) The d-opioid receptor: molecular pharmacology, signal transduction, and the determination of drug efficacy. Pharmacol Rev 51:503–532
Ramabadran K (1982) Effects of N-methylnaloxone and N-methylanaltrexone on nociception and precipitated abstinence in mice. Life Sci 31:1253–1256
Ross S, Peselow E (2009) The neurobiology of addictive disorders. Clin Neuropharmacol 32:269–276
Salvadori S, Guerrini R, Balboni G, Bianchi C, Bryant SD, Cooper PS, Lazaruz LH (1999) Further studies on the Dmt-Tic pharmacophore: hydrophobic substituents at the C-terminus endow delta antagonists to manifest mu agonism or mu antagonism. J Med Chem 42:5010–5019
Schiller PW (2009a) Bi- or multifunctional opioid peptide drugs. Life Sci 86:598–603
Schiller PW (2009b) Bi- or multifunctional opioid peptide drugs Life Sci
Schiller PW, Fundytus ME, Merovitz L, Weltrowska G, Nguten TM-D, Lemieux C, Chung NN, Coderre TJ (1999) The opioid mu agonist/delta antagonist DIPP-NH2(psi) produces a potent analgesic effect, no physical dependence and less tolerance than morphine in rats. J Med Chem 42:3520–3526
Wisler JW, Xiao K, Thomsen AR, Lefkowitz RJ (2014) Recent developments in biased agonism. Curr Opin Cell Biol 27:18–24
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Kenner Rice for his generous gift of SNC80 and John. R. Traynor for his generous gift of mu opioid receptor knockout mice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding and disclosure
The authors have no conflicts to disclose. This work was funded by NIH Grant DA003910 and R01 DA039997. J.P.A. was supported by the National Institutes of Health under Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award T32 DA007267. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anand, J.P., Boyer, B.T., Mosberg, H.I. et al. The behavioral effects of a mixed efficacy antinociceptive peptide, VRP26, following chronic administration in mice. Psychopharmacology 233, 2479–2487 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4296-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4296-8